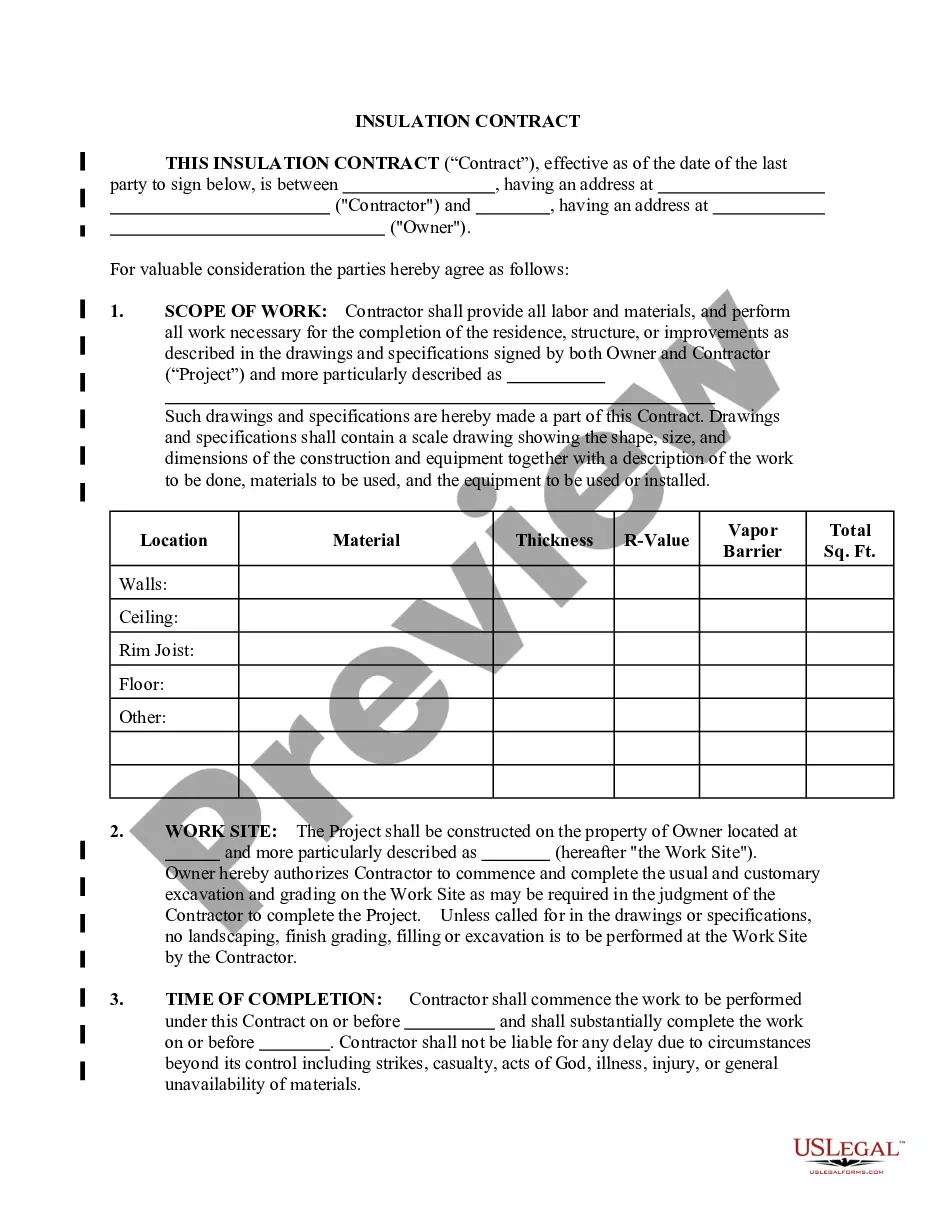
Form with which the stockholders of a corporation record the contents of a special meeting.
Asamblea Acta With English Subtitles In Maryland
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
When the Open Meetings Act applies, what does it require the public body to do? The Act requires the public body to give “reasonable advance notice” of its meetings, to make an agenda available in advance except in cases of emergency, to hold its meetings openly, to adopt minutes, and to retain them for 5 years.
How a Bill Becomes a Law STEP 1: The Creation of a Bill. Members of the House or Senate draft, sponsor and introduce bills for consideration by Congress. STEP 2: Committee Action. STEP 3: Floor Action. STEP 4: Vote. STEP 5: Conference Committees. STEP 6: Presidential Action. STEP 7: The Creation of a Law.
A bill consists of the bill number, the bill title, the purpose paragraph, the section of the Maryland code being changed and the body of the bill. The most relevant section is the body of the bill. CAPITALS INDICATE MATTER ADDED TO EXISTING LAW.
Maryland statutes are passed by the General Assembly, Maryland's legislative body. The Laws of the State of Maryland is a chronological collection of laws passed by the General Assembly.
In order to pass legislation and send it to the President for his or her signature, both the House and the Senate must pass the same bill by majority vote. If the President vetoes a bill, they may override his veto by passing the bill again in each chamber with at least two-thirds of each body voting in favor.
Both houses must pass the bill in identical form; if they are unable to reach an agreement, the bill dies. In Maryland, shortly after the General Assembly Session ends, bills that have been passed are presented to the Governor. The Governor then has 30 days to either veto or sign the bills.
Both houses must pass the bill in identical form; if they are unable to reach an agreement, the bill dies. In Maryland, shortly after the General Assembly Session ends, bills that have been passed are presented to the Governor. The Governor then has 30 days to either veto or sign the bills.
Citation Format The standard legal abbreviation for Michie's Annotated Code of Maryland is Md. Code Ann. The article or subject volume is subdivided into numbered title, subtitle, and section (preceded by the section symbol §) with further subdivisions as necessary. Examples: Education § 87-111 or Art.