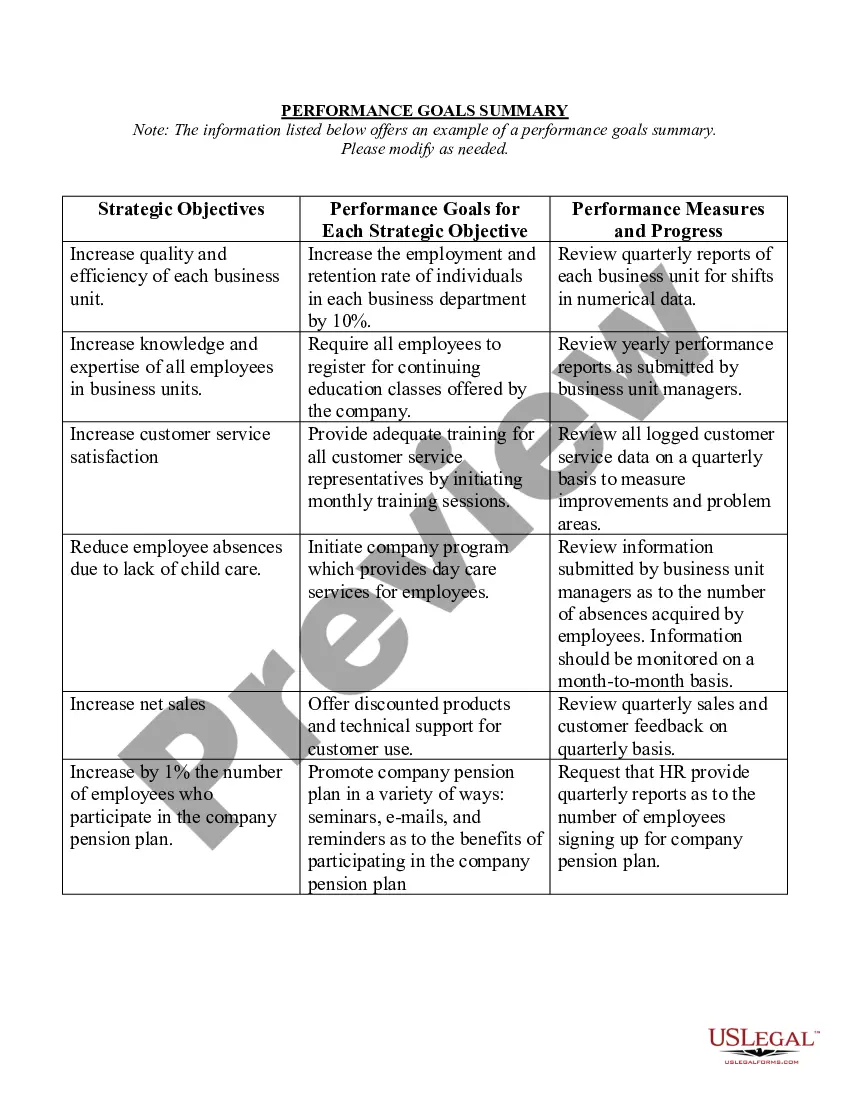
Washington Proposed Pairing Agreement
Description
How to fill out Proposed Pairing Agreement?
If you need to comprehensive, obtain, or print authorized file templates, use US Legal Forms, the most important collection of authorized forms, which can be found on-line. Take advantage of the site`s basic and hassle-free research to find the paperwork you want. A variety of templates for enterprise and specific functions are sorted by categories and says, or search phrases. Use US Legal Forms to find the Washington Proposed Pairing Agreement with a number of mouse clicks.
In case you are previously a US Legal Forms client, log in to your account and click the Down load switch to obtain the Washington Proposed Pairing Agreement. You can even accessibility forms you earlier downloaded inside the My Forms tab of your own account.
If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, refer to the instructions beneath:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the shape to the proper area/nation.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview solution to look over the form`s information. Never forget about to read through the description.
- Step 3. In case you are not satisfied with all the develop, use the Research area near the top of the screen to get other models in the authorized develop design.
- Step 4. Upon having located the shape you want, go through the Acquire now switch. Opt for the rates strategy you like and add your credentials to sign up on an account.
- Step 5. Method the deal. You may use your credit card or PayPal account to perform the deal.
- Step 6. Find the formatting in the authorized develop and obtain it in your gadget.
- Step 7. Comprehensive, edit and print or sign the Washington Proposed Pairing Agreement.
Every authorized file design you buy is your own for a long time. You might have acces to each and every develop you downloaded with your acccount. Click on the My Forms segment and pick a develop to print or obtain once again.
Contend and obtain, and print the Washington Proposed Pairing Agreement with US Legal Forms. There are millions of skilled and status-certain forms you may use for your enterprise or specific demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
In Washington, the basic maxim is ?An agreement is enforceable if its terms are reasonably certain.? The terms of a contract are ?reasonably certain? if they provide the ability for determining a breach/default and for giving an appropriate remedy in case of breach/default.
Put simply: yes. From a legal standpoint, verbal contracts can be just as valid as written contracts. There are, of course, nuances and exceptions, and a verbal contract may be much more difficult to enforce in court should something go wrong.
Whether an oral contract is enforceable in Washington depends upon the circumstances surrounding the terms of the agreement?most notably, whether the agreement falls under the provisions of the so-called ?Statute of Frauds,? requiring that certain types of contracts must always be in writing and signed by the parties ...
This type of situation occurs when one party commits a breach that fundamentally undermines the agreement written in the contract that the other party has no choice but to terminate the agreement. Material breaches of contract are situations where one party failed to perform his or her duty.