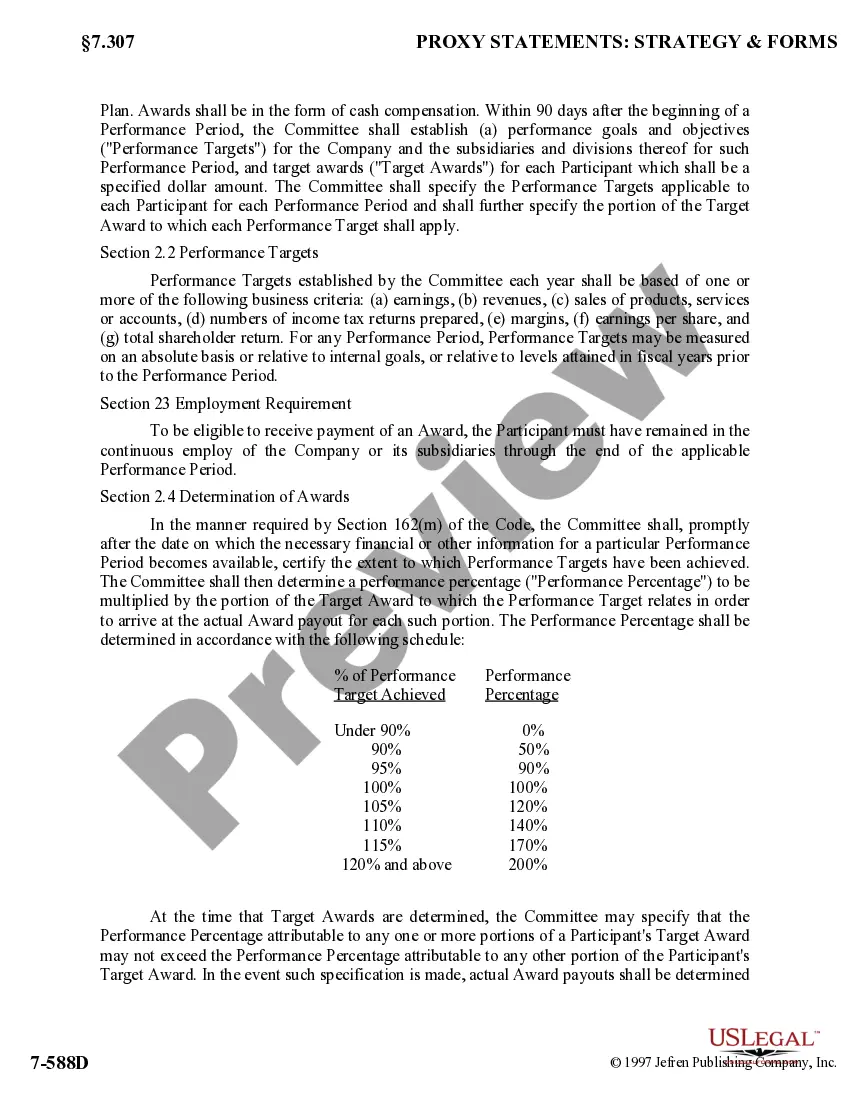
New York Short-Term Incentive Plan
Description
How to fill out Short-Term Incentive Plan?
If you need to comprehensive, down load, or produce authorized file templates, use US Legal Forms, the biggest variety of authorized forms, that can be found online. Make use of the site`s simple and easy practical search to obtain the files you require. Numerous templates for business and person reasons are sorted by categories and says, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the New York Short-Term Incentive Plan within a couple of clicks.
When you are presently a US Legal Forms client, log in for your account and then click the Obtain switch to find the New York Short-Term Incentive Plan. You can even access forms you previously delivered electronically in the My Forms tab of your respective account.
If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the instructions below:
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the shape for that right town/country.
- Step 2. Utilize the Review method to look through the form`s content. Never overlook to learn the explanation.
- Step 3. When you are unhappy with the develop, utilize the Lookup industry at the top of the monitor to discover other types in the authorized develop design.
- Step 4. Upon having found the shape you require, select the Purchase now switch. Select the pricing program you favor and put your references to sign up for the account.
- Step 5. Method the financial transaction. You may use your Мisa or Ьastercard or PayPal account to finish the financial transaction.
- Step 6. Pick the formatting in the authorized develop and down load it on your gadget.
- Step 7. Full, revise and produce or signal the New York Short-Term Incentive Plan.
Every single authorized file design you get is yours for a long time. You might have acces to every single develop you delivered electronically inside your acccount. Click on the My Forms area and choose a develop to produce or down load once more.
Remain competitive and down load, and produce the New York Short-Term Incentive Plan with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of expert and state-particular forms you can utilize for the business or person requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
Examples of monetary employee incentives Performance bonuses. Performance bonuses are regularly scheduled cash awards that reflect employee success. ... Merit-based raises. ... Profit-sharing. ... Referral bonuses. ... Improved equipment.
Defining of Short-term incentives STI have a performance term of 1 year or less, thus the term ?annual incentive.? These could be paid out annually, quarterly, or even monthly, based on a schedule laid out in a formal incentive plan. Employees can earn an STI bonus when they achieve specific short-term goals.
Sales promotion refers to short-term incentives that are designed to encourage the buyers to make an immediate purchase of a product or service in a short-term period.
The objective of an STIP is to reward key employees for their individual contribution for achieving the company's short-term business strategies and goals set by the compensation committee to increase the company's profitability. This plan is similar to a cash incentive plan.
Ing to the authors, incentives have three main components: economic, social, and moral.
term incentive plan (LTIP) incentivizes employees to take actions that will maximize shareholder value and promote longterm growth for the organization. In a standard LTIP, the employee, who is normally a senior executive, is required to meet a number of criteria to receive the incentive.
Some examples of short-term incentives include: Annual cash bonuses. Overtime pay. Holiday, weekend and shift work. Differentials and premiums. Payments for units produced.
March 01, 2022. Long-term incentives, or LTI as they're often called, are a valuable part of a total compensation package both for delivering rewards and focusing employees on desired future outcomes and objectives.