Virgin Islands Agreement to Dissolve and Wind up Partnership with Settlement and Lump Sum Payment
Description
How to fill out Agreement To Dissolve And Wind Up Partnership With Settlement And Lump Sum Payment?
If you desire to complete, obtain, or print legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the most extensive assortment of legal forms available online.
Leverage the site's simple and accessible search to locate the documents you require.
A range of templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Step 4. After you have found the form you need, click the Buy now button. Choose the pricing plan you prefer and enter your credentials to sign up for an account.
Step 5. Process the payment. You may use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to locate the Virgin Islands Agreement to Dissolve and Wind up Partnership with Settlement and Lump Sum Payment in just a few clicks.
- If you are currently a US Legal Forms member, Log In to your account and click the Purchase button to obtain the Virgin Islands Agreement to Dissolve and Wind up Partnership with Settlement and Lump Sum Payment.
- You can also access forms you previously obtained within the My documents tab of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the guidelines below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the form for the appropriate city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the form’s details. Be sure to read the information.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search area at the top of the screen to find alternative versions of the legal form template.
Form popularity
FAQ
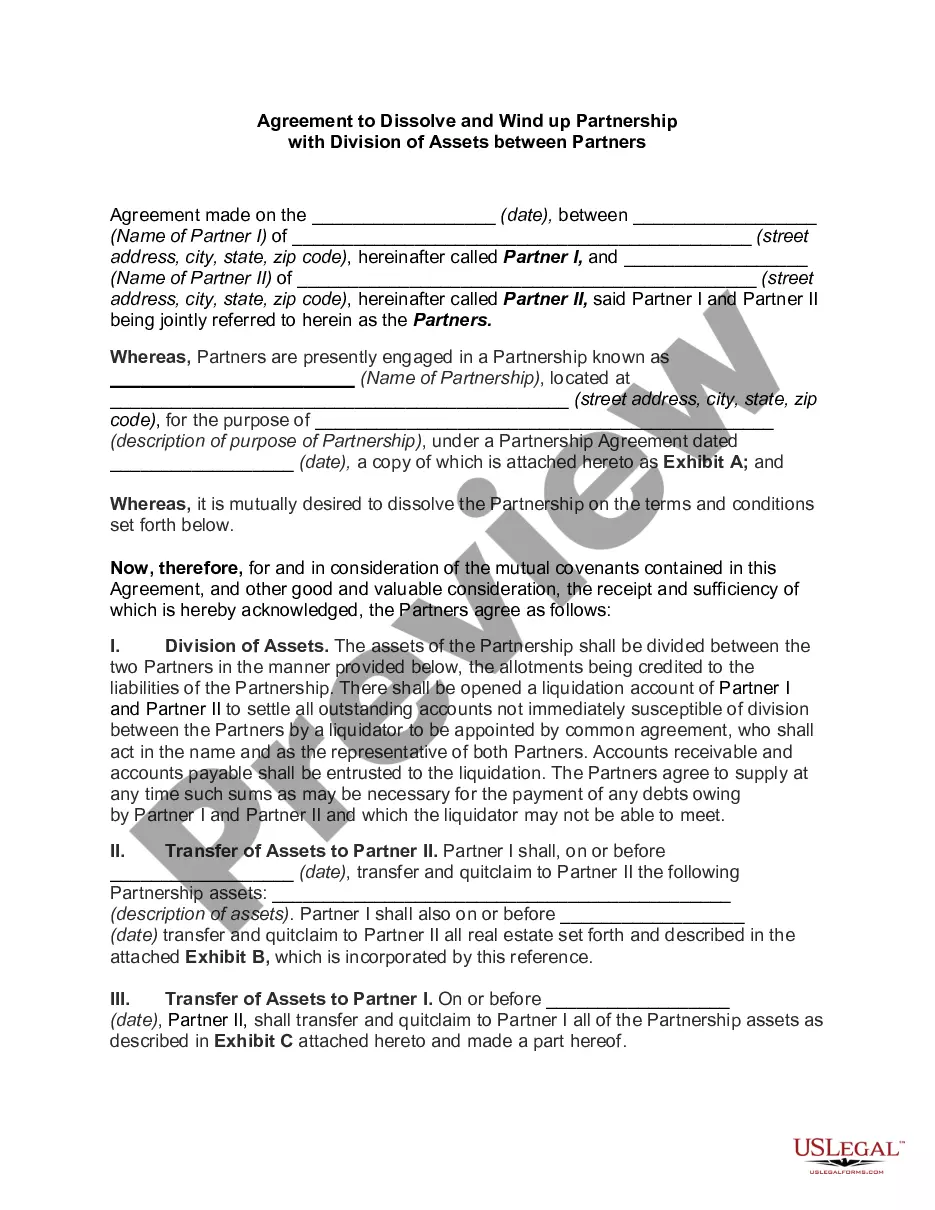
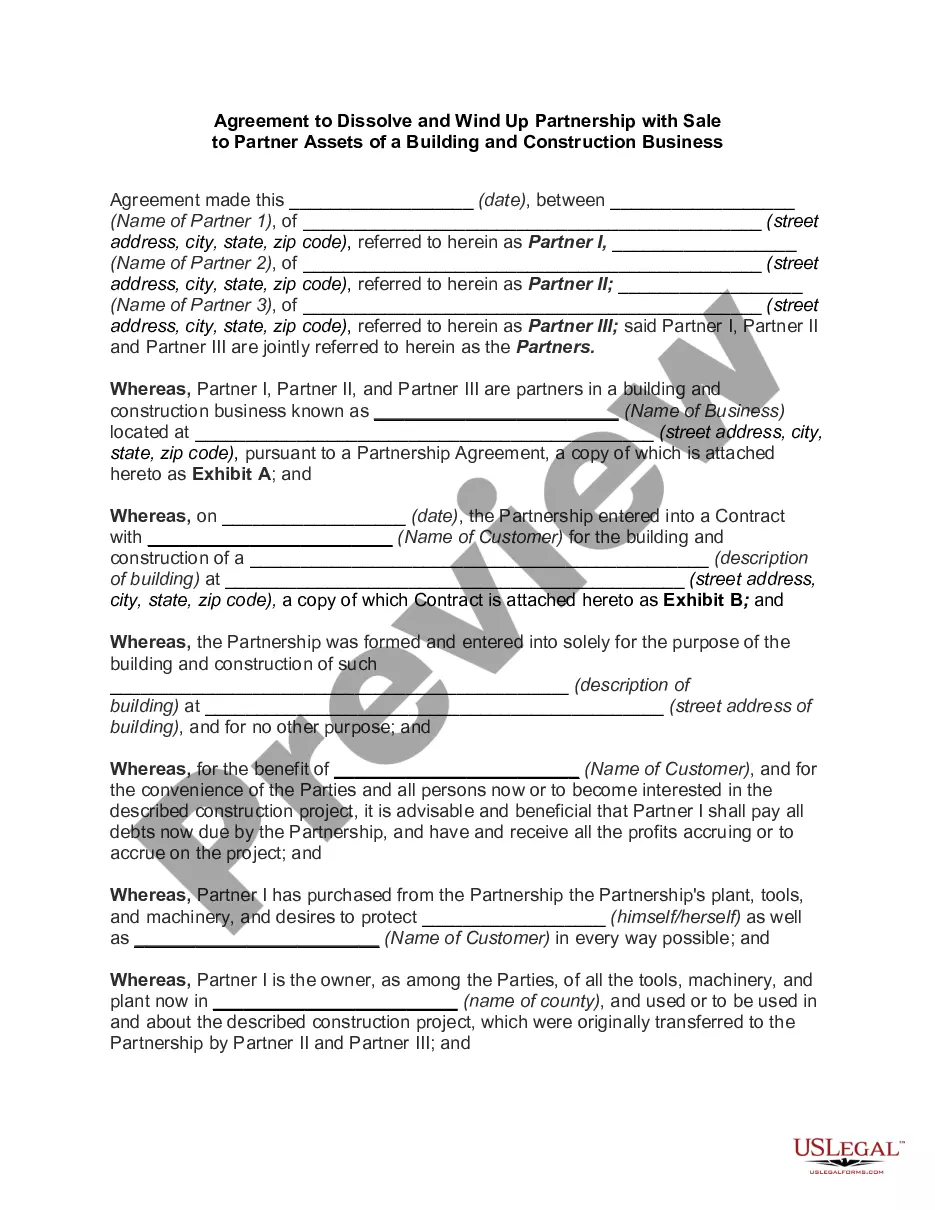
The first step in termination is known as dissolution. Dissolution occurs when any partner discontinues his or her involvement in the partnership business or when there is any change in the partnership relationship. The second step is known as winding up.
On the dissolution of a partnership every partner is entitled, as against the other partners in the firm, and all persons claiming through them in respect of their interests as partners, to have the property of the partnership applied in payment of the debts and liabilities of the firm, and to have the surplus assets
