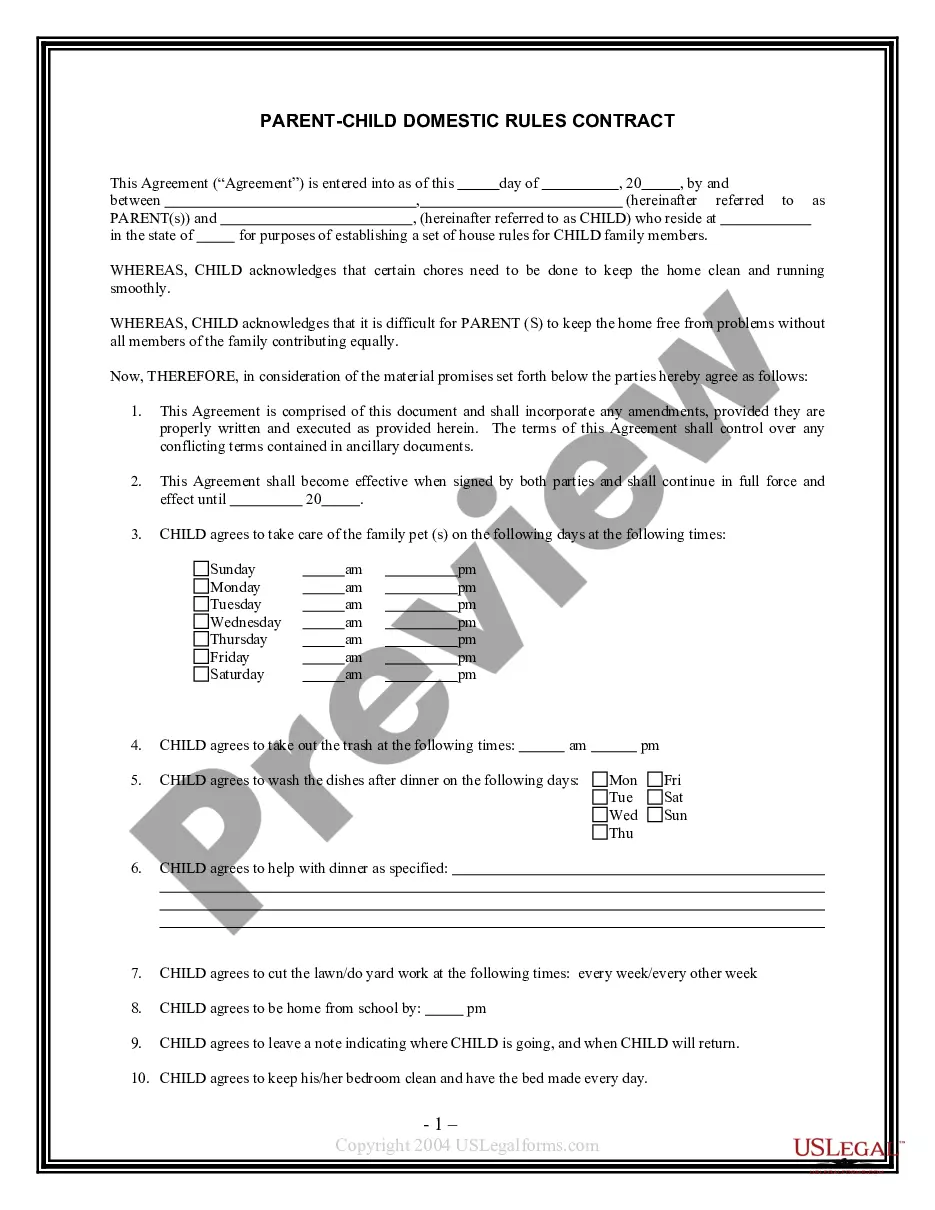
Share Agreement Contract With Vendor In Texas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Mutual Assent: A "Meeting of the Minds" of Offer & Acceptance. A legally recognized offer and an acceptance create a "meeting of the minds", or mutual assent, between the parties. The law requires the parties to a contract to demonstrate mutual assent to the contracts' terms.
A contract is a binding agreement between parties, such as businesses, individuals, or multiple people. It defines the obligations of each party to the other, including: Delivery of products and/or services. The quality of those products or services.
A shareholders' agreement is a legally binding contract entered between all or some of the shareholders in a company that regulates their rights and obligations and puts in place a framework of how the company should be managed.
A vendor agreement is a legally binding document that outlines the terms and conditions governing the work or services provided by a vendor. This contractual arrangement serves as a comprehensive framework defining the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of both the buyer and the vendor.
Types of Contracts – Based on Validity Valid Contracts. The Valid Contract as discussed in the topic on “Essentials of a Contract” is an agreement that is legally binding and enforceable. Void Contract Or Agreement. Voidable Contract. Illegal Contract. Unenforceable Contracts.
A vendor contract (otherwise known as a vendor agreement) is a business contract between two parties covering the exchange of goods or services in return for compensation. Vendor contracts establish the business relationship conditions and include details on each party's obligations under the contract.
A client contract is an agreement with a client as to the terms of service, which are legal, professional, or business between the service provider and the client.
A shareholders agreement is a binding contract between the shareholders of a company, which governs the relationship between the shareholders and specifies who controls the company, how the company will be owned and managed, how shareholders' rights may be protected and how shareholders can exit the company.
Shareholders agreements: important points to consider Introduction. Step 1: Decide on the issues the agreement should cover. Step 2: Identify the interests of shareholders. Step 4: Identify who will make decisions - shareholders or directors. Step 5: Decide how voting power of shareholders should add up.
Much like any other contract, a shareholders' agreement is legally binding. Therefore, in most cases, the standard rules of contract law will apply regarding enforceability and the remedies available if a breach of that agreement or a dispute occurs.