This informational guide reviews state laws that detail the specific circumstances that must be present when a court terminates the legal parent-child relationship.
South Carolina Grounds for Involuntary Termination of Parental Rights
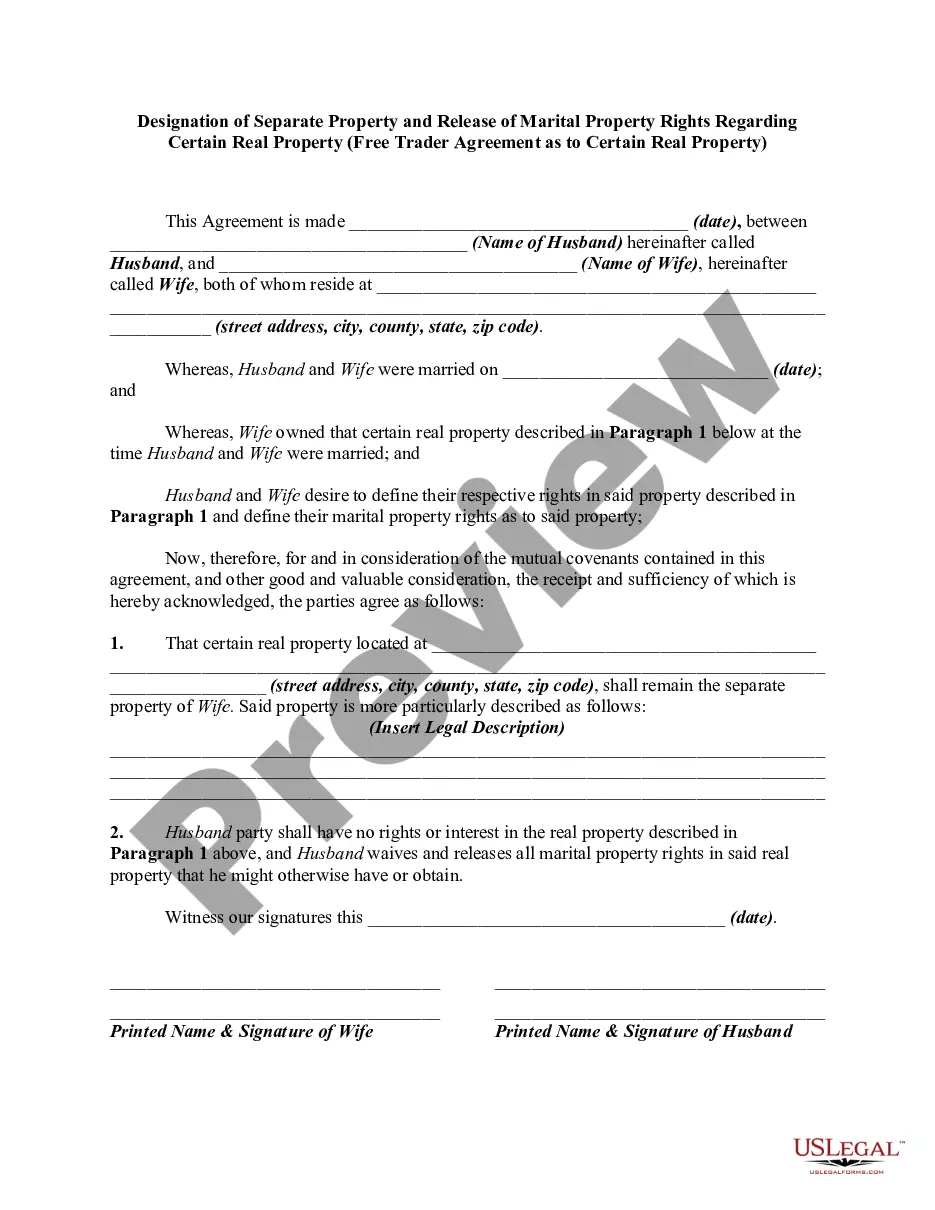
Description
How to fill out Grounds For Involuntary Termination Of Parental Rights?
If you wish to comprehensive, acquire, or print out lawful papers themes, use US Legal Forms, the largest variety of lawful types, which can be found on-line. Use the site`s simple and easy hassle-free look for to discover the papers you will need. A variety of themes for business and person reasons are categorized by classes and states, or key phrases. Use US Legal Forms to discover the South Carolina Grounds for Involuntary Termination of Parental Rights within a handful of click throughs.
When you are presently a US Legal Forms client, log in for your accounts and click on the Obtain option to obtain the South Carolina Grounds for Involuntary Termination of Parental Rights. Also you can access types you previously saved from the My Forms tab of your respective accounts.
If you are using US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions under:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the shape for that right town/country.
- Step 2. Make use of the Review solution to check out the form`s content. Don`t neglect to read the description.
- Step 3. When you are not happy together with the form, utilize the Lookup industry towards the top of the display to get other variations from the lawful form format.
- Step 4. When you have found the shape you will need, select the Acquire now option. Choose the rates strategy you choose and add your credentials to register on an accounts.
- Step 5. Method the deal. You should use your charge card or PayPal accounts to perform the deal.
- Step 6. Choose the formatting from the lawful form and acquire it on your own device.
- Step 7. Total, edit and print out or sign the South Carolina Grounds for Involuntary Termination of Parental Rights.
Every lawful papers format you get is the one you have permanently. You possess acces to each form you saved in your acccount. Select the My Forms section and select a form to print out or acquire once again.
Compete and acquire, and print out the South Carolina Grounds for Involuntary Termination of Parental Rights with US Legal Forms. There are many professional and condition-particular types you can use for the business or person requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
What to Do Encourage open communication. Let your child know that you're open to hearing what they have to say?even if you disagree. ... Set communication ground rules. While different opinions are welcome, rudeness is not. ... Be empathetic. ... If possible, bring your ex into the conversation. ... Express your fears.
If one parent abandons the child and does not visit the child or contribute financially to the child's upbringing for a period of at least six months, you may have grounds to seek a termination of parental rights.
In South Carolina, a custodial parent who wants to move out-of-state with the children must ask a judge for permission. If the other parent objects to the relocation, the court will hold a hearing to determine if the move is in the child's best interests.
There are two methods of obtaining TPR: voluntarily or involuntarily. The process of voluntary relinquishment is governed by S.C. Code § 63-9-330. The consent to relinquishment of parental rights must be witnessed by two persons, one of whom must be independent counsel for the relinquishing parent.
Many clients ask me whether there is an age can a child have to be to refuse visitation. Under South Carolina's family laws, there is no set age at which a child can refuse to go visit with the other parent.
5 Things to Do with Kids When They Don't Want to Be with You Don't take it personally. ... Don't live on their level emotionally. ... Stick to common ground experiences that can bridge the gap. ... Try taking on the Galactic Overlord for once.
Here's how to handle parental favoritism: Try not to take it personally. This is tricky: being rejected hurts, and it does feel personal. ... Don't put the emotional burden on your child. ... Validate their feelings, empathize, and reassure. ... Know when to let it go. ... Schedule one-on-one time with each adult. ... Be patient.
Speak with your child about why they don't want to visit. Approach the conversation from a position of understanding while still impressing upon them the importance of maintaining a healthy relationship with the co-parent. Allow them to express any feelings or concerns they may have without judgment.