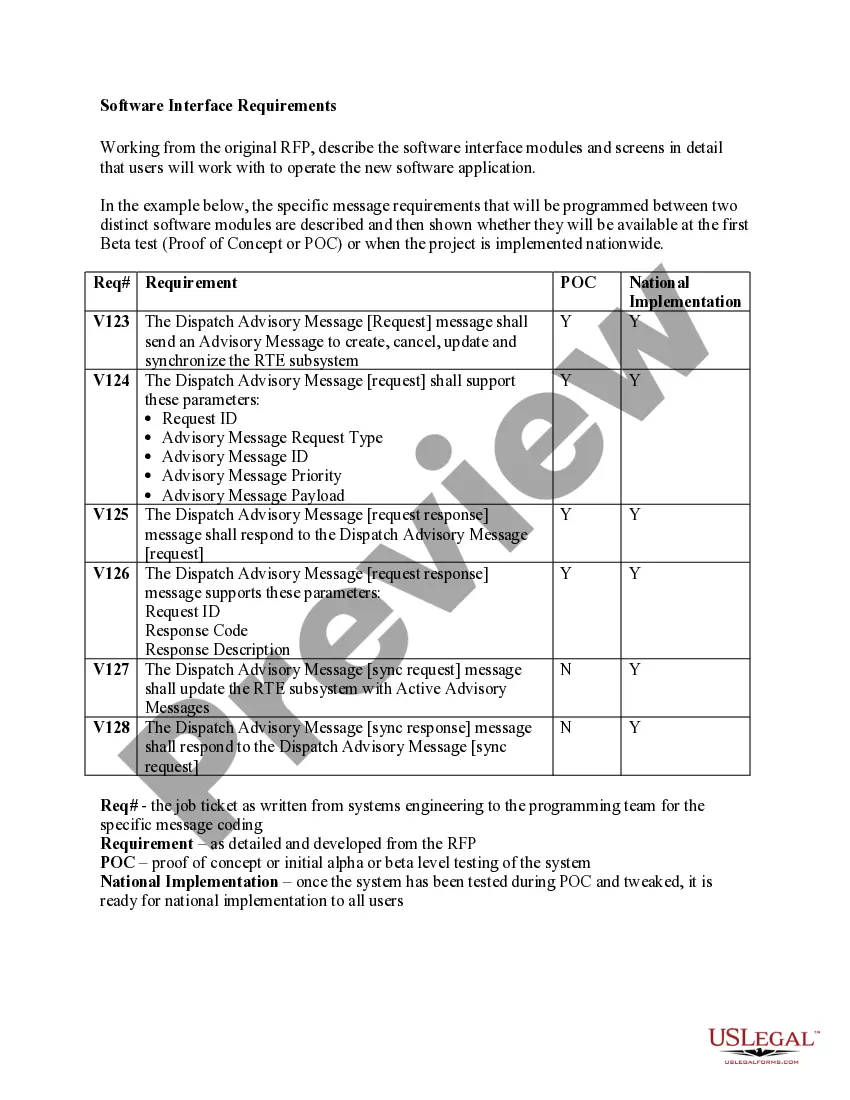
14th Amendment Document Without Comments In Wake
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside.
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
The Fourteenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution contains a number of important concepts, most famously state action, privileges or immunities, citizenship, due process, and equal protection—all of which are contained in Section One.
The amendment's first section includes the Citizenship Clause, Privileges or Immunities Clause, Due Process Clause, and Equal Protection Clause.
Why was the Fourteenth Amendment controversial in women's rights circles? This is because, for the first time, the proposed Amendment added the word "male" into the US Constitution.
The disqualification clause of the Fourteenth Amendment prevents public officials who engage in treason from holding a future public office. This amendment dates back to the Reconstruction Era to prevent members of the Confederacy from resuming power after the Civil War ended.
The clause has been seldom used, and the few times it has been used in the past mainly arose out of the Civil War—a very different context from the events of January 6. It is therefore unclear to what extent historical precedents provide useful guidance for its application to the events of January 6.