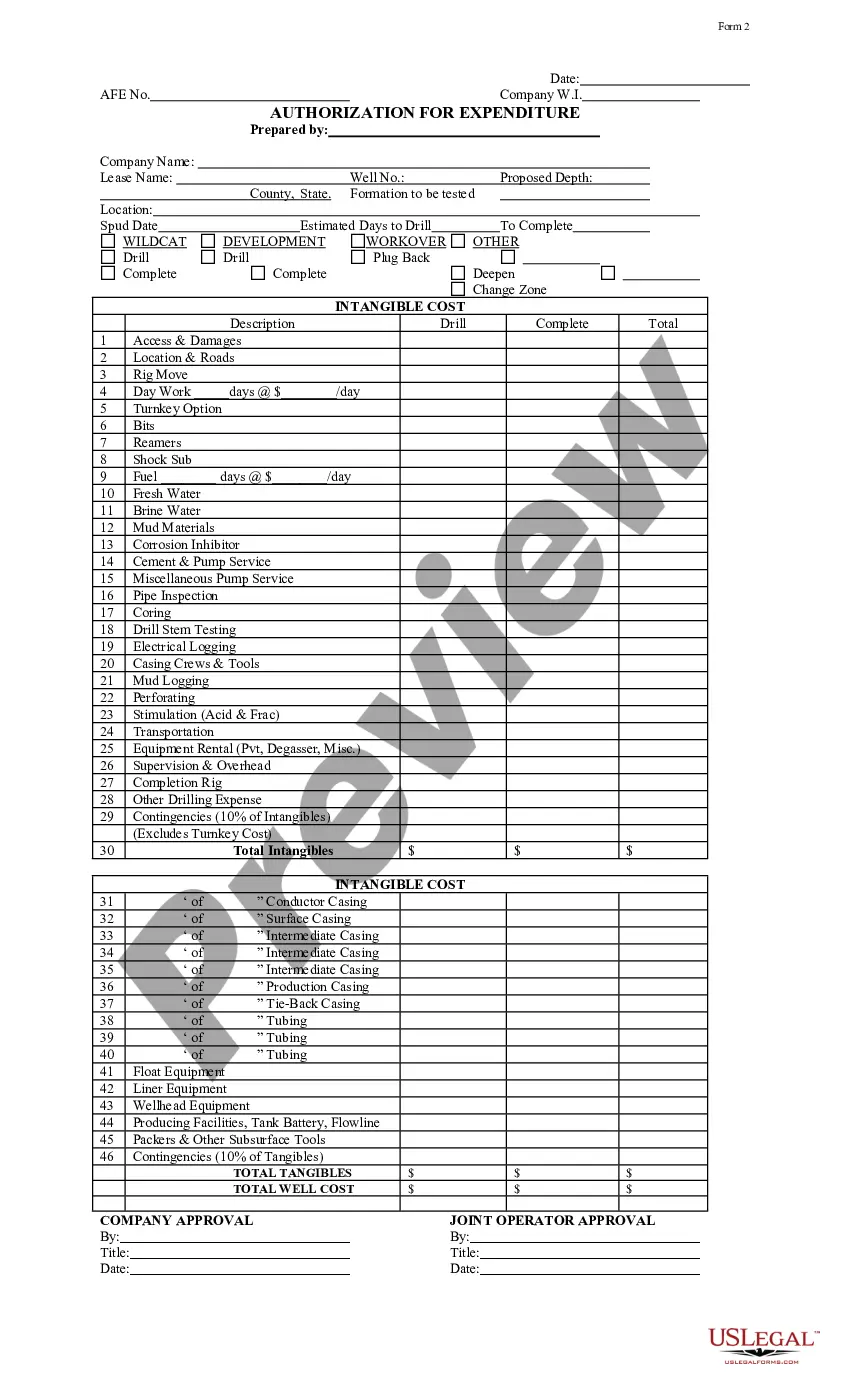
Homeowners Association Bylaws Template With Rules And Regulations In Texas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
House Bill 614 guarantees your right to a hearing before the HOA board to contest the violation or the proposed fine. This ensures a fair and transparent process where you can voice your concerns and advocate for your interests.
Texas law places limits on HOA power, including restrictions on their ability to prohibit certain types of construction like solar panels and rules against unreasonable fines or foreclosure practices. The exact limitations are outlined in state statutes, which are intended to protect homeowners' rights.
The maximum special assessment that a HOA in Texas can impose is five percent of the current year's budgeted gross expenses, though a community vote may be required to approve this. However, the vote must be approved by a majority of the members in the community.
There is no Texas state agency that oversees property owners' associations. Talking to the board or checking the association's rules can sometimes resolve misunderstandings and disagreements. The association's governing documents will often provide a way to submit a complaint directly to the association.
Disclosure Requirements Disclosure is mandated by law, often through public records and real property records. Before purchasing a home, buyers must receive a set of documents detailing the HOA's health, such as its covenants, conditions, restrictions, bylaws, rules, and financial statements.
HOA board members in Texas can be sued personally if they engage in negligent, willful misconduct, bad faith, fraud, criminal activity or actions beyond their board authority.
Depending on the organizational form of the entity, however, the home or property owners' association may not be required to register with the secretary of state.
House Bill 614 guarantees your right to a hearing before the HOA board to contest the violation or the proposed fine. This ensures a fair and transparent process where you can voice your concerns and advocate for your interests.