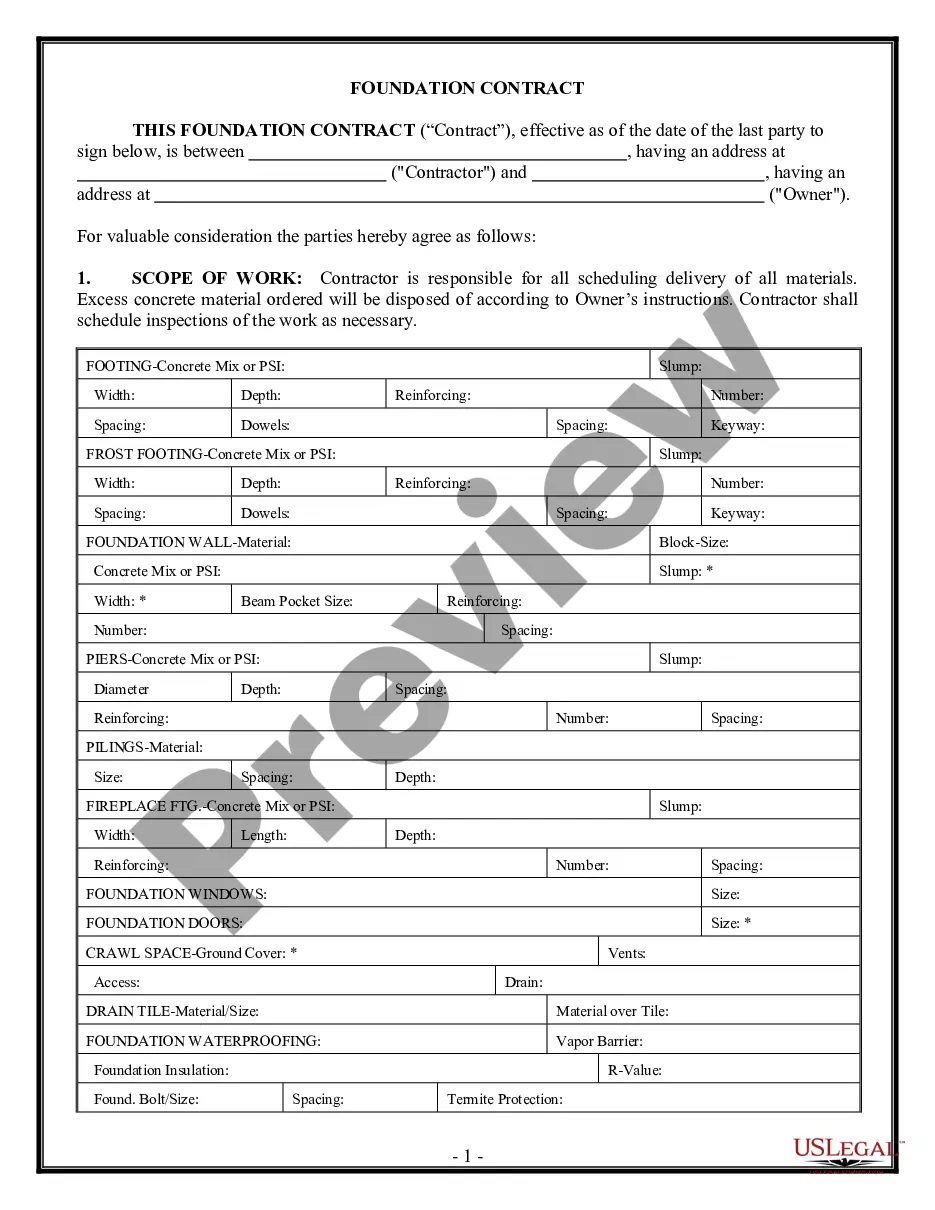
Virginia Grantor Retained Annuity Trust
Description
How to fill out Grantor Retained Annuity Trust?
Are you in a circumstance where you frequently need to acquire documents for both business or personal purposes nearly every day? There are numerous legal document templates accessible online, but locating versions you can rely on is challenging.
US Legal Forms offers a vast selection of form templates, such as the Virginia Grantor Retained Annuity Trust, that are designed to comply with federal and state regulations.
If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In. Then, you can download the Virginia Grantor Retained Annuity Trust template.
Select a preferred file format and download your copy.
Access all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section. You can obtain another copy of the Virginia Grantor Retained Annuity Trust anytime you need. Just click the desired form to download or print the template.
Utilize US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive collection of legal documents, to save time and minimize mistakes. The service provides professionally crafted legal document templates that you can use for a variety of purposes. Create an account on US Legal Forms and start making your life a bit easier.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Locate the form you need and verify that it is for your correct jurisdiction.
- Use the Preview button to examine the form.
- Check the description to confirm that you have selected the right document.
- If the form is not what you are looking for, use the Search field to find the document that suits your needs and requirements.
- Once you find the correct form, click on Buy now.
- Choose the pricing plan you desire, fill in the necessary information to create your account, and complete the transaction using your PayPal or credit card.
Form popularity
FAQ
Setting up a Virginia Grantor Retained Annuity Trust involves several steps, which can be efficiently navigated with the right guidance. Begin by selecting the assets you wish to transfer into the trust. Next, determine the annuity payment amount and duration. Finally, working with a legal expert or utilizing user-friendly services like US Legal Forms can ensure compliance with IRS regulations and provide necessary documentation.
Tax Implications of the GRAT During the term of the GRAT, the Donor will be taxed on all of the income and capital gains earned by the trust, without regard to the amount of the annuity paid to the Donor.
If the grantor dies during the GRAT term, the value of the remainder interest in the trust is included in the grantor's taxable estate under either section 2036 (retained income, possession, or enjoyment of property) or 2039 (retained right to receive annuity in transferred property).
Pros. There are a number of benefits to setting up a GRAT. For one, the annuities can provide a steady stream of income for those who may need it in retirement. However, the main benefit of establishing a GRAT is the potential to transfer large amounts of money to a beneficiary while paying little-to-no gift tax.
The annuity amount is paid to the grantor during the term of the GRAT, and any property remaining in the trust at the end of the GRAT term passes to the beneficiaries with no further gift tax consequences.
Grantor retained annuity trusts (GRAT) are estate planning instruments in which a grantor locks assets in a trust from which they earn annual income. Upon expiry, the beneficiary receives the assets with minimal or no gift tax liability. GRATS are used by wealthy individuals to minimize tax liabilities.
In other words, during the initial term of the GRAT (the term that the Grantor is to receive the annuity payments) the Grantor will be taxed on all of the income earned by the GRAT during each such year, including capital gains.
With respect to income taxes, the grantor is treated as the owner of the assets during the GRAT term and reports all income earned by the GRAT on his individual income tax return. To avoid having to file its own fiduciary income tax return, the GRAT should not apply for a separate taxpayer identification number.
GRATs are irrevocable trusts that last for a specific period of time of at least two years. The term you choose depends on your goals and expectations for asset growth potential, but we typically recommend a term between two and five years.
How Are GRATs Taxed? GRATs are taxed in two ways: Any income you earn from the appreciation of your assets in the trust is subject to regular income tax, and any remaining funds/assets that transfer to a beneficiary are subject to gift taxes.