If a company goes into liquidation, all of its assets are distributed to its creditors. Secured creditors are first in line. Next are unsecured creditors, including employees who are owed money. Stockholders are paid last.
Limiting Your Future Liability Partners are personally liable for the debts and obligations of the partnership, but your obligations end once the partnership closes. You might be personally responsible for any contracts that you entered into during the partnership, depending on the language in the contract.
Only partnership assets are to be divided among partners upon dissolution. If assets were used by the partnership, but did not form part of the partnership assets, then those assets will not be divided upon dissolution (see, for example, Hansen v Hansen, 2005 SKQB 436).
Liability for partnership debtsPartners are 'jointly and severally liable' for the firm's debts. This means that the firm's creditors can take action against any partner. Also, they can take action against more than one partner at the same time.
An agreement can spell out the order in which liabilities are to be paid, but if it does not, UPA Section 40(a) and RUPA Section 807(1) rank them in this order: (1) to creditors other than partners, (2) to partners for liabilities other than for capital and profits, (3) to partners for capital contributions, and
After the dissolution of the partnership, the partner is liable to pay his debt and to wind up the affairs regarding the partnership. After the dissolution, partners are liable to share the profit which they have decided in agreement or accordingly.
Once the debts owed to all creditors are satisfied, the partnership property will be distributed to each partner according to their ownership interest in the partnership. If there was a partnership agreement, then that document controls the distribution.
Whether the former partner dies or otherwise quits the firm, the noncontinuing one or his, her, or its legal representative is entitled to an accounting and to be paid the value of the partnership interest, less damages for wrongful dissolution.