Basis For Objections In Court
Description
How to fill out New York Information Concerning Filing Of Objections And Rebuttal In Proceeding Before Hearing Examiner?
It’s no secret that you can’t become a legal professional overnight, nor can you figure out how to quickly draft Basis For Objections In Court without the need of a specialized set of skills. Putting together legal documents is a long venture requiring a certain education and skills. So why not leave the preparation of the Basis For Objections In Court to the professionals?
With US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive legal document libraries, you can access anything from court papers to templates for in-office communication. We understand how important compliance and adherence to federal and local laws are. That’s why, on our platform, all forms are location specific and up to date.
Here’s how you can get started with our platform and obtain the document you need in mere minutes:
- Find the form you need with the search bar at the top of the page.
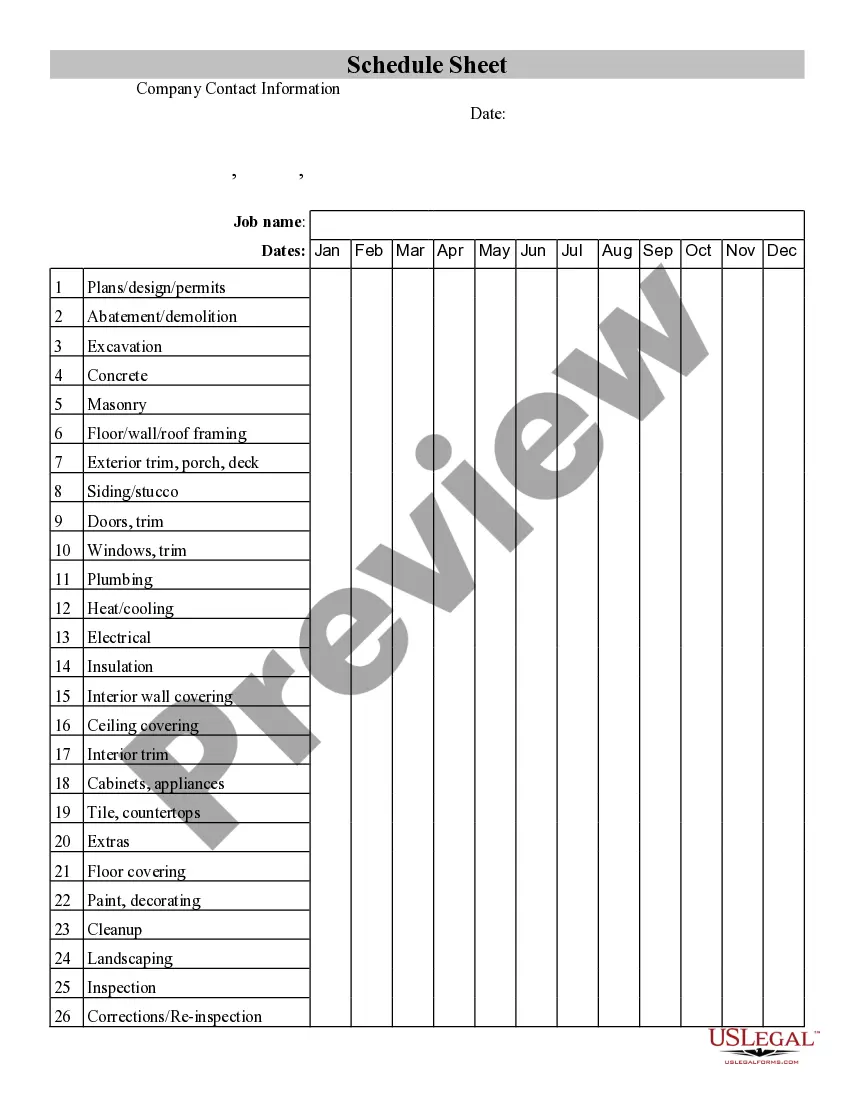
- Preview it (if this option available) and check the supporting description to figure out whether Basis For Objections In Court is what you’re searching for.
- Start your search over if you need a different template.
- Register for a free account and select a subscription plan to purchase the form.
- Pick Buy now. As soon as the payment is through, you can download the Basis For Objections In Court, fill it out, print it, and send or mail it to the necessary individuals or entities.
You can re-gain access to your forms from the My Forms tab at any time. If you’re an existing client, you can simply log in, and locate and download the template from the same tab.
Regardless of the purpose of your documents-be it financial and legal, or personal-our platform has you covered. Try US Legal Forms now!
Form popularity
FAQ
Common Objections in Court: Hearsay, Character Evidence, Leading, and Asked and Answered.
The following types of objections in court are generally based on the rules of evidence most common in American jurisdictions. Relevance. A relevance objection is based on the argument that the evidence is not relevant to the case. ... Leading question. ... Compound question. ... Asked and answered. ... Vague. ... Speculation. ... Hearsay. ... Privilege.
You can object to the relevance of evidence if you think a piece of evidence or something a witness is saying has nothing to do with the case or it is not important in determining who should win in court. Example: Asking how many sexual partners someone has had wouldn't be relevant in a protection order case.
The objections must be in writing and contain the name and docket number of the case. The reasons for your objections and the parts of the order objected to must be clearly stated.
Say ?Objection,? and then state your objection clearly and concisely. You can interrupt a witness, if necessary when raising your objection. Make your objection before the opposing side goes on to the next question. The judge may offer the other side the chance to respond to the objection.