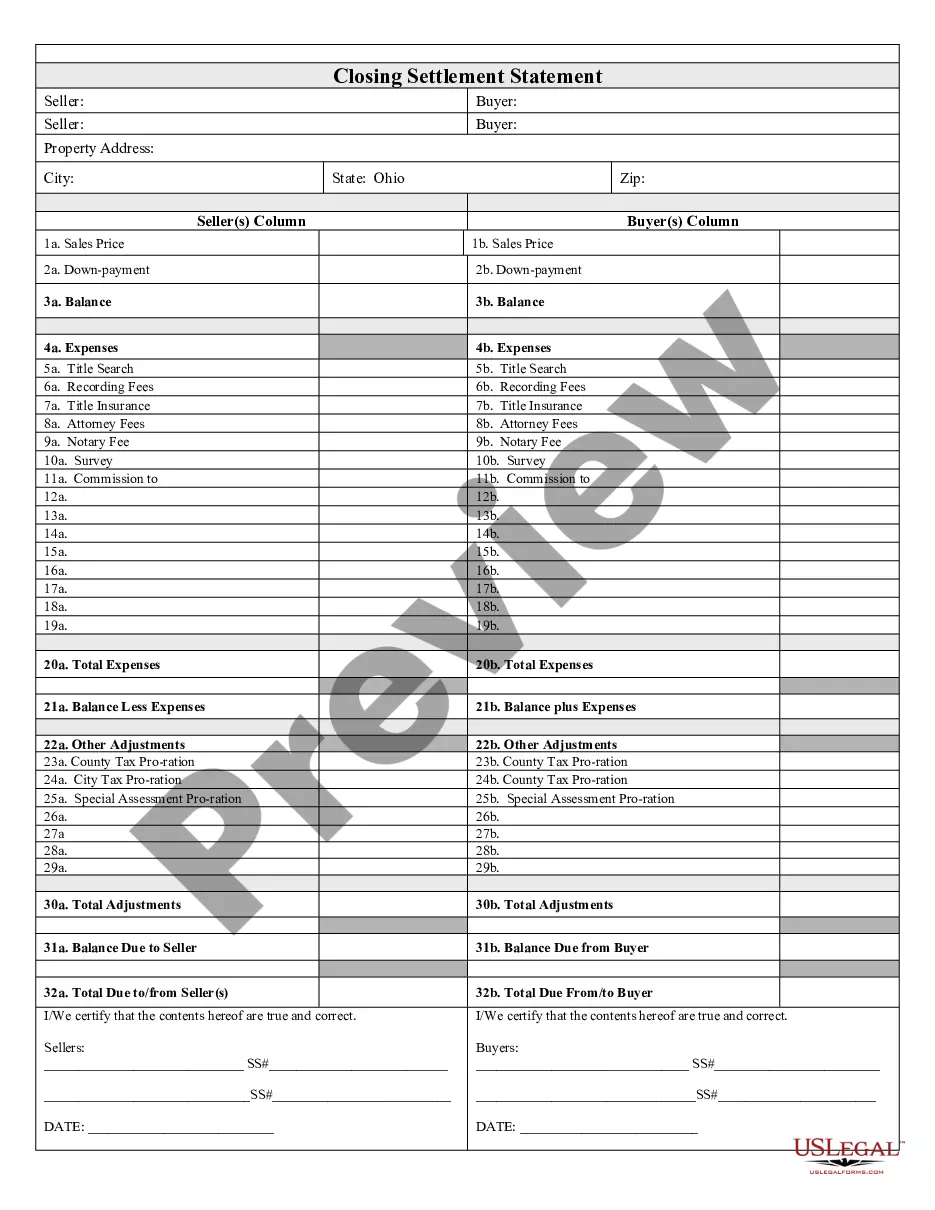
Federal Arbitration Act Confirmation Of Award In Queens
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
"(1) The award shall be made within a period of twelve months from the date the arbitral tribunal enters upon the reference.
After the briefing is complete, the arbitrator issues a written decision, usually 30-90 days after receipt of the last brief. In all, it may take up to six months from the conclusion of the hearing until the issuance of a decision. unDer What CirCumstanCes Will the Case be settleD?
§ 1290.6.) Confirmation is mandatory when a party does not respond; thus, when a party has moved to confirm the arbitration award, it effectively shortens the 100-day period to file a motion to vacate because a court lacks jurisdiction to vacate the award where a party failed to file a response within 10 days.
Requests for confirmation of an arbitral award must be submitted by motion or petition (9 U.S.C. § 13). Together with the petition or motion, a party seeking confirmation under Chapter 1 of the FAA must file: ∎ The arbitration agreement.
The Labour Relations Act (LRA) does not allow any party to appeal against an arbitration award. However, such awards can be overturned by other means. In fact, there are two ways of going about setting aside an arbitration award: by Labour Court review or by rescission application.
There are generally five parts to an award, which appear in the following order: 1. Caption - states the parties' names and the case number; 2. Preamble - contains basic introductory language; 3. Body - addressing all issues raised, as well as the allocation of the expenses and the arbitrators' compensation, if any; 4.
Necessary Elements Details of the Parties. Details of the relationship between the parties. Demand for Arbitration. The mention of agreement/contract (if any). The mention of already existing arbitration agreement between the parties pursuant to which the concerned notice of arbitration has been sent (if any).
A typical reasoned award will contain five elements: (1) an opening, (2) a summary of issues, questions, claims and defenses, (3) a statement of facts, (4) a discussion, analysis and application of relevant facts and law if necessary, and (5) a disposition of the issues, questions, claims and defenses.
The Scope of the Clause. This section of the clause is critical; it sets the boundaries for which disputes the tribunal is authorised to determine. Choice of Rules. The Number of Arbitrators. Appointing Authority. Choice of Venue. The language of the proceedings. Finality. Exclusion of the right of appeal.