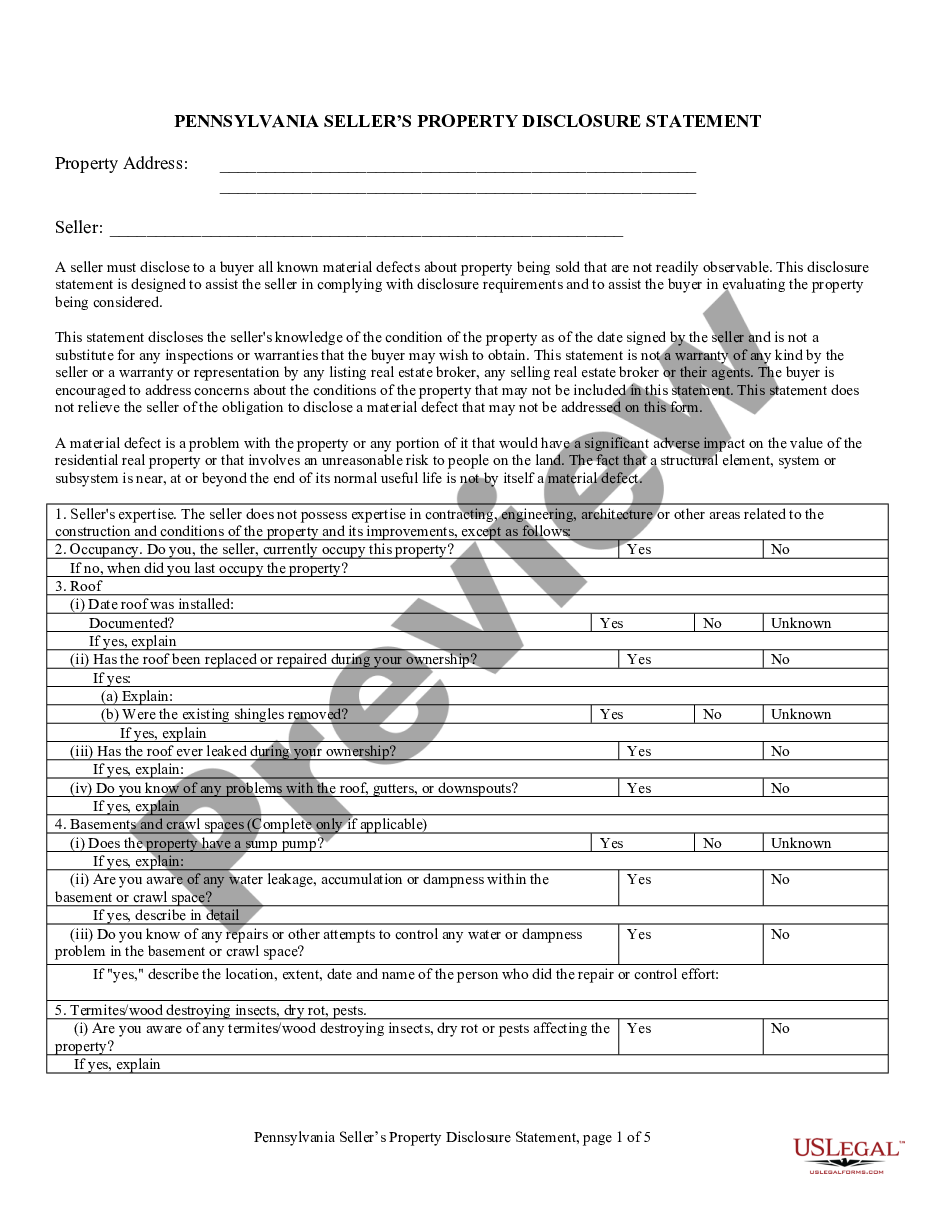
Equity Share Statement With Others In Ohio
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Ohio corporate bylaws are a set of rules presented in a written document to govern a corporation's structure and management. While certain statutes of Ohio regulate how corporations conduct business, the company bylaws are internal regulations that officers, directors, and shareholders must follow.
The purpose of corporate bylaws is to establish an internal decision-making structure and clarify the relationships between key stakeholders in a company. These parties include: Shareholders who own the corporation. Directors responsible for the overall direction of the company.
Specifically, corporations must: hold annual shareholders' and directors' meetings. keep minutes of shareholders' and directors' major decisions. make sure that corporate officers and directors sign documents in the name of the corporation. maintain separate bank accounts from their owners.
What should corporate bylaws include? Corporate bylaws are the internal rules of your corporation. Bylaws should include information about your policies and procedures for topics such as meetings, voting, stocks, dividends, financial records, directors, officers, amendments, and emergencies.
(1) The shareholders of the issuing public corporation who hold shares as of the record date of such corporation entitling them to vote in the election of directors authorize the acquisition at the special meeting held for that purpose at which a quorum is present by an affirmative vote of a majority of the voting ...
Bylaws generally define things like the group's official name, purpose, requirements for membership, officers' titles and responsibilities, how offices are to be assigned, how meetings should be conducted, and how often meetings will be held.
The certificate of the secretary of state, or a copy of the certificate of merger or consolidation certified by the secretary of state, may be filed for record in the office of the recorder of any county in this state and, if filed, shall be recorded in the official records of that county.
Right to Vote - Minority shareholders typically have the right to vote at general meetings of the company. This includes voting on key decisions such as the appointment of directors or significant corporate transactions.
If you are a minority shareholder, you have limited automatic rights and protections in law, so a well-drafted shareholders' agreement is essential to protect your position. A clear and thought through agreement can also help avoid conflict between shareholders.