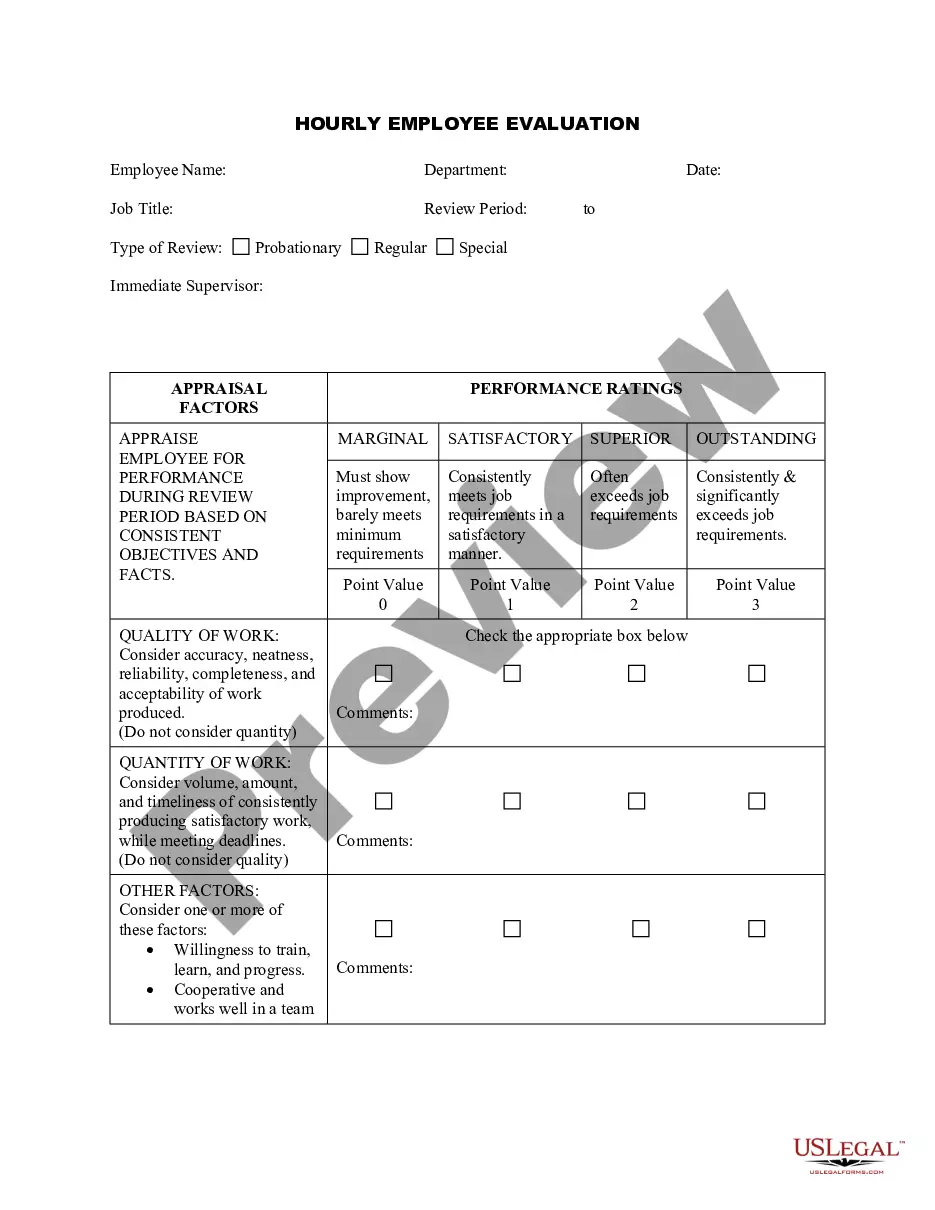
Oklahoma Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees
Description
How to fill out Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form For Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, And Managerial Employees?
It is feasible to spend hours online searching for the appropriate legal document template that complies with federal and state requirements you will need. US Legal Forms offers thousands of legal documents that are reviewed by professionals.
You can easily download or print the Oklahoma Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees from our service.
If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click on the Obtain button. Next, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Oklahoma Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees. Every legal document template you obtain is your property permanently. To get another copy of any purchased form, go to the My documents tab and select the corresponding option.
Choose the format of the document and download it to your device. Make changes to your document if necessary. You have the ability to complete, modify, sign, and print the Oklahoma Model Performance Evaluation - Appraisal Form for Hourly, Exempt, Nonexempt, and Managerial Employees. Download and print thousands of document templates using the US Legal Forms website, which provides the largest collection of legal documents. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to address your business or personal needs.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure you have chosen the correct document template for the state/city of your selection. Review the form outline to confirm you have selected the right form.
- If available, utilize the Preview option to examine the document template as well.
- If you wish to find another version of the form, make use of the Lookup section to find the template that meets your needs and requirements.
- Once you have discovered the template you desire, click Purchase now to move forward.
- Select the pricing plan you prefer, enter your details, and create an account on US Legal Forms.
- Finalize the purchase. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to pay for the legal form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Employees whose jobs are governed by the FLSA are either "exempt" or "nonexempt." Nonexempt employees are entitled to overtime pay. Exempt employees are not. Most employees covered by the FLSA are nonexempt.
The FLSA exemption test refers to the status of a job as outlined in the Fair Labor Standards Act. The FLSA determines whether a job is exempt or nonexempt as it relates to overtime obligations.
To classify an employee's FLSA status, you must answer three questions covering the following areas:Salary basis: Does the employee earn a salary?Salary level: How much does the employee earn per week or year?More items...?
The regular rate is calculated by dividing the total pay for employment (except for the statutory exclusions) in any workweek by the total number of hours actually worked to determine the regular rate. Covered means an employee is protected by the FLSA.
Exempt employees are mostly paid on a salary basis and not per hour. Unlike non-exempt employees, employers may decide whether to pay exempt employees for any extra work outside the official 40 working hours per week. As a business owner, this allows you flexibility in your payment and employee benefits policies.
The learned professional exemption is restricted to professions where specialized academic training is a standard prerequisite for entrance into the profession. The best evidence of meeting this requirement is having the appropriate academic degree.
The FLSA, identifies two types of employees: non-exempt employees and exempt employees: Non-exempt employees are employees who, based on the duties performed and the manner of compensation, are required to account for time worked and sick leave, vacation, and other leave on an hourly and fractional hourly basis.
The four main components or elements covered by the FLSA are: payment of a minimum wage. overtime pay for working 40+ hours in a week. recordkeeping by the employer on employees: accurate information identifying the worker and the hours worked and the wages earned.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).