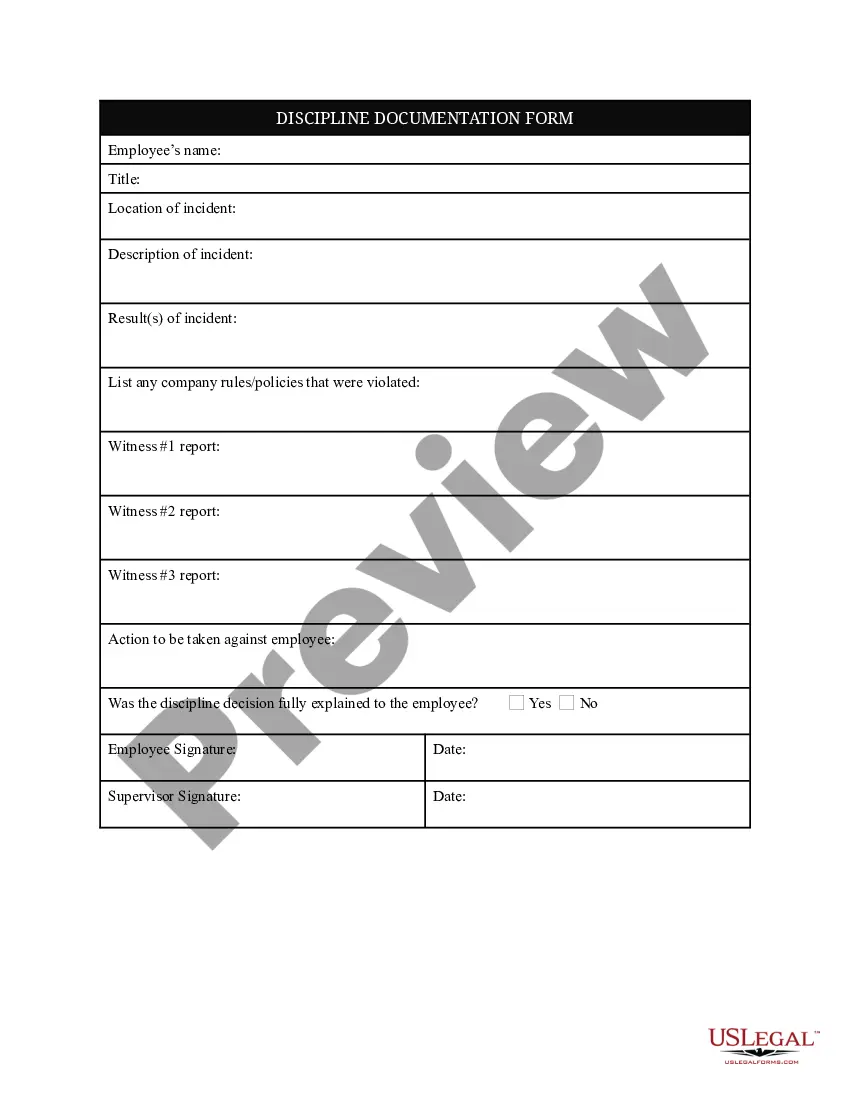
Closure Any Property With Addition With Example In Cuyahoga
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Closure Property of Multiplication ing to this property, if two integers a and b are multiplied then their resultant a × b is also an integer. Therefore, integers are closed under multiplication. Examples: 2 x -1 = -2.
Closure Property of Addition for Whole Numbers Addition of any two whole numbers results in a whole number only. We can represent it as a + b = W, where a and b are any two whole numbers, and W is the whole number set. For example, 0+21=21, here all numbers fall under the whole number set.
Closure Property of Whole Numbers Under Addition Set of whole numbers{1, 2, 3, 4, 5...} Pick any two whole numbers from the set 7 and 4 Add 7 + 4 = 11 Does the sum lie in the original set? Yes Inference Whole numbers are closed under addition
Closure property It says that when we sum up or multiply any two natural numbers, it will always result in a natural number. Here, 3, 4, and 7 are natural numbers. So this property is true. Here, 5,6, and 30 are natural numbers.
Closure property means when you perform an operation on any two numbers in a set, the result is another number in the same set or in simple words the set of numbers is closed for that operation.
Closure Property of Rational Numbers Let us take two rational numbers 1/3 and 1/4, and perform basic arithmetic operations on them. For Addition: 1/3 + 1/4 = (4 + 3)/12 = 7/12. Here, the result is 7/12, which is a rational number. We say that rational numbers are closed under addition.
Property 1: Closure Property The closure property of integers under addition and subtraction states that the sum or difference of any two integers will always be an integer. if p and q are any two integers, p + q and p − q will also be an integer. Example : 7 – 4 = 3; 7 + (−4) = 3; both are integers.
Closure Property When a and b are two natural numbers, a+b is also a natural number. For example, 2+3=5, 6+7=13, and similarly, all the resultants are natural numbers. For two natural numbers a and b, a-b might not result in a natural number. E.g. 6-5 = 1 but 5-6=-1.