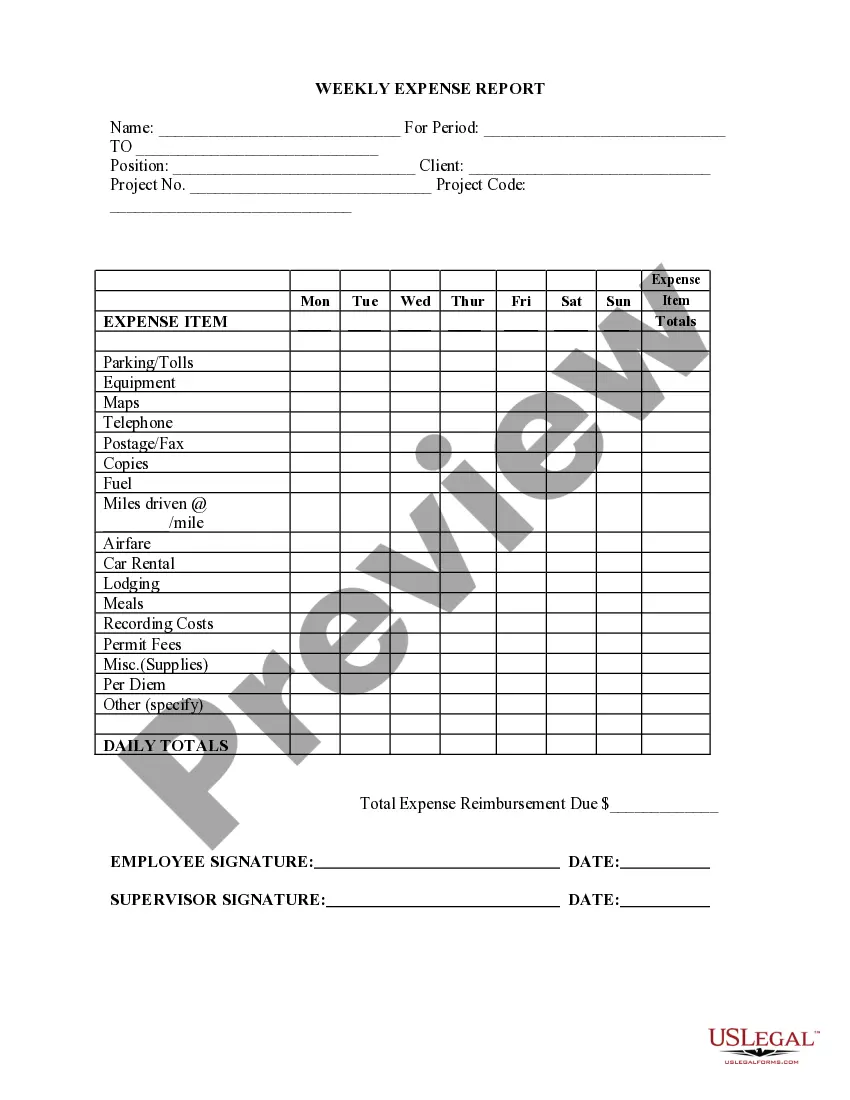
Virginia Employee Time Report (Nonexempt)
Description
How to fill out Employee Time Report (Nonexempt)?
Selecting the appropriate legal document format can be quite a challenge.
Of course, there are numerous templates available online, but how do you obtain the legal form you need.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers a vast array of templates, including the Virginia Employee Time Report (Nonexempt), which can be utilized for both professional and personal purposes.
If the form does not fulfill your requirements, use the Search area to find the correct form.
- All forms are reviewed by experts and comply with federal and state regulations.
- If you are currently registered, Log In to your account and click the Obtain button to locate the Virginia Employee Time Report (Nonexempt).
- Use your account to browse the legal forms you have previously purchased.
- Navigate to the My documents tab in your account to acquire another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple instructions for you to follow.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/region. You can view the form using the Review button and read the form description to confirm this is indeed the right one for you.
Form popularity
FAQ
Virginia's new non-compete law, effective July 2020, restricts non-compete agreements for low-wage employees. These agreements must be in writing, and employers cannot impose them on workers earning less than a specified income. Understanding this law is crucial for employers to develop effective employee time reporting systems, like the Virginia Employee Time Report (Nonexempt).
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
Comp time is calculated by multiplying 1.5 times overtime hours worked.
Non-exempt status indicates a Veteran is not exempt from paying the funding fee. Contact RLC indicates a system-generated determination is not available, or any loan may need to be submitted to VA as prior approval.
The FLSA sets the maximum amount of comp time that may be accumulated: nonexempt employees who work in "a public safety activity, emergency response activity, or seasonal activity" may accumulate up to a maximum of 480 hours of comp time, while other employees are limited to 240 hours.
An employee who, based on salary and duties performed, is not exempt from the minimum wage and overtime provisions of the Fair Labor Standards Act and must be compensated at a rate of one and one-half times his/her regular rate of pay for hours worked in excess of 40 in a workweek.
Exempt employees are mostly paid on a salary basis and not per hour. Unlike non-exempt employees, employers may decide whether to pay exempt employees for any extra work outside the official 40 working hours per week. As a business owner, this allows you flexibility in your payment and employee benefits policies.
No mandatory compensatory time off is permitted for wage employees or in lieu of FLSA overtime pay.
Examples of non-exempt employees include contractors, freelancers, interns, servers, retail associates and similar jobs. Even if non-exempt employees earn more than the federal minimum wage, they still take direction from supervisors and do not have administrative or executive positions.
A. Yes, you are entitled to one hour of reporting time pay. Under the law, if an employee is required to report to work a second time in any one workday and is furnished less than two hours of work on the second reporting, he or she must be paid for two hours at his or her regular rate of pay.