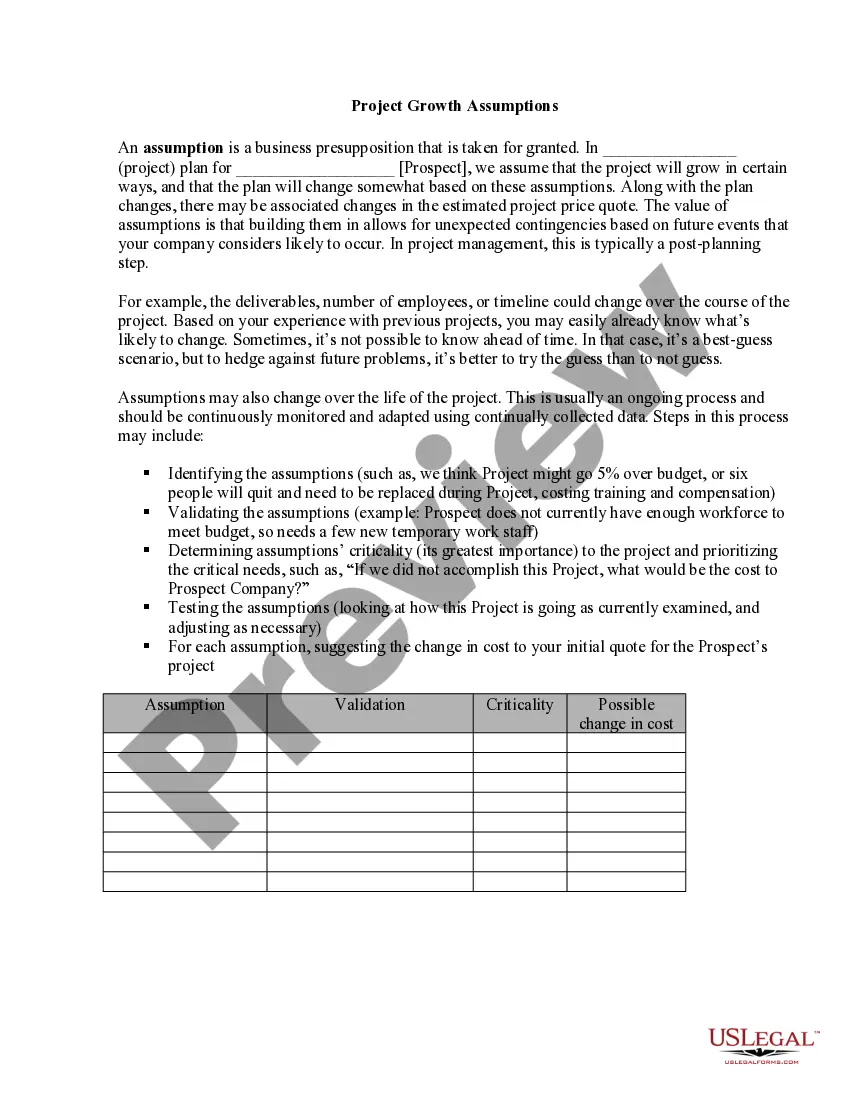
Condominium Common Element For Neurodegenerative Diseases In Cuyahoga
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Neurodegenerative diseases result from the gradual and progressive loss of neural cells, leading to nervous system dysfunction. ing to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, there are more than 600 neurologic disorders, with approximately 50 million Americans affected each year.
Alzheimer disease is the most common form and may contribute to 60–70% of cases.
We present evidence for the following eight hallmarks of NDD: pathological protein aggregation, synaptic and neuronal network dysfunction, aberrant proteostasis, cytoskeletal abnormalities, altered energy homeostasis, DNA and RNA defects, inflammation, and neuronal cell death.
1. Headache. Headaches are one of the most common neurological disorders—and there are a variety of different kinds of headaches, such as migraines, cluster headaches, and tension headaches.
As mentioned above, other risk factors for neurodegenerative disease may include gender, endocrine conditions, oxidative stress, infection and inflammation, nutrition, vascular conditions, depression, head trauma, tumors, and level of education.
LLPS is compared between a healthy neuron and a neuron that is deteriorating in neurodegenerative disease. (A) Disease-linked mutations or conditions can affect the ability of the protein to undergo LLPS, and in some cases the ability is enhanced while conversely in others it is diminished.
Neurodegenerative diseases affect millions of people worldwide. Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are the most common neurodegenerative diseases. In the United States, as many as 6.2 million people may have Alzheimer's disease, ing to a report from the Alzheimer's Disease Association in 2022.
Alzheimer's disease It is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Even with billions of dollars being used to find a treatment for Alzheimer's disease, no effective treatments have been found. Within clinical trials stable and effective AD therapeutic strategies have a 99.5% failure rate.