Closing Disclosure Statement Withholding Tax
Description
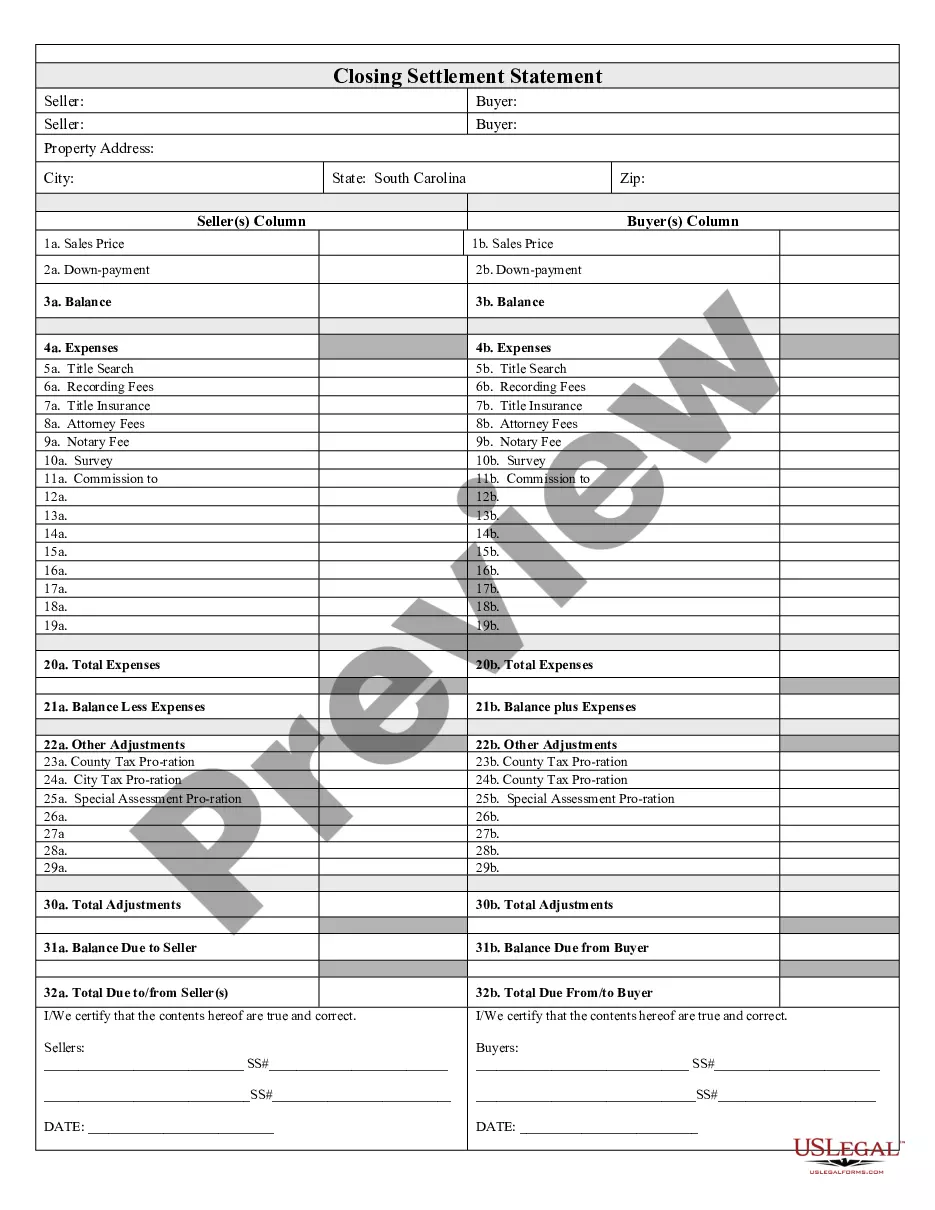
How to fill out South Carolina Closing Statement?
Finding a go-to place to take the most current and relevant legal samples is half the struggle of working with bureaucracy. Finding the right legal documents needs accuracy and attention to detail, which explains why it is important to take samples of Closing Disclosure Statement Withholding Tax only from trustworthy sources, like US Legal Forms. An improper template will waste your time and delay the situation you are in. With US Legal Forms, you have little to worry about. You can access and check all the details about the document’s use and relevance for the situation and in your state or county.
Take the following steps to complete your Closing Disclosure Statement Withholding Tax:
- Utilize the catalog navigation or search field to find your sample.
- View the form’s description to see if it fits the requirements of your state and county.
- View the form preview, if available, to make sure the template is the one you are looking for.
- Return to the search and find the appropriate document if the Closing Disclosure Statement Withholding Tax does not fit your needs.
- If you are positive regarding the form’s relevance, download it.
- If you are an authorized user, click Log in to authenticate and gain access to your picked templates in My Forms.
- If you do not have an account yet, click Buy now to obtain the form.
- Pick the pricing plan that suits your requirements.
- Proceed to the registration to complete your purchase.
- Finalize your purchase by choosing a payment method (credit card or PayPal).
- Pick the document format for downloading Closing Disclosure Statement Withholding Tax.
- When you have the form on your device, you may change it with the editor or print it and complete it manually.
Get rid of the inconvenience that accompanies your legal documentation. Explore the comprehensive US Legal Forms catalog where you can find legal samples, examine their relevance to your situation, and download them immediately.
Form popularity
FAQ
A taxpayer may bring you a document known as a closing disclosure or settlement statement (Form HUD-1, ALTA Settlement Statement, or similar), providing information about the property they have purchased and, if applicable, the mortgage loan they took out.
Page 3: Calculating Cash to Close: On page 1 of the closing disclosure under cost at closing, there was an amount that you need to bring to closing for your cash to close. This section gives you a full breakdown of the money needed to close.
A mortgage closing statement lists all of the costs and fees associated with the loan, as well as the total amount and payment schedule. A closing statement or credit agreement is provided with any type of loan, often with the application itself.
Ing to 12 C.F.R. § 1026.37(g)(4), ?amounts in connection with the transaction that the consumer is likely to pay or has contracted with a person other than the creditor or loan originator to pay at closing? are to be disclosed in Section H of the LE.
Page 4: This section tells you what your late fee will be and whether your lender accepts partial payments. Information about your loan's escrow account ? odds are you have one ? is also on this page. You'll see what is included, usually homeowners insurance and property taxes.