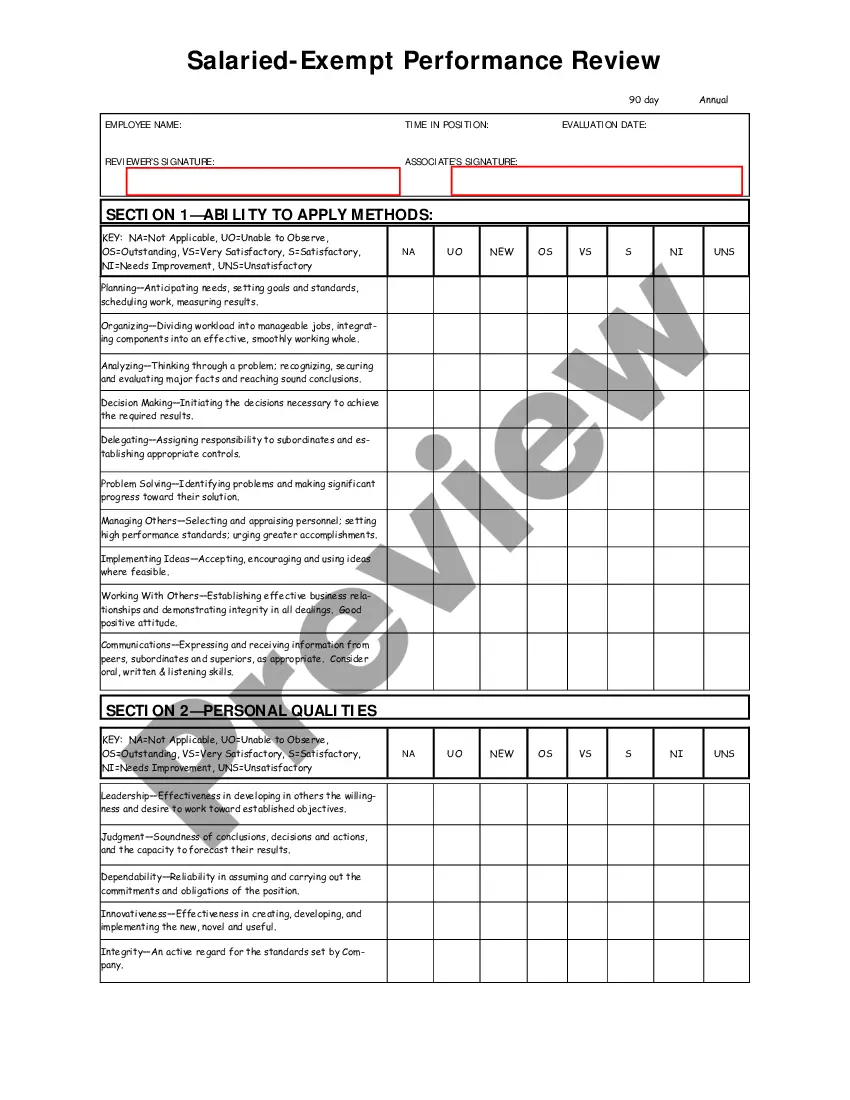
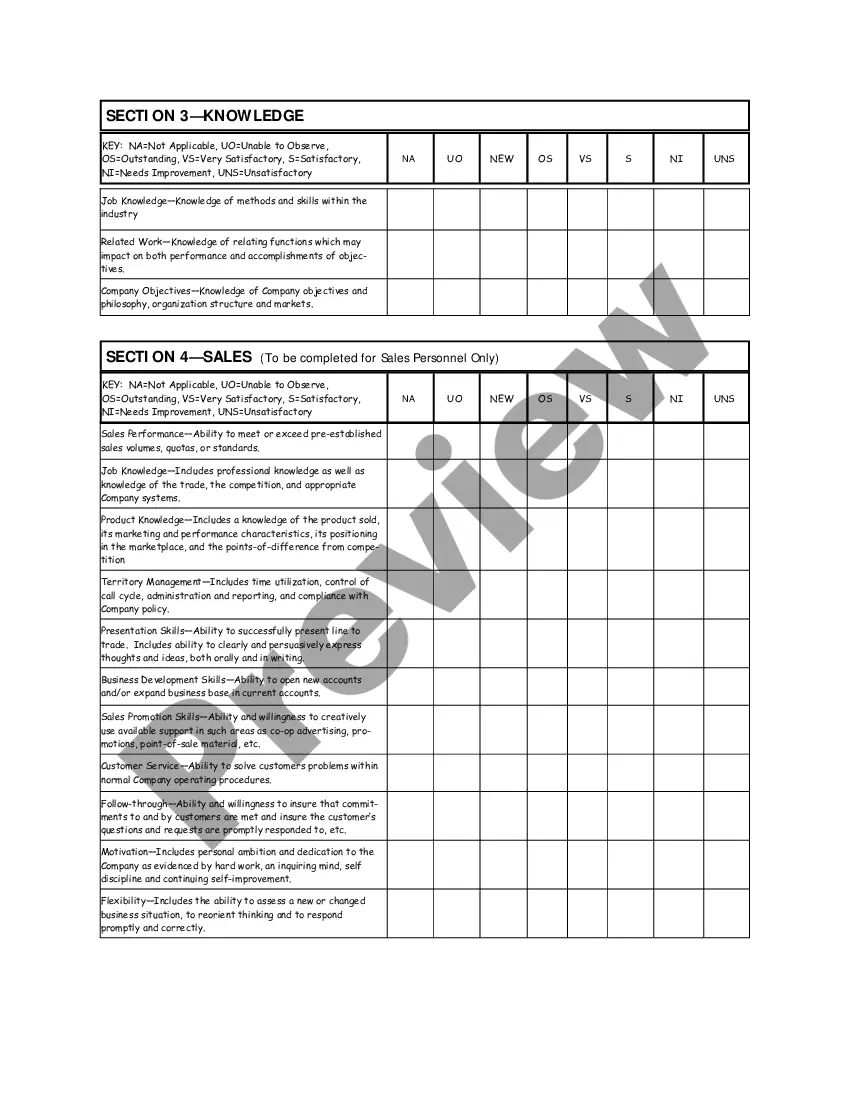
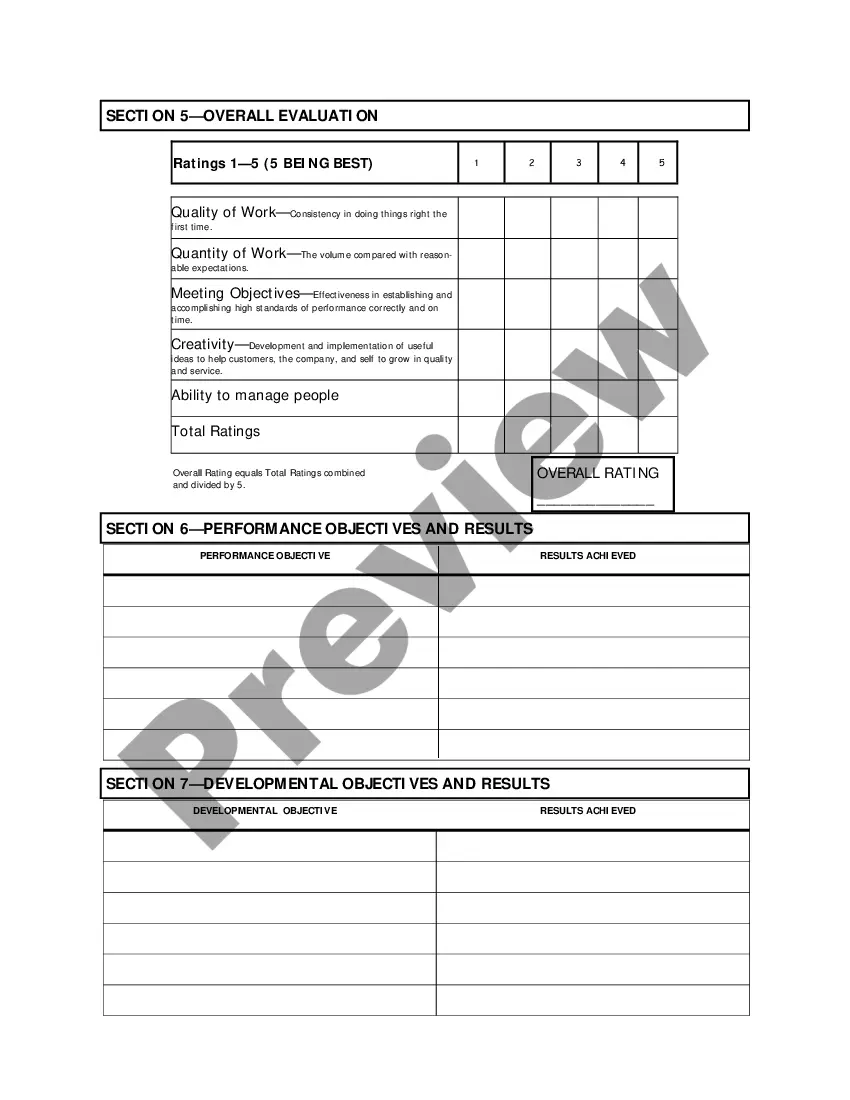
Texas Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form
Description
How to fill out Salary - Exempt Employee Review And Evaluation Form?
