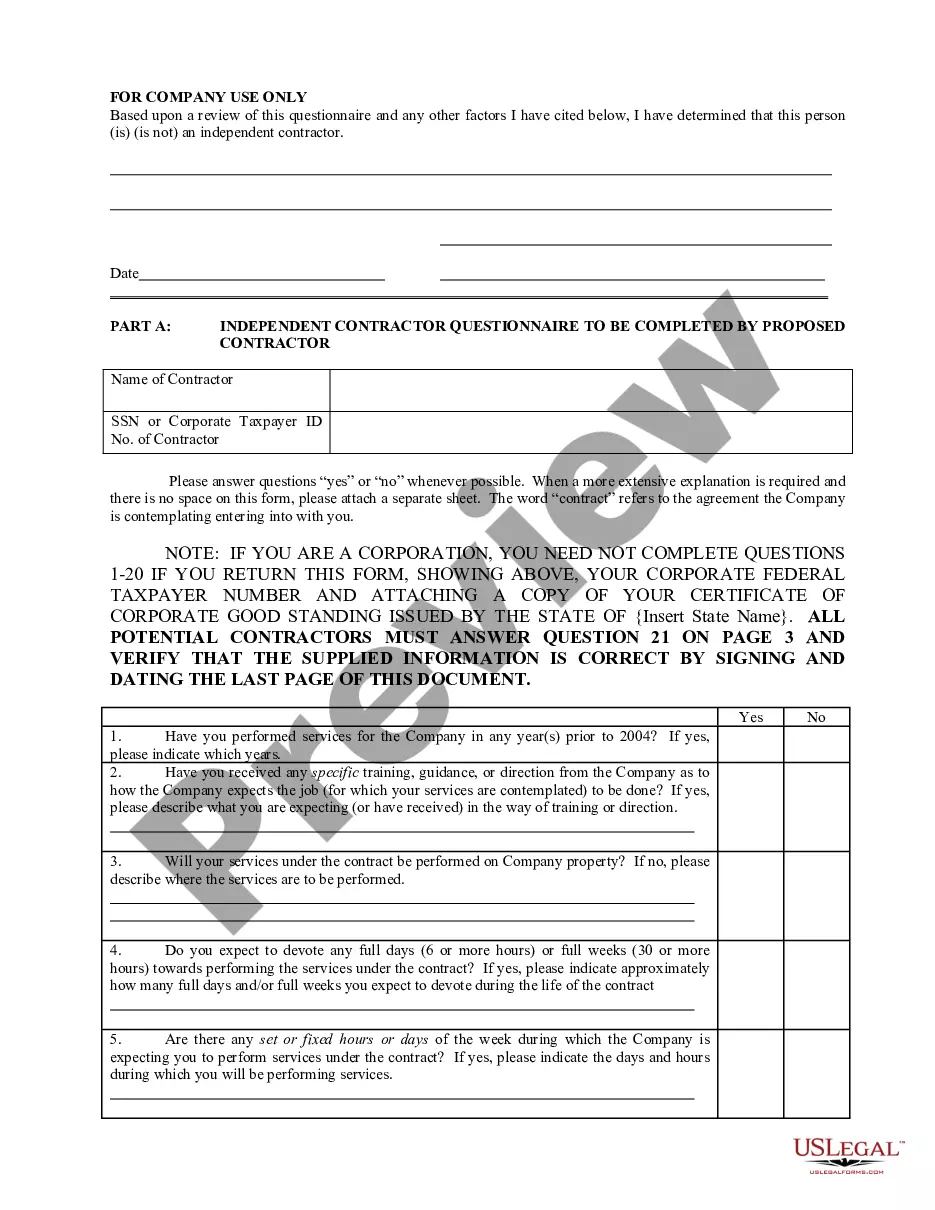
Montana Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status?
You can spend hours online looking for the valid document template that meets the state and federal standards you require.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of valid forms that are evaluated by professionals.
You can conveniently acquire or print the Montana Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status from my service.
If available, use the Preview option to review the document template as well.
- If you possess a US Legal Forms account, you may Log In and select the Download option.
- Subsequently, you may complete, modify, print, or sign the Montana Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status.
- Every valid document template you purchase is yours permanently.
- To obtain another copy of the purchased form, navigate to the My documents tab and click the relevant option.
- If you are visiting the US Legal Forms site for the first time, follow the straightforward instructions below.
- First, ensure you have picked the correct document template for the area/city of your choosing.
- Review the form description to verify you have selected the appropriate form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Simply put, being an independent contractor is one way to be self-employed. Being self-employed means that you earn money but don't work as an employee for someone else.
Becoming an independent contractor is one of the many ways to be classified as self-employed. By definition, an independent contractor provides work or services on a contractual basis, whereas, self-employment is simply the act of earning money without operating within an employee-employer relationship.
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
Independent contractors provide goods or services according to the terms of a contract they have negotiated with an employer. Independent contractors are not employees, and therefore they are not covered under most federal employment statutes.
To perform contractor work in the state of Montana, you will need to obtain a business license to do so. Furthermore, you will need to acquire the proper permits and additional paperwork to bid or perform contractor work in the state of Montana.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
What is an independent contractor? (b) is engaged in an independently established trade, occupation, profession or business. Additionally, an independent contractor must obtain either an independent contractor exemption certificate or self-elected coverage under a Montana workers' compensation insurance policy.
All work required of the contract is performed by the independent contractor and employees. Independent contractors are not typically considered employees of the principal. A "general contractor" is an entity with whom the principal/owner directly contracts to perform certain jobs.