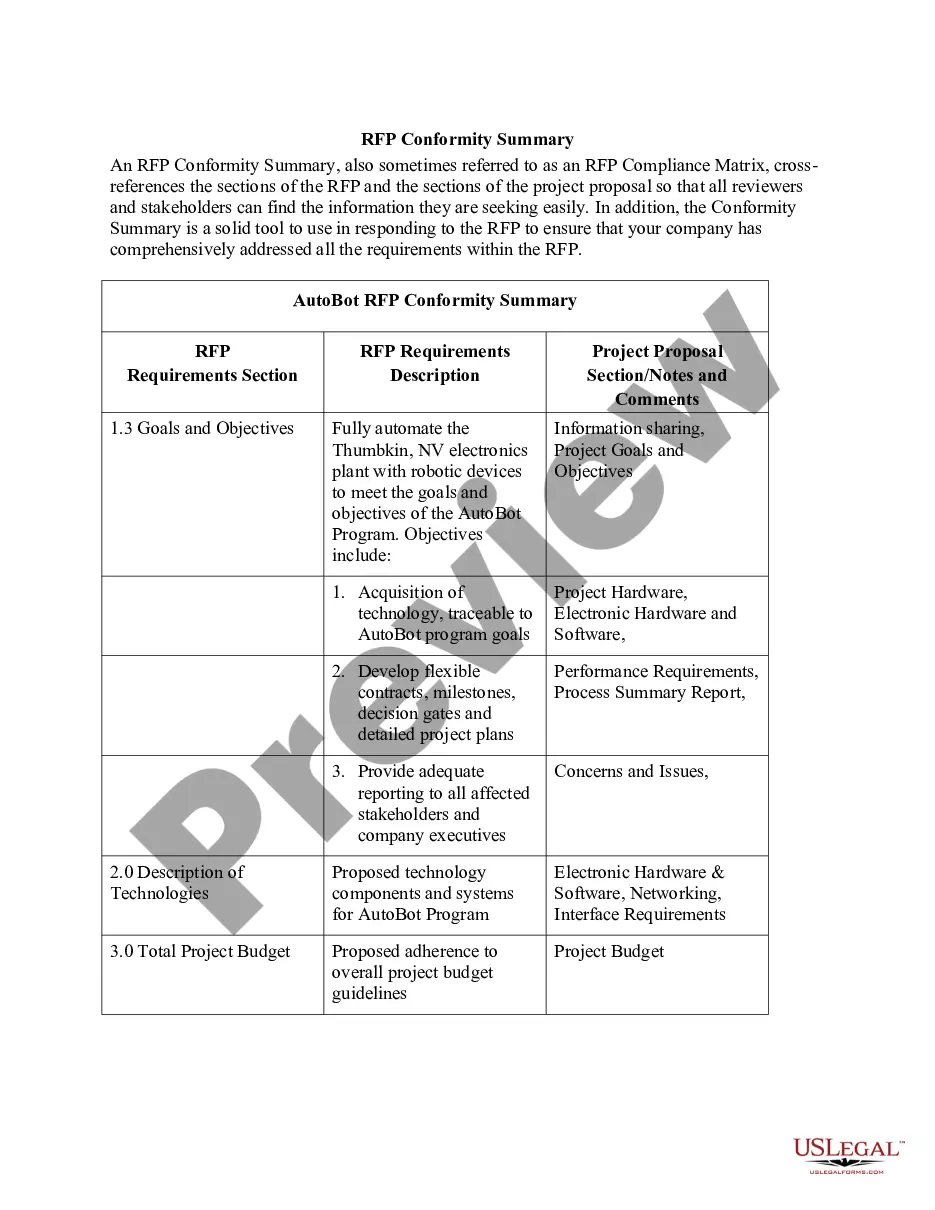
4th Amendment Us Constitution For Dummies In Washington
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Once an amendment has passed with a two-thirds majority in both the House and Senate, the people of the state must vote in favor of it. You can read more about this process in Article XXIII, Section 1 of the Washington State Constitution. The people have amended the Washington State Constitution 109 times.
A constitutional amendment can be initiated by the Legislature if it passes both houses by a two-thirds vote. A constitutional amendment does not need the Governor's signature, but becomes part of the constitution only if the electorate approves it at the next general election.
Constitutional Amendments Proposal by convention of the states, with ratification by state conventions. Proposal by convention of the states, with ratification by state legislatures. Proposal by Congress, with ratification by state conventions. Proposal by Congress, with ratification by the state legislatures.
Any amendment or amendments to this Constitution may be proposed in either branch of the legislature; and if the same shall be agreed to by two-thirds of the members elected to each of the two houses, such proposed amendment or amendments shall be entered on their journals, with the ayes and noes thereon, and be ...
To claim a violation of Fourth Amendment rights as the basis for suppressing relevant evidence, courts have long required that the claimant must prove that they were the victim of an invasion of privacy to have a valid standing.
An amendment may be proposed by a two-thirds vote of both Houses of Congress, or, if two-thirds of the States request one, by a convention called for that purpose. The amendment must then be ratified by three-fourths of the State legislatures, or three-fourths of conventions called in each State for ratification.
The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no Warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by Oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things ...
The Fourth Amendment has two basic clauses. One focuses on the reasonableness of a search and seizure; the other, on warrants.
Summarize the Fourth Amendment: "The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no Warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by Oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be ...
Constitutional clauses are parts of the U.S. Constitution that explain how the government should work. There are many clauses, but some are more important than others. These important clauses have special names, like the Commerce Clause, Due Process Clause, and Equal Protection Clause.