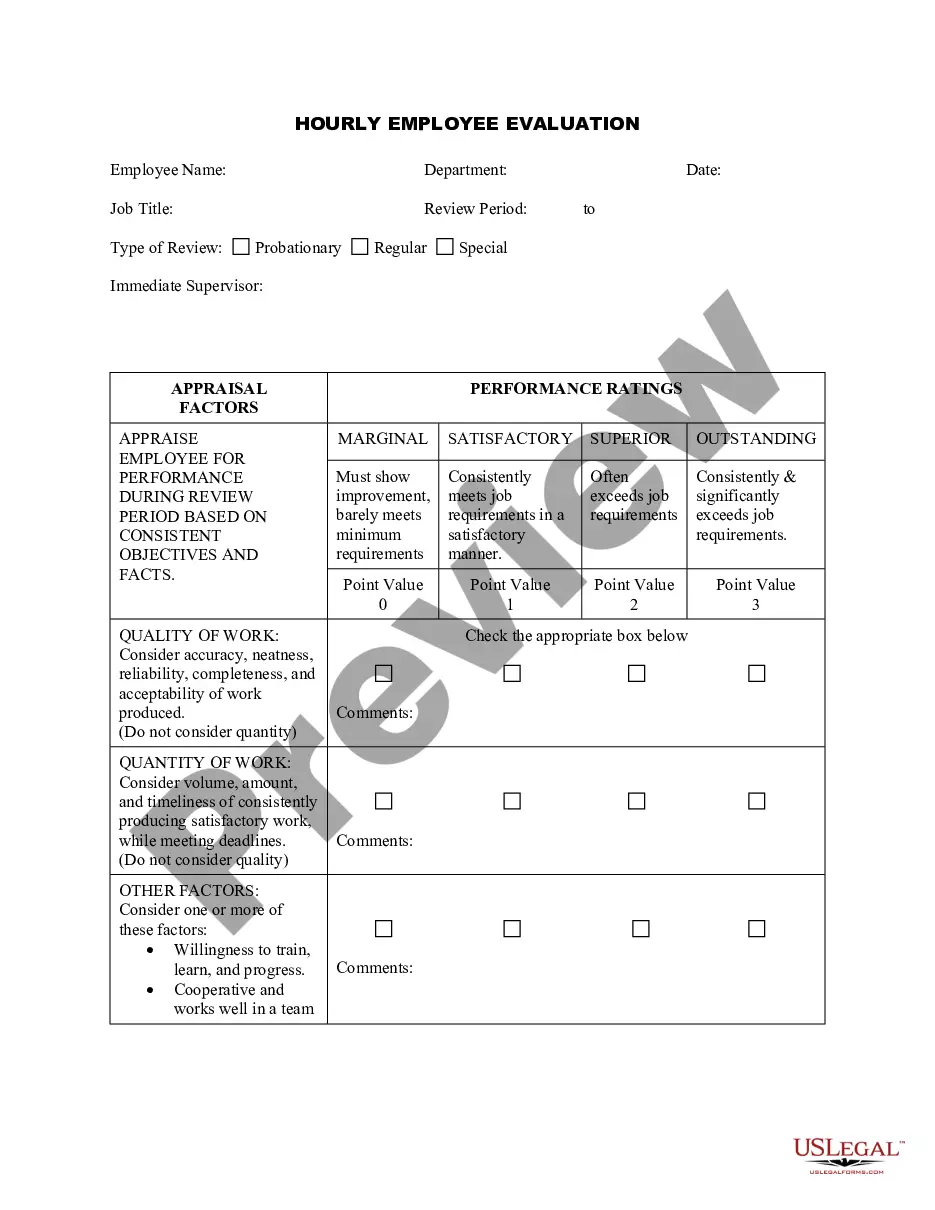
Wisconsin Hourly Employee Evaluation
Description
How to fill out Hourly Employee Evaluation?
US Legal Forms - one of the most extensive collections of authorized documents in the United States - provides a vast selection of legal form templates that you can download or print.
While using the site, you can discover numerous forms for business and personal use, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can find the latest versions of forms like the Wisconsin Hourly Employee Evaluation within moments.
If you already have a subscription, Log In and download the Wisconsin Hourly Employee Evaluation from the US Legal Forms collection. The Download button will appear on each form you view. You have access to all previously downloaded forms from the My documents section of your profile.
Process the payment. Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
Select the format and download the form to your device. Make adjustments. Complete, modify, print, and sign the downloaded Wisconsin Hourly Employee Evaluation. Each template you add to your account has no expiration date and is yours permanently. So, if you want to download or print another copy, just go to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Wisconsin Hourly Employee Evaluation with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive collection of legal form templates. Utilize countless professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal requirements and specifications.
- Ensure you have chosen the correct form for your city/state.
- Click the Preview button to review the form's content.
- Read the form description to ensure you have selected the right form.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search box at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- Once you are satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Buy now button.
- Then, choose your preferred payment plan and provide your details to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
California's ban prohibits private and public employers from seeking a candidate's pay history. Even if an employer already has that information or an applicant volunteers it, it still can't be used in determining a new hire's pay.
Currently, there is one state, Oregon, with full state predictive scheduling regulations that apply to every city. Additionally, Vermont and New Hampshire have specific regulations in place around flexible working hours for employees.
An employee whose job function involves access to company wage and payroll information may not disclose employee pay information to other employees unless directed to by the employer or an investigating agency.
Effective January 1, 2018, Labor Code section 432.3 prohibits an employer from, either orally or in writing, personally or through an agent, asking any information concerning an applicant's salary history information, which includes compensation as well as benefits.
Effective April 18, 2018, under Wisconsin law, local governments are forbidden from prohibiting employers from soliciting applicants' pay histories. Thus, employers are legally allowed to request information about applicants' previous wages.
It's illegal to ask for salary history in several states including California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Oregon and Vermont, which all have some form of ban for private employers.
When you and another employee have a conversation or communication about your pay, it is unlawful for your employer to punish or retaliate against you in any way for having that conversation.
Under the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), non-supervisory private sector employees have a right to discuss their pay and other terms and conditions of employment with their fellow employees and with union organizers.
In general, the federal notice requirements under the Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) Act apply to employers with 100 or more employees. The notice requirements under Wisconsin's Business Closing and Mass Layoff (WBCML) law apply to employers with 50 or more employees in Wisconsin.