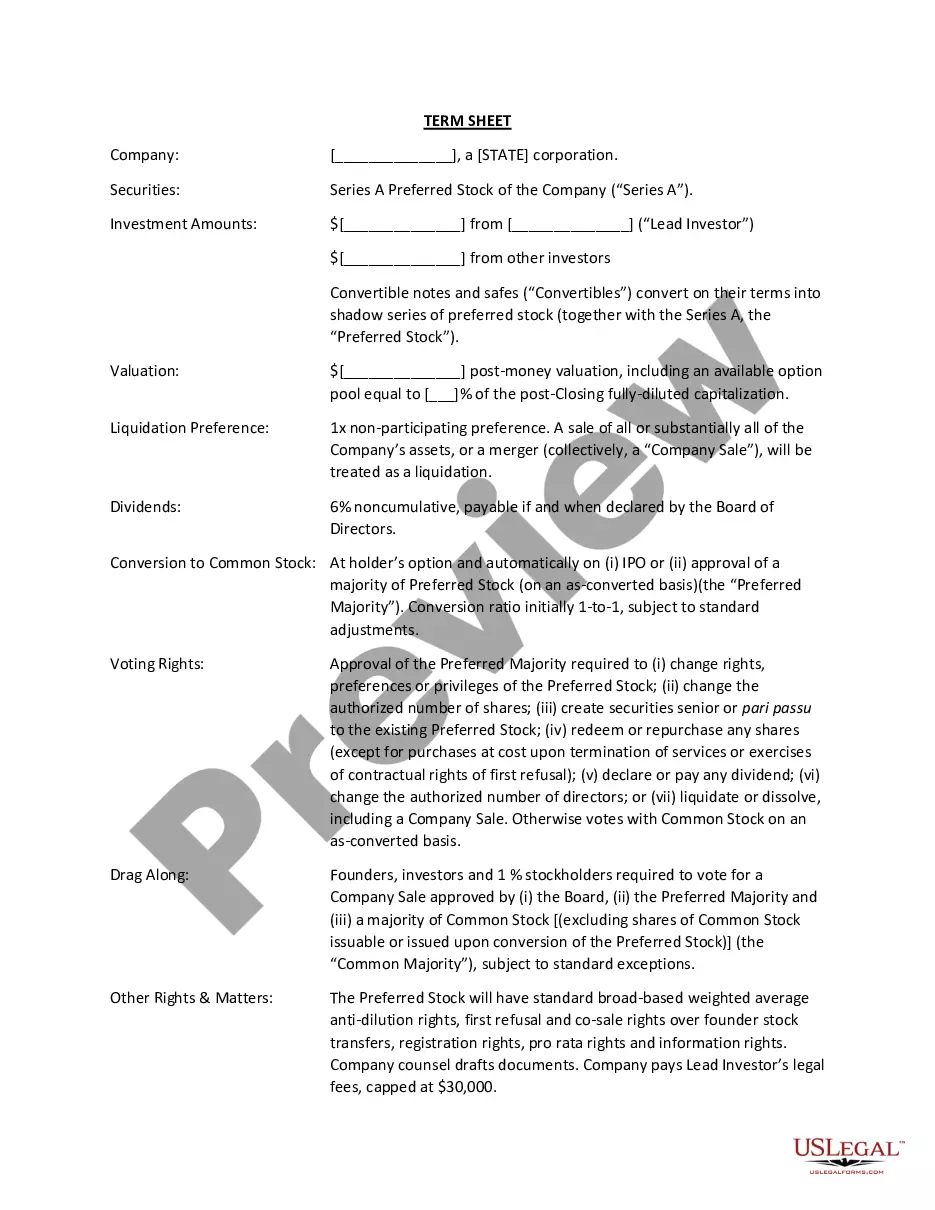
Loan Amortization Schedule Excel With Balloon Payment In Orange
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In some cases, you may be able to negotiate with your finance provider to spread the balloon payment over monthly instalments – this is essentially what refinancing is. Doing this can help make the payment more manageable and reduce the financial strain of a large lump sum payment.
However, the larger balloon payment at the end represents a substantial financial obligation that needs to be carefully planned and managed. Accounting Treatment: The balloon payment is usually recorded as a liability in the financial statements until it becomes due.
The formula for using the PMT function in Excel is as follows. =PMT(rate, nper, pv, fv, type) =IF(E8=”Monthly”,12,IF(E8=”Quarterly”,4,IF(E8=”Semi-Annual”,2,IF(E8=”Annual”,1)))) =PMT(0.50%,240,400k)
If there is a "balloon payment" (final balance), enter it into B4 as a positive value, and use the formula =PMT(B2, B3, -B1, B4). Those formulas also assume that payments are at the end of the period (i.e. end of month).
If there is a "balloon payment" (final balance), enter it into B4 as a positive value, and use the formula =PMT(B2, B3, -B1, B4). Those formulas also assume that payments are at the end of the period (i.e. end of month). That is typical.
This large amount is called a balloon payment, which pays down the remaining balance when the term ends. A balloon mortgage has a short term that does not fully amortize, but the payment is usually based on a 30-year amortization schedule. Balloon mortgages are usually associated with commercial real estate loans.
Firstly, measure the dimensions of the balloon, such as its radius or diameter. The volume of a balloon can be approximated as that of a sphere, so you can use the formula for the volume of a sphere to calculate it. The formula is V = (4/3)πr³, where V represents the volume and r denotes the radius.
Fortunately, Excel can be used to create an amortization schedule. The amortization schedule template below can be used for a variable number of periods, as well as extra payments and variable interest rates.