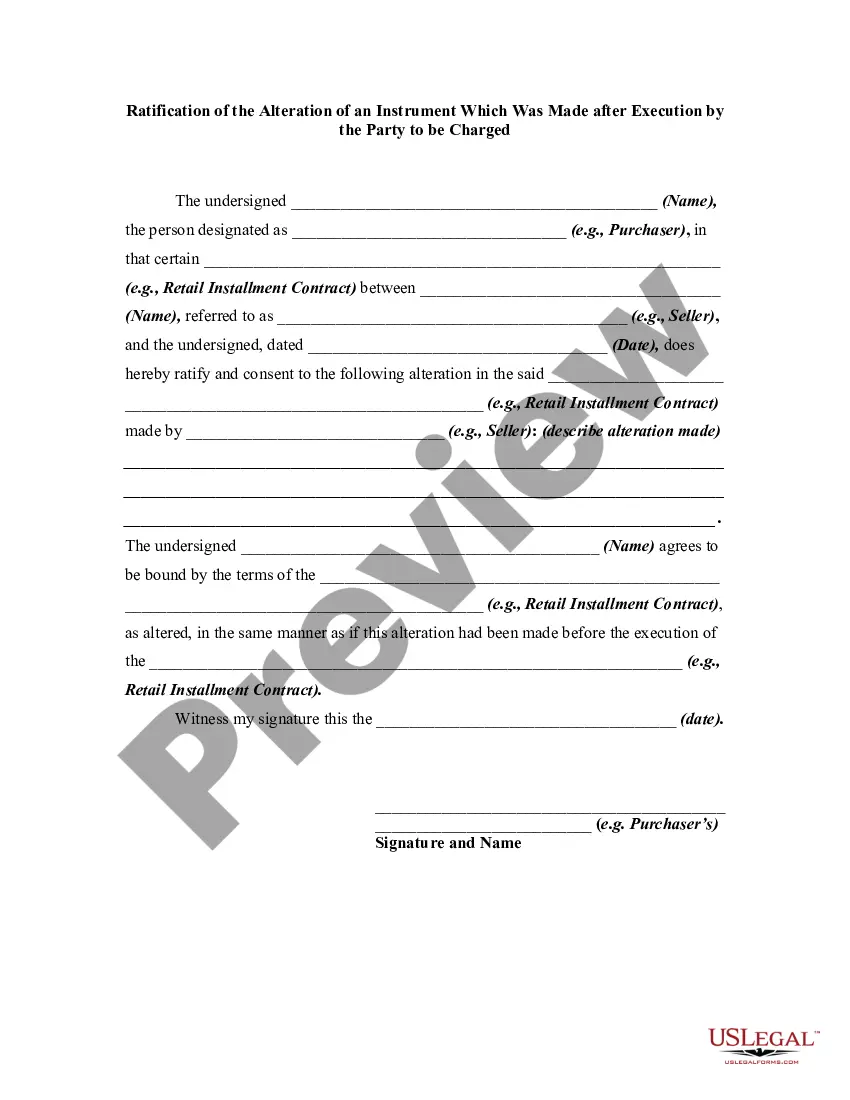
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged
Description
How to fill out Ratification Of The Alteration Of An Instrument Which Was Made After Execution By The Party To Be Charged?
It is feasible to spend hours online attempting to locate the valid document template that satisfies the federal and state criteria you require.
US Legal Forms offers numerous valid forms that are assessed by experts.
You can easily obtain or print the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged from your service.
If available, take advantage of the Review button to examine the document template as well. To obtain another version of the form, utilize the Search field to find the template that suits your needs and specifications.
- If you currently possess a US Legal Forms account, you may Log In and click on the Download button.
- Afterward, you may fill out, modify, print, or sign the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
- Every valid document template you acquire is yours permanently.
- To get an additional copy of any purchased form, navigate to the My documents section and click on the relevant button.
- If you are visiting the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the easy instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for your region/area of preference.
- Review the form description to confirm you have chosen the appropriate template.
Form popularity
FAQ
In West Virginia, rule 41 specifically addresses the ratification process for alterations made to legal instruments post-execution, central to the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. This rule ensures that any changes to original agreements are legally recognized, thereby protecting the interests of the parties involved. It is essential for individuals and businesses to understand this rule to avoid potential disputes over contract modifications. To help you grasp these concepts better, USLegalForms offers comprehensive resources and forms tailored for West Virginia residents.
The rule of 41 relates to provisions in legal contexts that allow parties to amend or alter instruments after execution, focusing on the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. This rule ensures that all parties are aware of any amendments and that such changes are made transparently. Understanding this rule is crucial for anyone involved in legal contracts and agreements in West Virginia. For further assistance, you may consider using USLegalForms to navigate these complexities.
Rule 37 outlines the consequences of failing to comply with discovery orders in West Virginia's civil procedures. It provides mechanisms to address noncompliance, including potential sanctions. Recognizing the importance of Rule 37 can be crucial when dealing with matters related to the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, as it emphasizes the need for adherence to the legal process.
Rule 34 in West Virginia's civil procedure governs the request for production of documents and tangible things. This rule facilitates the discovery process, ensuring parties can obtain necessary evidence to support their case. By understanding Rule 34, you can better grasp the implications for the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Rule 45 of the West Virginia Rules of Civil Procedure addresses the issuance of subpoenas. It allows parties to compel the attendance of witnesses or the production of documents in legal proceedings. Familiarity with Rule 45 is essential, particularly in cases involving the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, where proper documentation can significantly influence outcomes.
West Virginia's constitution was ratified in 1863, marking the state’s admission into the Union. This foundational document provides the framework for governance and legal procedures, including those applicable to the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. Knowing this history can enhance your understanding of current legal practices in the state.
The 3-term rule in West Virginia refers to the limits on the use of certain legal instruments in specific types of proceedings. It ensures that a legal instrument can only be altered or ratified within three terms of court. Understanding this rule can help you navigate the complexities of the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Adverse possession law in West Virginia allows someone to claim ownership of land under certain conditions. Specifically, it requires continuous, open, and notorious occupation of the property for a statutory period. Understanding the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged can provide insight into how legal alterations can impact property claims. If you are considering this route, reaching out to a legal professional can guide you through the intricate details.
In West Virginia, the squatting code addresses how individuals can occupy land without the owner's permission. It essentially sets the framework for property rights and protections. If you believe your rights are affected by someone squatting, understanding the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged will help clarify legal options. It is essential to consult legal experts or resources to navigate these laws effectively.
Rule 41 A provides specific guidelines on how a plaintiff can dismiss a case, with or without prejudice, in civil procedure. This rule is essential because it outlines the procedural steps for dismissals, fostering informed decision-making by parties. If you are considering issues related to the West Virginia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, understanding these guidelines is particularly relevant.