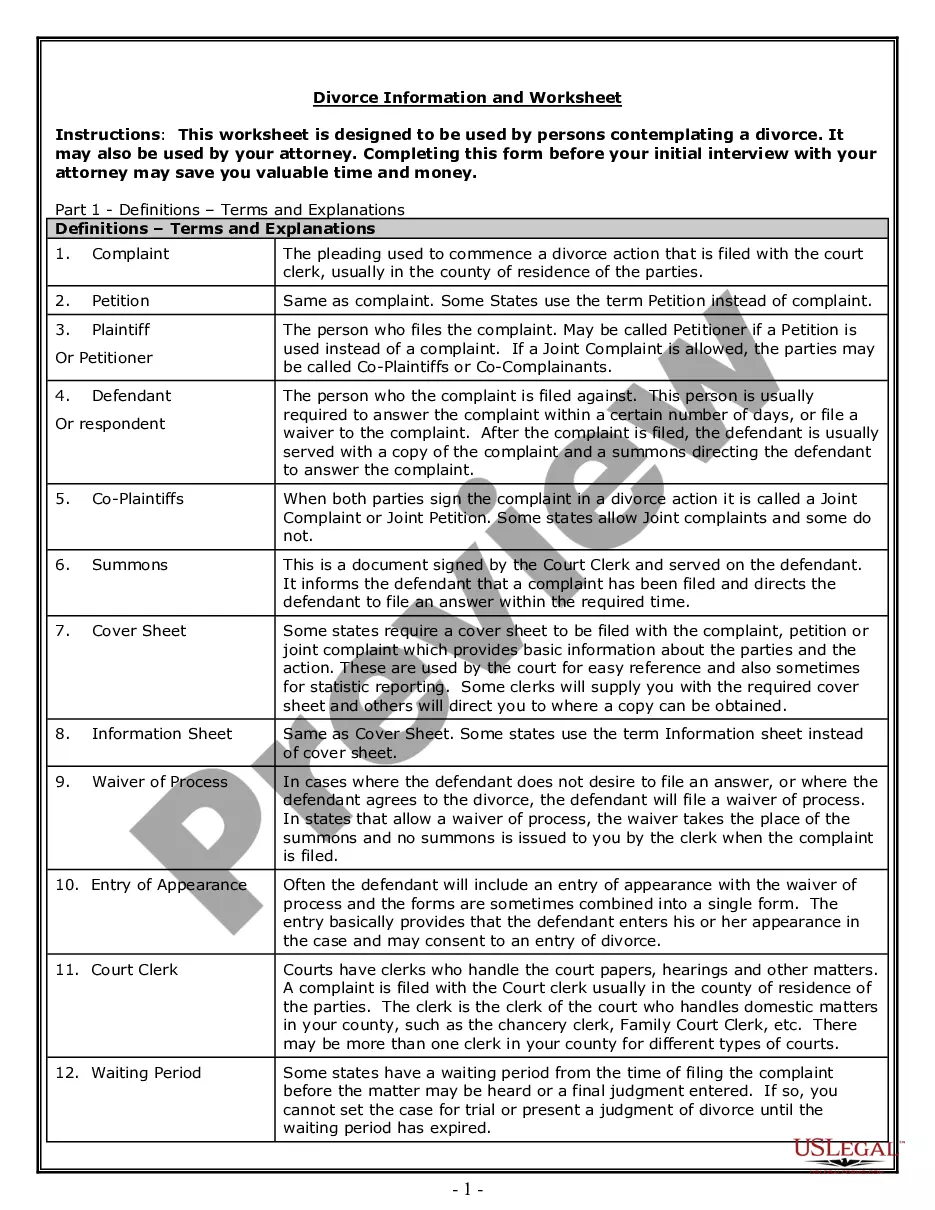
Agreement General Form For A Linear Equation In Bronx
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In the form y = mx+c. The equation ax+by +c = 0 is the most general equation for a straight line, and can be used where other forms of equation are not suitable.
The standard form or the general form of linear equations in one variable is written as, Ax + B = 0; where A and B are real numbers, and x is the single variable. The standard form of linear equations in two variables is expressed as, Ax + By = C; where A, B and C are any real numbers, and x and y are the variables.
Standard Form of Linear Equation ax + b = 0, where, a ≠ 0 and x is the variable. ax + by + c = 0, where, a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0 , x and y are the variables. ax + by + cz + d = 0, where a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0, c ≠ 0, x, y, z are the variables.
The general form of a linear equation in one variable is ax+b=c, where a ≠ 0 and a, b, c are real numbers .
A linear function is of the form f(x) = mx + b where 'm' and 'b' are real numbers. Isn't it looking like the slope-intercept form of a line which is expressed as y = mx + b? Yes, this is because a linear function represents a line, i.e., its graph is a line.
The general solution to a system of linear equations Ax= b describes all possible solutions. You can find the general solution by: Solving the corresponding homogeneous system Ax = 0.
To find the slope using a general or standard form equation, use the slope formula: m=-A/B where A and B are integer variables found in the equation. The m is the slope.
The general form of a linear function is: y=ax+b y = a x + b For the given function we can see that a=3 and b=−5 so the slope of the function is 3 and the y -intercept is −5 . To find the x -intercept we must first rearrange the function to make x the subject.
A linear function is expressed by the equation y=mx+b, where y is the dependent variable, m is the slope, x is the independent variable, and b is the y-intercept.
The general form of a linear equation is expressed as Ax + By + C = 0, where A, B, and C are any real numbers and x and y are the variables.