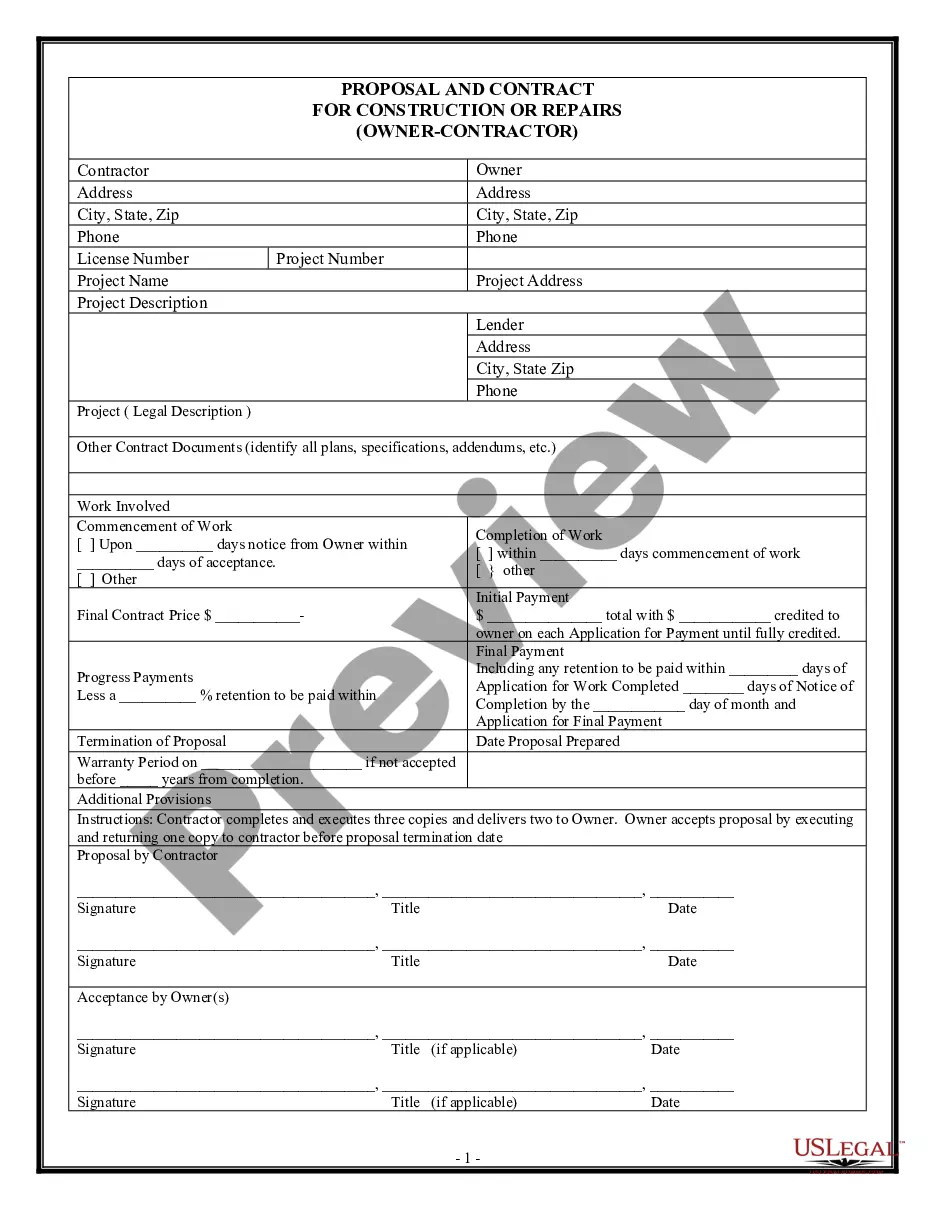
Demand For Bond
Description
How to fill out Demand Bond?
Legal document managing might be overwhelming, even for the most experienced experts. When you are interested in a Demand For Bond and do not have the time to commit trying to find the appropriate and up-to-date version, the procedures may be nerve-racking. A robust web form library can be a gamechanger for anyone who wants to manage these situations effectively. US Legal Forms is a market leader in web legal forms, with more than 85,000 state-specific legal forms available whenever you want.
With US Legal Forms, you may:
- Access state- or county-specific legal and organization forms. US Legal Forms covers any needs you could have, from personal to organization documents, in one place.
- Utilize advanced tools to complete and control your Demand For Bond
- Access a resource base of articles, tutorials and handbooks and resources highly relevant to your situation and needs
Help save effort and time trying to find the documents you will need, and employ US Legal Forms’ advanced search and Preview feature to find Demand For Bond and acquire it. If you have a subscription, log in for your US Legal Forms account, look for the form, and acquire it. Take a look at My Forms tab to see the documents you previously downloaded as well as to control your folders as you can see fit.
Should it be the first time with US Legal Forms, register an account and acquire unrestricted use of all benefits of the platform. Listed below are the steps to take after downloading the form you need:
- Confirm it is the right form by previewing it and reading through its information.
- Ensure that the sample is acknowledged in your state or county.
- Pick Buy Now when you are all set.
- Choose a subscription plan.
- Pick the format you need, and Download, complete, eSign, print and deliver your document.
Enjoy the US Legal Forms web library, backed with 25 years of expertise and stability. Change your daily document managing in a easy and intuitive process today.
Form popularity
FAQ
For example, if a bond is quoted at 99 in the market, the price is $990 for every $1,000 of face value and the bond is said to be trading at a discount. If the bond is trading at 101, it costs $1,010 for every $1,000 of face value and the bond is said to be trading at a premium.
The bond demand curve is the relationship between the price and the quantity of bonds that investors demand, all else equal. The price of bonds is inversely related to the yield, the demand curve implies that the higher the demand for bonds, the higher the yield. The bond demand curve slopes downward.
Yield is a figure that shows the return you get on a bond. The simplest version of yield is calculated by the following formula: yield = coupon amount/price. When the price changes, so does the yield.
An increase in y raises the demand for money, an increase in R reduces the demand for money, and an increase in w raises the demand for money. By the budget constraint (4), the demand for money sets the demand for bonds, bd = w?md = w?(10y?5R+.