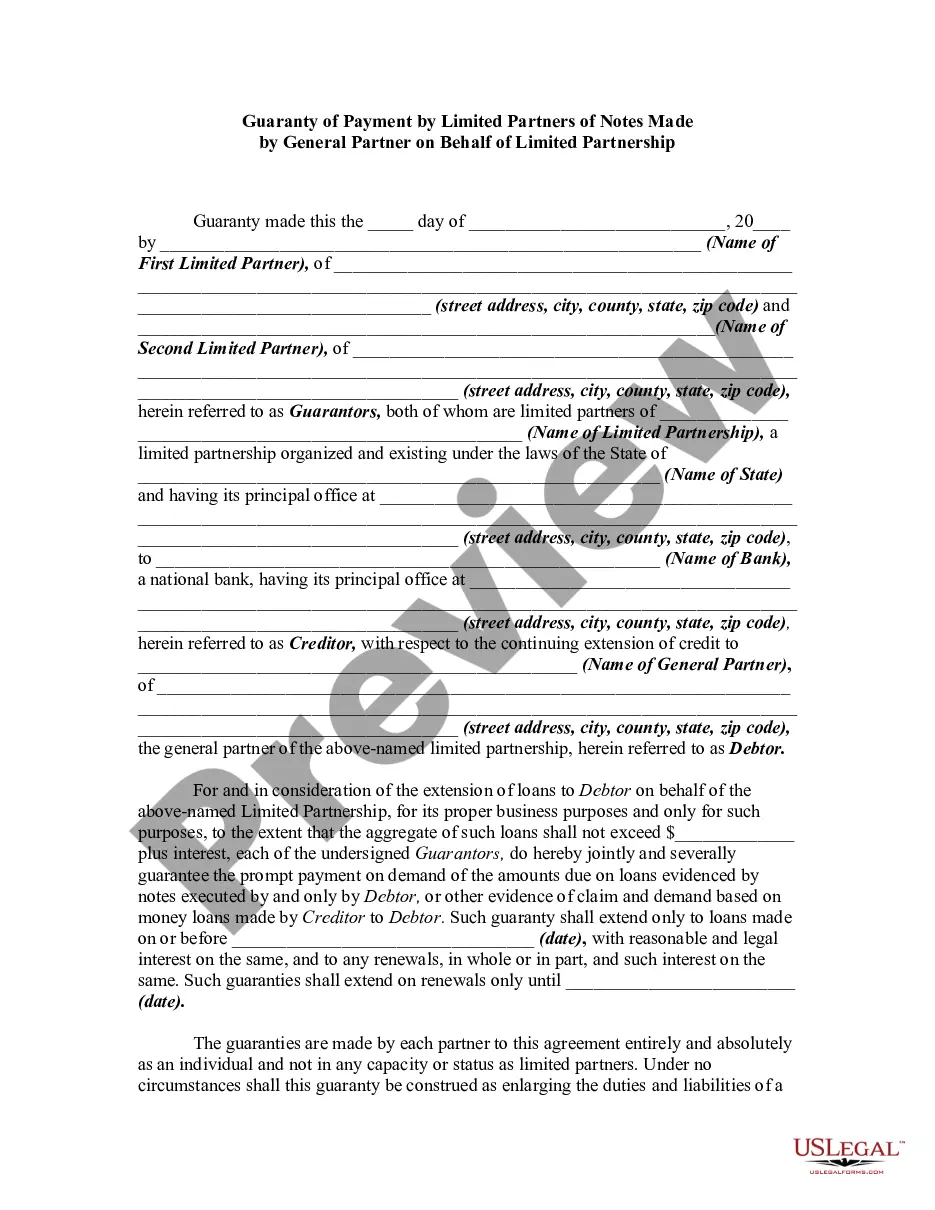
Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy
Description
How to fill out Leave Of Absence For Pregnancy?
You can spend multiple hours online searching for the official document template that meets the state and federal requirements you need.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal forms that can be reviewed by professionals.
You can download or print the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy from the platform.
First, ensure that you have selected the correct document template for your state/city of choice. Review the form description to verify you have chosen the right one. If available, use the Preview button to browse through the document template as well.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click on the Download button.
- Afterward, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy.
- Every legal document template you obtain is yours permanently.
- To get another copy of the purchased form, go to the My documents section and click on the corresponding button.
- If this is your first time using the US Legal Forms site, follow the simple instructions below.
Form popularity
FAQ
Exceptions to maternity leave in Washington may include scenarios where the employer has fewer than eight employees or if the employee has not been with the company long enough. Companies might also have specific policies outlining unique circumstances that affect eligibility. Knowing these exceptions can better prepare you for the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy.
If you have just started a job, your eligibility for maternity leave may depend on the company’s policies. Federal and state laws require you to have worked for a qualifying period to be eligible for leave. However, some employers may offer benefits sooner. It’s advisable to consult your HR department regarding their specific policies on the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy.
The Pregnancy Discrimination Act is a federal law that prohibits discrimination based on pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions. In Washington state, this law complements state maternity leave provisions, ensuring pregnant employees receive fair treatment. Knowing the act empowers you as you navigate the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy.
In Washington, pregnancy itself is not classified as a disability. However, complications arising from pregnancy may be considered disabilities under the law, thus qualifying for additional protections. Understanding these nuances is crucial for advocating your rights under the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy.
Washington laws require employers to provide maternity leave and protect pregnant employees from discrimination. Eligible employees can take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave under the Family Leave Act. These laws support your rights and ensure you can take necessary time off during pregnancy while maintaining job security.
In Washington, employees qualify for maternity leave if they meet certain criteria, including working for an employer with at least eight employees. Additionally, employees must have worked for their employer for at least 12 months and have logged 1,050 hours in the previous year. Knowing if you qualify can guide your experience with the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy.
A pregnant employee in Washington is entitled to a leave of absence under the state's pregnancy discrimination laws. Employees may take time off for prenatal care, childbirth, and recovery. Moreover, employers must maintain health insurance coverage during this period. Understanding your rights helps you navigate the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy effectively.
You can go on maternity leave starting at 30 weeks pregnant, but most opt to start around 36 weeks. It is crucial to review your employer’s policies alongside the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy to ensure that you make an informed decision. Your comfort and readiness to embrace motherhood should guide your timing.
You may begin your maternity leave as early as 30 days prior to your due date, but it depends on your situation. Many women take leave around 36 weeks, allowing for a buffer before labor begins. The Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy is designed to support your transitional needs as you prepare for childbirth.
Going on maternity leave at 32 weeks can be too early for some but may be the right choice for others, depending on factors like your health and job demands. Carefully consider your needs, as well as the guidelines in the Washington Leave of Absence for Pregnancy. Ultimately, your health and well-being are the most important.