Contract Law With Examples In Georgia
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Q1: “A person A agrees to sell his house to a person B for 50 lakh.” This is an example of: A contract.
To wrap up, understanding the 5 elements of contract law—offer, acceptance, consideration, legal capacity, and lawful purpose—is crucial for creating legally binding and enforceable agreements.
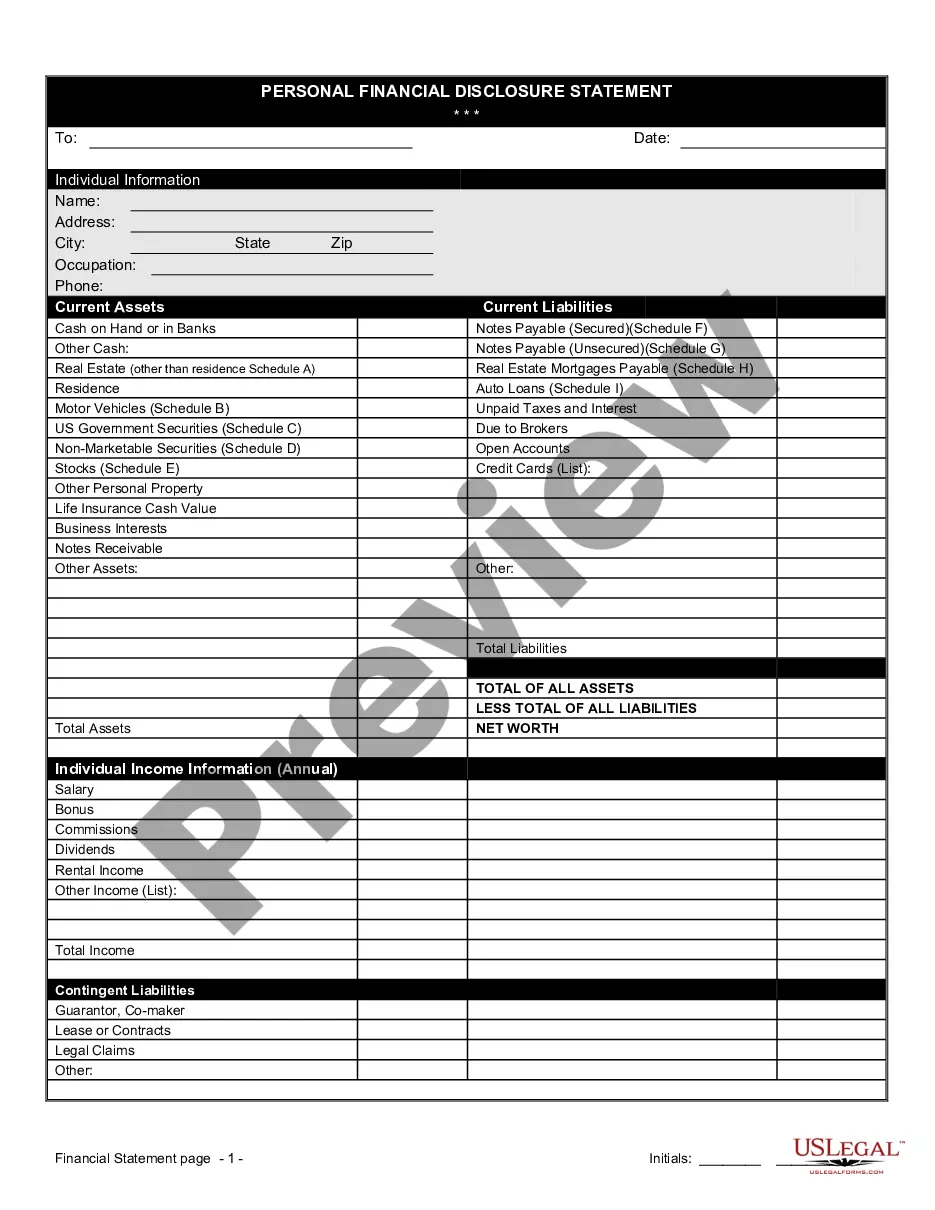
For a contract to be valid and recognized by the common law, it must include certain elements-- offer, acceptance, consideration, intention to create legal relations, authority and capacity, and certainty. Without these elements, a contract is not legally binding and may not be enforced by the courts.
Under Georgia law, for a contract to be valid, there must be an offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual assent. See O.C.G.A. § 13-3-1. In the context of email communications, an offer can be made through an email, or contemporaneous emails, containing terms of a proposed agreement.
Contracts are promises that the law will enforce. Contract law is generally governed by state common law , and while general overall contract law is common throughout the country, some specific court interpretations of a particular element of the contract may vary between the states.
For a contract to be legally binding, and therefore enforceable, it needs to satisfy four principles: offer, acceptance, consideration and the intention to create legal relations. Consideration requires the exchange of something of value and to make a contract there has to be a clear intention.