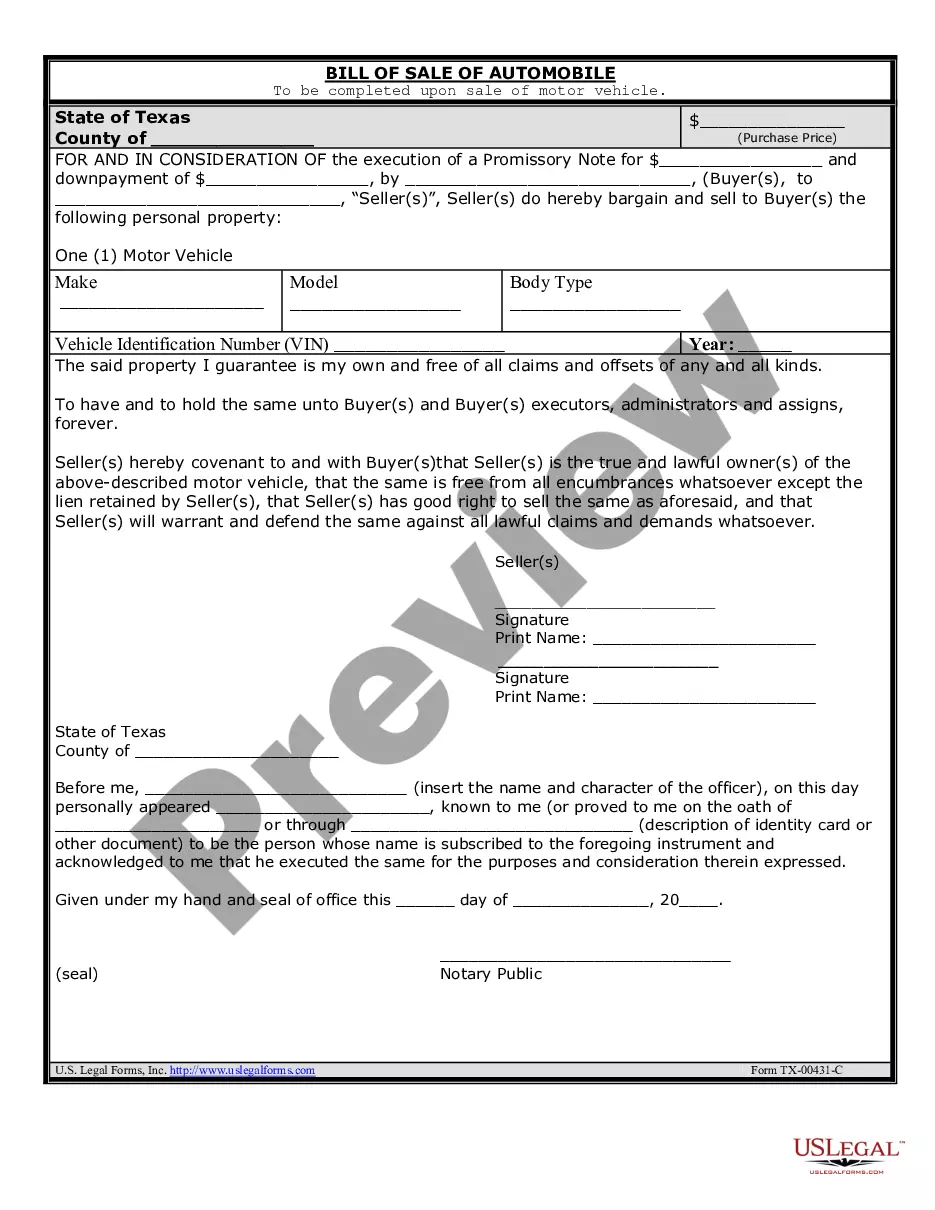
Commercial Lease Agreement With Option To Purchase In Middlesex
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
There are many reasons why a Landlord and Tenant may choose to include an “option” in a commercial lease. The most common type of option is one that gives the Tenant the right to extend the lease term, usually for additional — sometimes two or more — terms of equal length to the original term.
An option clause is a term in a commercial lease that allows a tenant to renew their lease at the end of the original lease period, if they meet certain conditions. Landlords are not obliged to offer a renewal option.
An option clause is a term in a commercial or retail lease, permitting a tenant to renew their lease at the end of the initial lease period.
For example, a tenant and landlord may agree to a five-year lease with a five-year option to renew. At the end of the first five years, the tenant is given the chance to continue the lease for another five years. If you think you may renew, be sure to bring up extension provisions with your landlord.
The triple net (NNN) lease is often considered the most prevalent form of commercial lease, particularly for retail and industrial properties, due to its predictability for landlords and clear delineation of expense responsibilities for tenants.
Types of leasehold estates The first type is most common: Estate for years: An agreement that permits occupancy between two specified dates, at the end of which the property must be vacated. Estate from period to period: A monthly tenancy that has no specified end date.
1. Gross Lease. Gross leases are most common for commercial properties such as offices and retail space. The tenant pays a single, flat amount that includes rent, taxes, utilities, and insurance.