A factor is a person who sells goods for a commission. A factor takes possession of goods of another and usually sells them in his/her own name. A factor differs from a broker in that a broker normally doesn't take possession of the goods. A factor may be a financier who lends money in return for an assignment of accounts receivable (A/R) or other security.
Many times factoring is used when a manufacturing company has a large A/R on the books that would represent the entire profits for the company for the year. That particular A/R might not get paid prior to year end from a client that has no money. That means the manufacturing company will have no profit for the year unless they can figure out a way to collect the A/R.
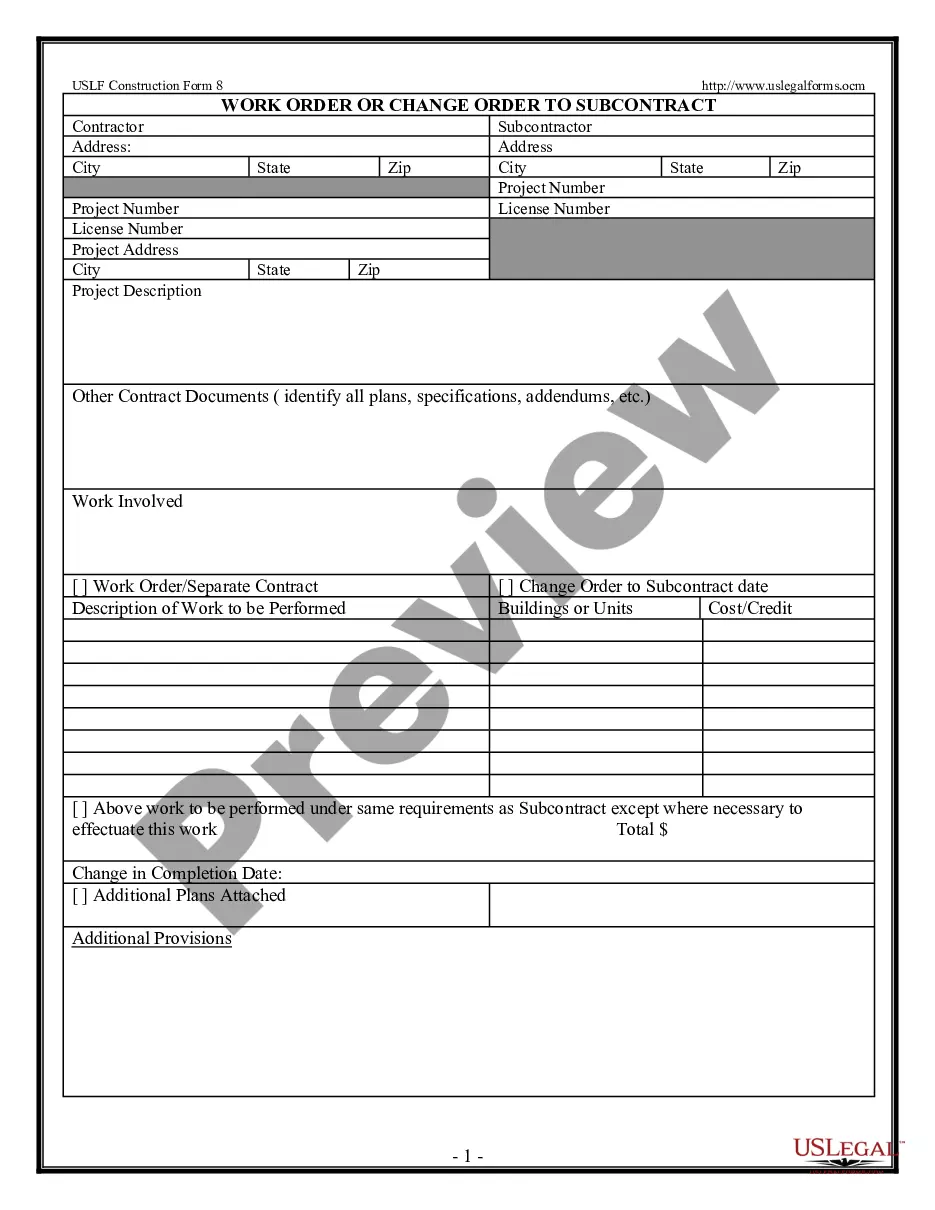
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.