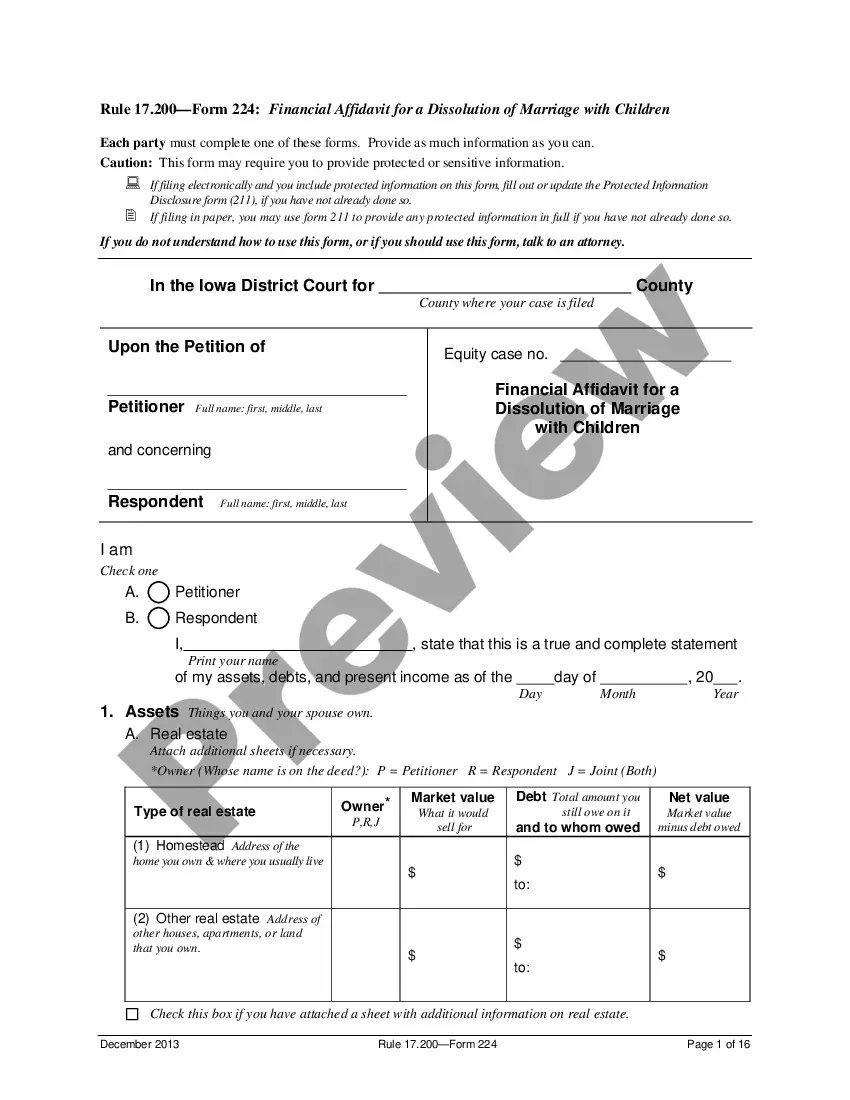
Proper Format For Bylaws In Salt Lake
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Bylaws can be easy to write and even easier to change if you are well-organized and have a good plan in place for how to go about it.
Your bylaws are not an employee handbook or policy manual designed to run the day-to-day operations of your nonprofit organization. For example, employee absences, vacation policies, and no-smoking policies have no place in an organization's bylaws.
Bylaws are the legally binding rules that outline how the board of a nonprofit will operate. While they are unique to each organization, bylaws generally have a similar structure and use.
Corporate bylaws are a company's foundational governing document. They lay out how things should run day-to-day and the processes for making important decisions. They serve as a legal contract between the corporation and its shareholders, directors, and officers and set the protocol for how the organization operates.
Bylaws serve as the legal guidelines of the organization, and the organization could be challenged in court for its actions if it violates them. For non-profits, at least, they often have to be filed with the Secretary of State of the state in which you're incorporated or registered.
The By-Laws outline the rules on annual and special meetings, voting, quorum, notice of meeting and auditors and inspectors of election. They further emphasize procedures for qualification, nomination, election and compensation of the directors. The By-Laws also identify the officers of the company and their functions.
10 steps for writing bylaws for an association Research. Form a committee. Create the structure. Outline your organization's key roles and responsibilities. Establish your meeting rules. Define your membership. Address finances. Outline the amendment process.
But here's an overall look at what's typically included: Board of directors: The bylaws define the board's structure, powers, and operations. This includes how the business elects directors, how long they serve, and what happens if they need to be replaced.
A bylaw is a law made by a local authority in ance with the powers conferred by or delegated to it under a statute, in this case the MGA. Council may pass a bylaw to govern the affairs within the council (the procedural bylaw) and bylaws that govern within the municipality.
South African municipal by-laws serve as legal frameworks established by local governments to govern specific areas within their jurisdictions. By-laws cover a wide range of aspects, including zoning, noise control, waste management, building regulations, and more.