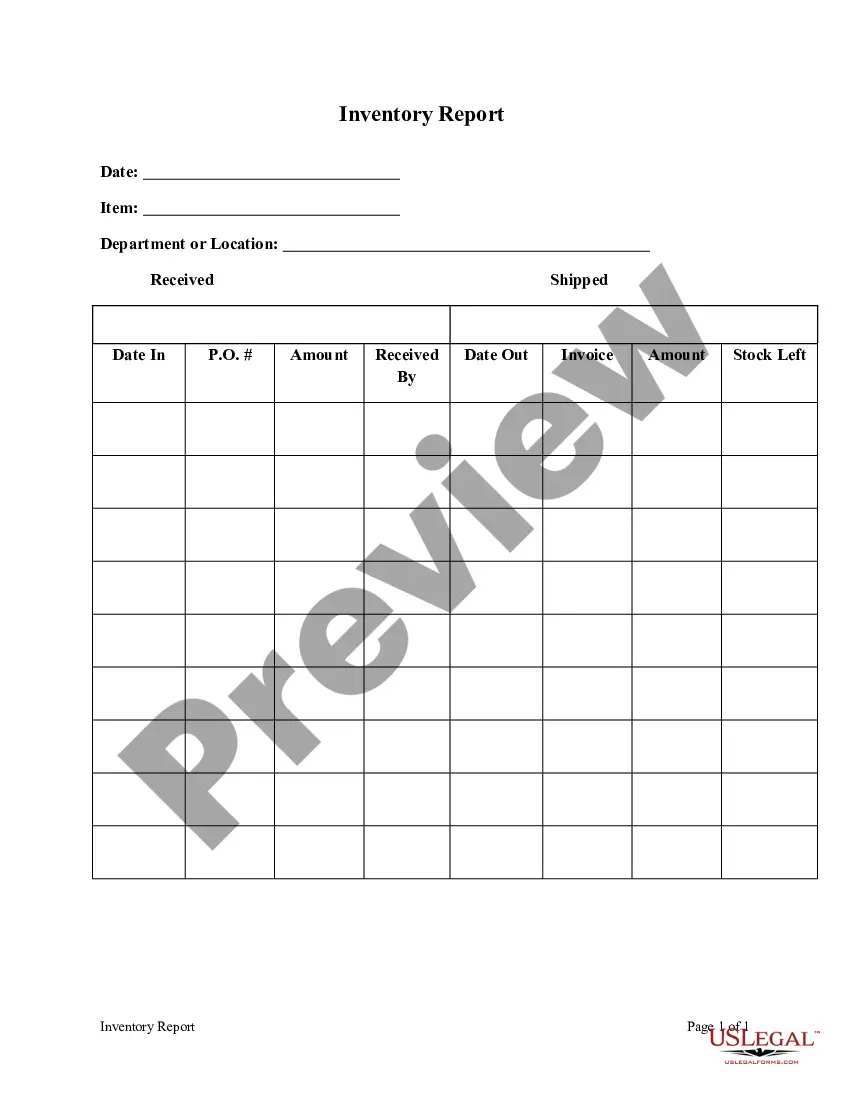
Law On Construction 2014 In Harris
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Monthly construction output is estimated to have fallen by 0.4% in volume terms in October 2024; this follows an increase of 0.1% in September 2024. The decrease in monthly output came solely from a fall in repair and maintenance (1.3%) as new work grew by 0.2%.
The area of construction law deals with matters such as infrastructure, housing, planning permissions and construction and engineering. The key to understanding construction law is that it has two main categories: non-contentious and contentious. Below is a brief overview of construction law and its branches.
Construction law Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015. Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations (COSHH) 2002. Health and Safety (Consultation with Employees) Regulations 1996. Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974. Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) 1998.
The Building Act 1984 is the primary legislation. Its stated purpose is to “secure the health, safety, welfare and convenience of persons in or about buildings and of others who may be affected by buildings or matters connected with buildings”.
While the 3 elements of contract law—offer, acceptance, and consideration—are crucial, there are additional elements that ensure a contract is valid and enforceable. These include capacity, legality, and awareness.
A Legal Construct is a abstract human-created construct that pertains to the legal systems and legal norms. Context: It can encompasses the ideas and frameworks that inform and shape legal institutions, laws, and justice systems.
A Rule of Construction is a guideline used in contract law to interpret the terms of a contract. These rules help clarify the intent of the parties involved, especially when the contract language is ambiguous or unclear.
Definition: A rule or principle that is accepted as fundamental. It is also known as the canon of construction. Example: When interpreting a law, the rule of construction is to give effect to the intention of the legislature.
Construction Acts means any act done as part of, or in relation to, the construction or operation of a Pre-Prep Facility including, but not limited to, survey activities, geotechnical investigations and the grant of any licenses, permits or authorities; Sample 1.