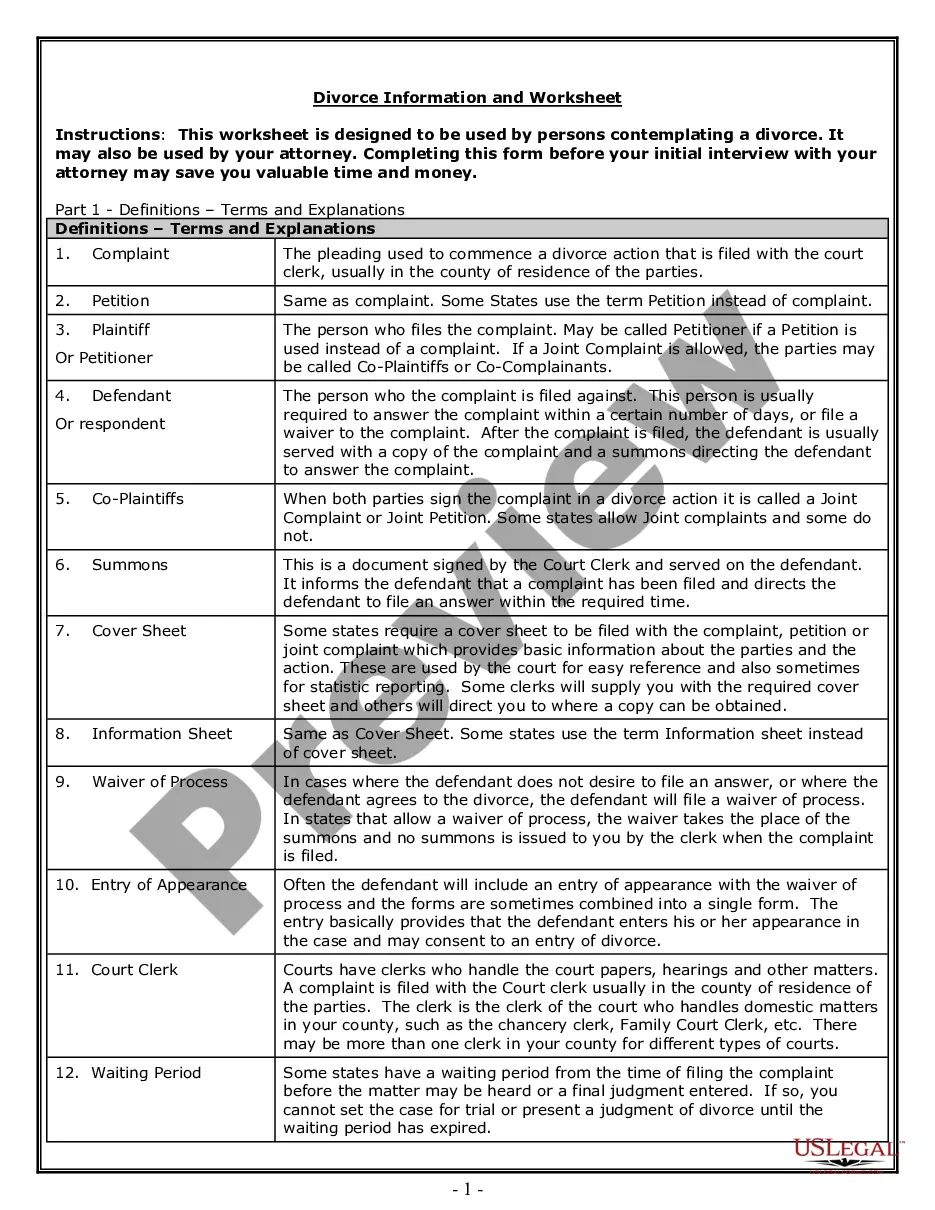
14th Amendment Agreement For Slaves In Pima
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
Not only did the 14th Amendment fail to extend the Bill of Rights to the states; it also failed to protect the rights of Black citizens. A legacy of Reconstruction was the determined struggle of Black and White citizens to make the promise of the 14th Amendment a reality.
In a unanimous decision, the U.S. Supreme Court overturns its 1896 ruling in Plessy v. Ferguson that separate but equal is constitutional and rules that segregation is a violation of the Fourteenth Amendment's equal protection clause.
In a unanimous decision, the U.S. Supreme Court overturns its 1896 ruling in Plessy v. Ferguson that separate but equal is constitutional and rules that segregation is a violation of the Fourteenth Amendment's equal protection clause.
The Fourteenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution contains a number of important concepts, most famously state action, privileges or immunities, citizenship, due process, and equal protection—all of which are contained in Section One.
Finally, it granted Congress the power to enforce this amendment, a provision that led to the passage of other landmark legislation in the 20th century, including the Civil Rights Act of 1964, and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
Fourteenth Amendment, Section 5: The Congress shall have power to enforce, by appropriate legislation, the provisions of this article. 82 Stat.
Passed by the Senate on June 8, 1866, and ratified two years later, on July 9, 1868, the Fourteenth Amendment granted citizenship to all persons "born or naturalized in the United States," including formerly enslaved people, and provided all citizens with “equal protection under the laws,” extending the provisions of ...
The Congress shall have power to enforce, by appropriate legislation, the provisions of this article.