Tennessee User oriented Source Code Escrow Agreement
Description
How to fill out User Oriented Source Code Escrow Agreement?
US Legal Forms - among the largest libraries of lawful forms in the States - provides a variety of lawful record themes it is possible to acquire or produce. Making use of the web site, you may get a large number of forms for organization and person purposes, categorized by types, claims, or key phrases.You will discover the latest versions of forms much like the Tennessee User oriented Source Code Escrow Agreement within minutes.
If you have a subscription, log in and acquire Tennessee User oriented Source Code Escrow Agreement from your US Legal Forms local library. The Down load switch will show up on every single type you view. You have accessibility to all previously saved forms inside the My Forms tab of your own accounts.
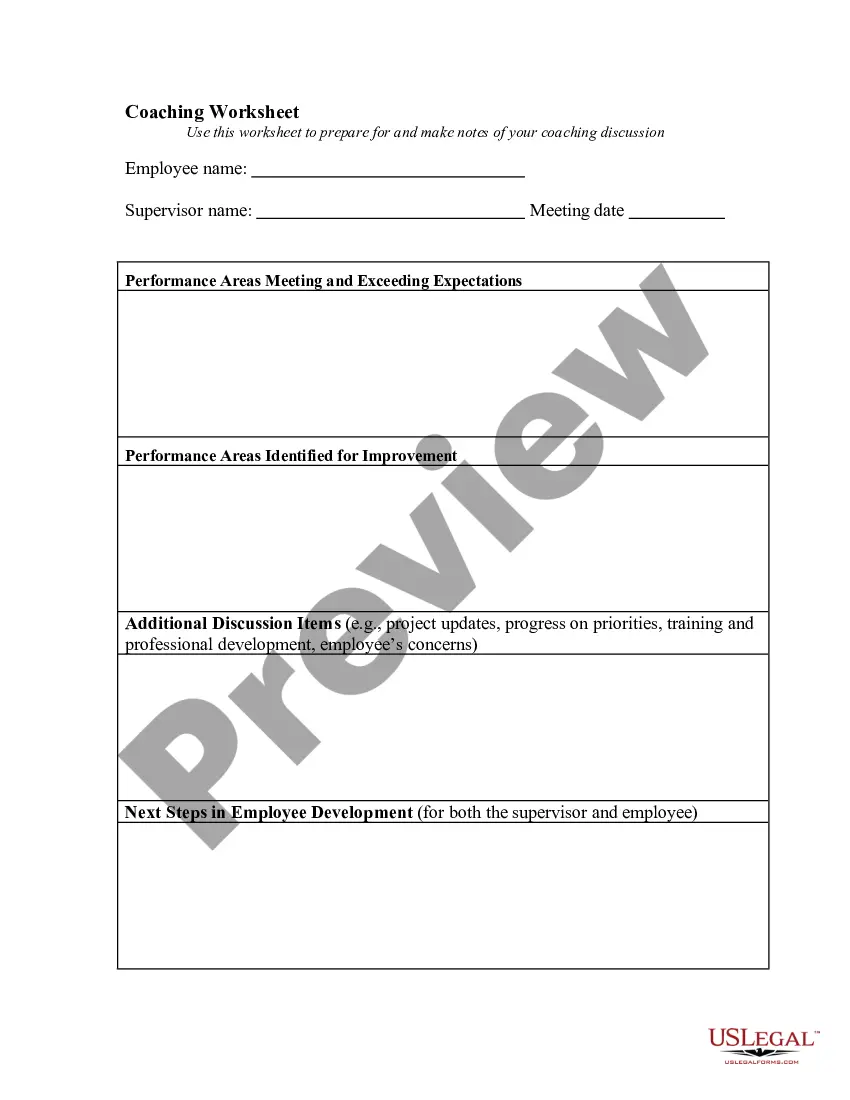
If you want to use US Legal Forms the very first time, listed below are easy guidelines to help you get began:
- Be sure you have chosen the best type for your personal metropolis/area. Select the Review switch to analyze the form`s information. Look at the type description to actually have chosen the correct type.
- When the type doesn`t fit your demands, use the Look for area near the top of the screen to get the one which does.
- If you are pleased with the shape, verify your option by simply clicking the Buy now switch. Then, opt for the prices program you prefer and give your credentials to sign up to have an accounts.
- Approach the transaction. Make use of your charge card or PayPal accounts to perform the transaction.
- Choose the structure and acquire the shape on the device.
- Make modifications. Fill out, change and produce and indication the saved Tennessee User oriented Source Code Escrow Agreement.
Every single template you included in your account does not have an expiry date and it is yours permanently. So, if you would like acquire or produce one more copy, just go to the My Forms portion and click on about the type you will need.
Obtain access to the Tennessee User oriented Source Code Escrow Agreement with US Legal Forms, by far the most substantial local library of lawful record themes. Use a large number of specialist and state-specific themes that meet up with your business or person requirements and demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
Release Conditions: Details the specific circumstances under which the escrow agent may release the deposited materials to the beneficiary, such as bankruptcy, failure to meet support obligations, or a predetermined trigger event.
Source code escrow is the deposit of the source code of software with a third-party escrow agent. Escrow is typically requested by a party licensing software (the licensee), to ensure maintenance of the software instead of abandonment or orphaning.
A source code escrow agreement typically instructs the agent to release the source code to the licensee if and when a specified event occurs, such as the licensor becoming insolvent or defaulting on its maintenance obligations under the principal license agreement.
Under the Software Escrow Agreement, the supplier periodically deposits a copy of the software source code and associated materials for secure storage within NCC Group's secure physical or virtual vaults, ensuring that the material can be accessed and released should the need arise.
Source code escrow is the deposit of the source code of software with a third-party escrow agent. Escrow is typically requested by a party licensing software (the licensee), to ensure maintenance of the software instead of abandonment or orphaning.
The objective of a source code escrow agreement is to provide comfort to the beneficiary that if the software developer is unable or unwilling to support the software, the source code and other critical components such as databases, deployment scripts, and documentation can be released to them.
A source code escrow agreement typically instructs the agent to release the source code to the licensee if and when a specified event occurs, such as the licensor becoming insolvent or defaulting on its maintenance obligations under the principal license agreement.
The escrow agreement will provide the conditions under which you will receive a copy of the source code. The most common release conditions are (1) the software vendor ceases business or goes bankrupt and (2) the software vendor ceases to provide support and maintenance services.