You may spend several hours on the Internet trying to find the legal record template which fits the federal and state specifications you want. US Legal Forms offers thousands of legal types that are reviewed by experts. You can actually acquire or printing the Texas Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form from our services.
If you have a US Legal Forms bank account, you may log in and then click the Download switch. After that, you may complete, edit, printing, or sign the Texas Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form. Each legal record template you purchase is yours permanently. To get an additional version for any acquired develop, check out the My Forms tab and then click the related switch.
Should you use the US Legal Forms website the very first time, keep to the simple guidelines below:
- Initially, ensure that you have chosen the proper record template for the state/area that you pick. Read the develop outline to make sure you have chosen the right develop. If available, utilize the Preview switch to appear with the record template at the same time.
- If you wish to find an additional variation of your develop, utilize the Look for discipline to get the template that meets your needs and specifications.
- When you have identified the template you would like, just click Purchase now to move forward.
- Pick the costs program you would like, enter your accreditations, and sign up for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the purchase. You should use your bank card or PayPal bank account to pay for the legal develop.
- Pick the formatting of your record and acquire it to your device.
- Make alterations to your record if needed. You may complete, edit and sign and printing Texas Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form.
Download and printing thousands of record themes making use of the US Legal Forms Internet site, that offers the greatest assortment of legal types. Use specialist and express-particular themes to deal with your company or specific demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
Overtime Requirements Federal overtime laws and Texas overtime laws stipulate that salaried workers must be paid overtime pay for any hours worked beyond 40 in a work week.
An employee who fits this exemption may be paid either a salary of at least $684 per week, or on an hourly basis with no premium for overtime work, i.e., straight-time pay for all hours worked, as long as the hourly rate is at least $27.63 per hour.
These exemptions also apply in Texas. So if you're paid an annual salary and earning more than a certain amount set by law, you are considered "exempt" and not covered by the FLSA. This means exempt employees are not entitled to overtime pay for working more than 40 hours in a week.
Under federal overtime law and Texas overtime law, salaried employees must receive overtime pay for hours worked over 40 in any workweek unless two specific requirements are met: (1) the salary exceeds $455 per workweek; and (2) the employee performs duties satisfying one of the narrowly-defined FLSA overtime
Employees Not Entitled to Overtime PayThose not covered by FLSA are known as exempt employees. These exemptions also apply in Texas. So if you're paid an annual salary and earning more than a certain amount set by law, you are considered "exempt" and not covered by the FLSA.
Section 52.001 of the Texas Labor Code forbids an employer in the business of selling merchandise at retail from requiring an employee to work seven consecutive days. The employee cannot be denied "at least one period of 24-consecutive hours of time off for rest or worship" in each workweek.
Maximum hours an exempt employee can be required to work The law does not provide a maximum number of hours that an exempt worker can be required to work during a week. This means that an employer could require an exempt employee to work well beyond 40 hours a week without overtime compensation.
Generally, an employee "must receive his full salary for any week in which he performs any work without regard to the number of days or hours worked". However, the regulation recognizes "the general rule that an employee need not be paid for any workweek in which he performs no work".
Under federal overtime law and Texas overtime law, salaried employees must receive overtime pay for hours worked over 40 in any workweek unless two specific requirements are met: (1) the salary exceeds $455 per workweek; and (2) the employee performs duties satisfying one of the narrowly-defined FLSA overtime