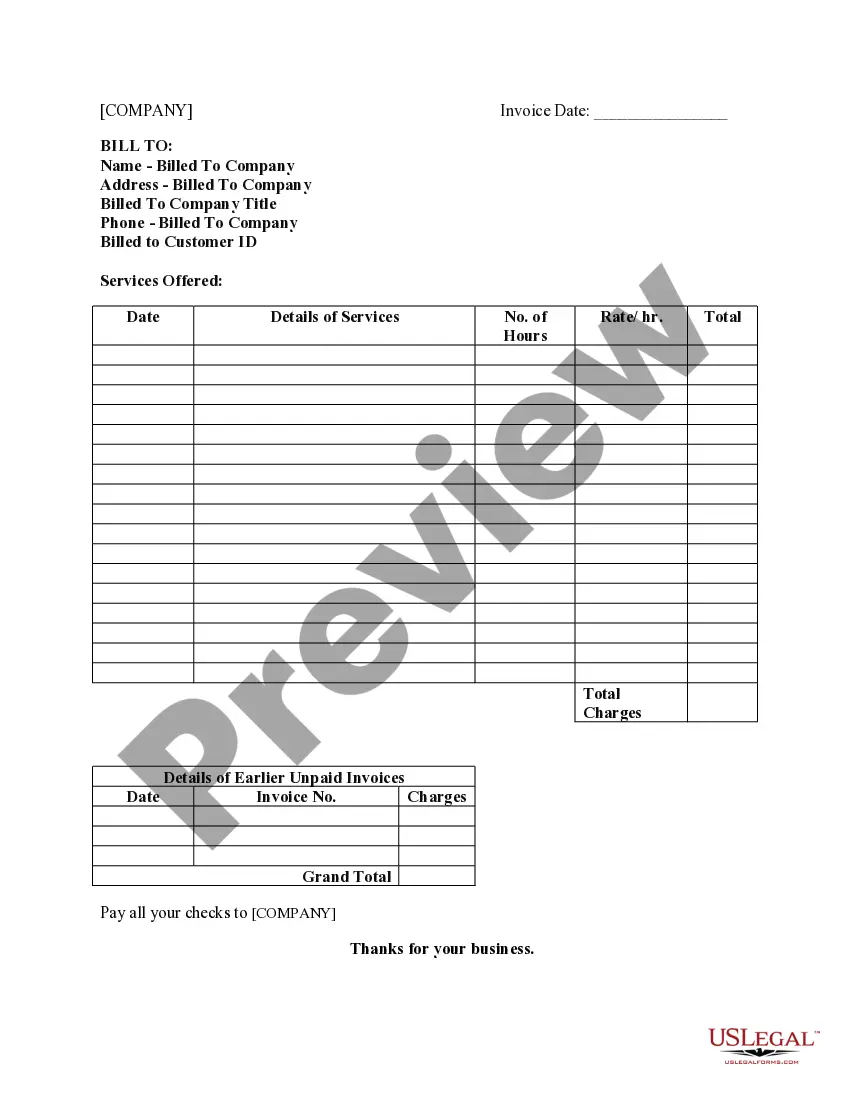
Defamation Without Mentioning Name In Utah
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In Utah, person claiming defamation must prove that: The information was false and unprivileged. In publishing the statements, the defendant acted with the “requisite degree of fault.” When applied to a private individual, this requires simple negligence, while a public figure must prove actual malice.
In general, pursuing a defamation lawsuit may be worthwhile if: The defamatory statement(s) are demonstrably false and have caused significant harm to your reputation or career. You have strong evidence to support your claim. The potential damages are substantial enough to justify the costs and risks of litigation.
The tort of slander of title and the related tort of disparagement of property are based on an intentional interference with economic relations. They are not personal torts; unlike slander of the person, they do not protect a person's reputation.” Bass v. Planned Mgmt.
Utah Code Section 76-9-404.
Defamation Law in Utah Utah law requires that a plaintiff, the person claiming defamation, proves certain elements for a successful claim. These elements include the false statement being “published” to a third party, the statement causing harm, and the statement being made without adequate research into the truth.
What Is the Difference Between Libel and Slander? As we've discussed, libel is written defamation. Slander is spoken defamation. Courts typically consider libel to be more harmful than slander because written statements last longer than spoken statements and can be distributed more widely.
Defamation is defined as an unlawful publication of a statement made by a person (“defamer”) about another person (“defamed”). Publication generally refers to instances where a third party hears or reads the statement. The statement causes harm to the defamed's good name, reputation and dignity.
In Utah, person claiming defamation must prove that: The information was false and unprivileged. In publishing the statements, the defendant acted with the “requisite degree of fault.” When applied to a private individual, this requires simple negligence, while a public figure must prove actual malice.
Utah Criminal Code § 76-5-106. Harassment. (1) A person is guilty of harassment if, with intent to frighten or harass another, he communicates a written or recorded threat to commit any violent felony.
Utah Code Section 76-9-404.