Slander Vs Libel Vs Defamation In Bronx
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
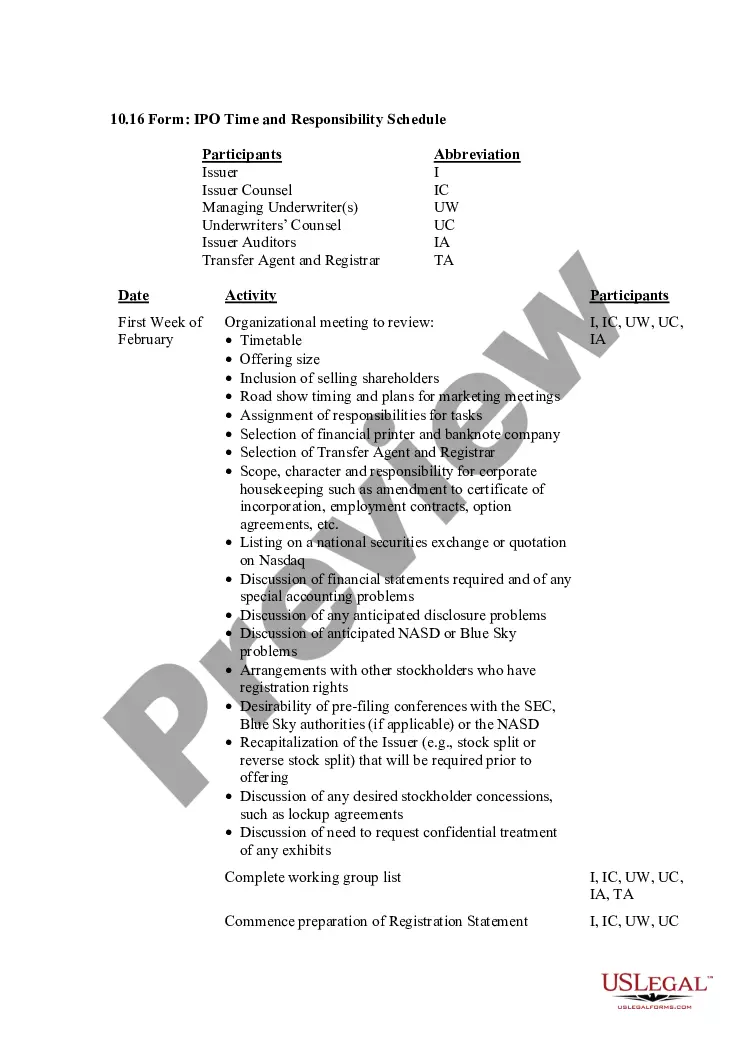
Defamation of Character Law in NY Defamation is an offense that occurs when someone makes one or more false statements about someone else's character, resulting in harm. You can view defamation in two ways: libel and slander.
If someone has written something about you or said something about you out loud, and it has a negative impact on your professional reputation, you may have a case. It is important to find out immediately if you have a case for defamation in New York.
To prove prima facie defamation, a plaintiff must show four things: 1) a false statement purporting to be fact; 2) publication or communication of that statement to a third person; 3) fault amounting to at least negligence ; and 4) damages , or some harm caused to the reputation of the person or entity who is the ...
To plead a claim of defamation, the plaintiff must satisfy the following elements: “a false statement, published without privilege or authorization to a third party, constituting fault as judged by, at a minimum, a negligence standard, and it must either cause special harm or constitute defamation per se.”1 There are ...
Slander can be hard to prove, as the complainant must show the slanderer was driven by malice and knew their claims were false. Slander is different from libel, which are false statements made through print or broadcast.
Libel: Libel is a defamation that is written, such as in a newspaper, magazine or on the internet. Slander: Slander is a defamation that is orally published, such as in a speech, over the airwaves, or in casual conversation.
The plaintiff bears the burden of proving that the harmful statements are false. By examining whether the defendant's statement would have an effect different from a proposed statement by the plaintiff, courts test whether a statement is false.
In New York, defamation is a civil matter. A person who suffers financial or emotional damages following another person's false statement may choose to sue the offender, which would bring about a case in the appropriate New York court.
“Absolute privilege … entirely immunizes an individual from liability in a defamation action regardless of the declarant's motives.”12 It is “generally reserved for communications made by 'individuals participating in a public function, such as judicial, legislative, or executive proceedings.