Massachusetts Corrective Action - Problem Solution
Description
How to fill out Corrective Action - Problem Solution?
Selecting the appropriate legal document template can be quite challenging.
Naturally, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how can you locate the legal document you desire.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. This resource offers a vast array of templates, such as the Massachusetts Corrective Action - Problem Solution, which you can employ for business and personal purposes.
You can preview the form using the Preview button and read the document description to confirm it is suitable for you.
- All of the documents are verified by experts and comply with state and federal regulations.
- If you are currently registered, Log In to your account and click the Acquire button to retrieve the Massachusetts Corrective Action - Problem Solution.
- Use your account to browse the legal documents you have previously acquired.
- Navigate to the My documents tab in your account to obtain another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple steps to follow.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document for your city/area.
Form popularity
FAQ
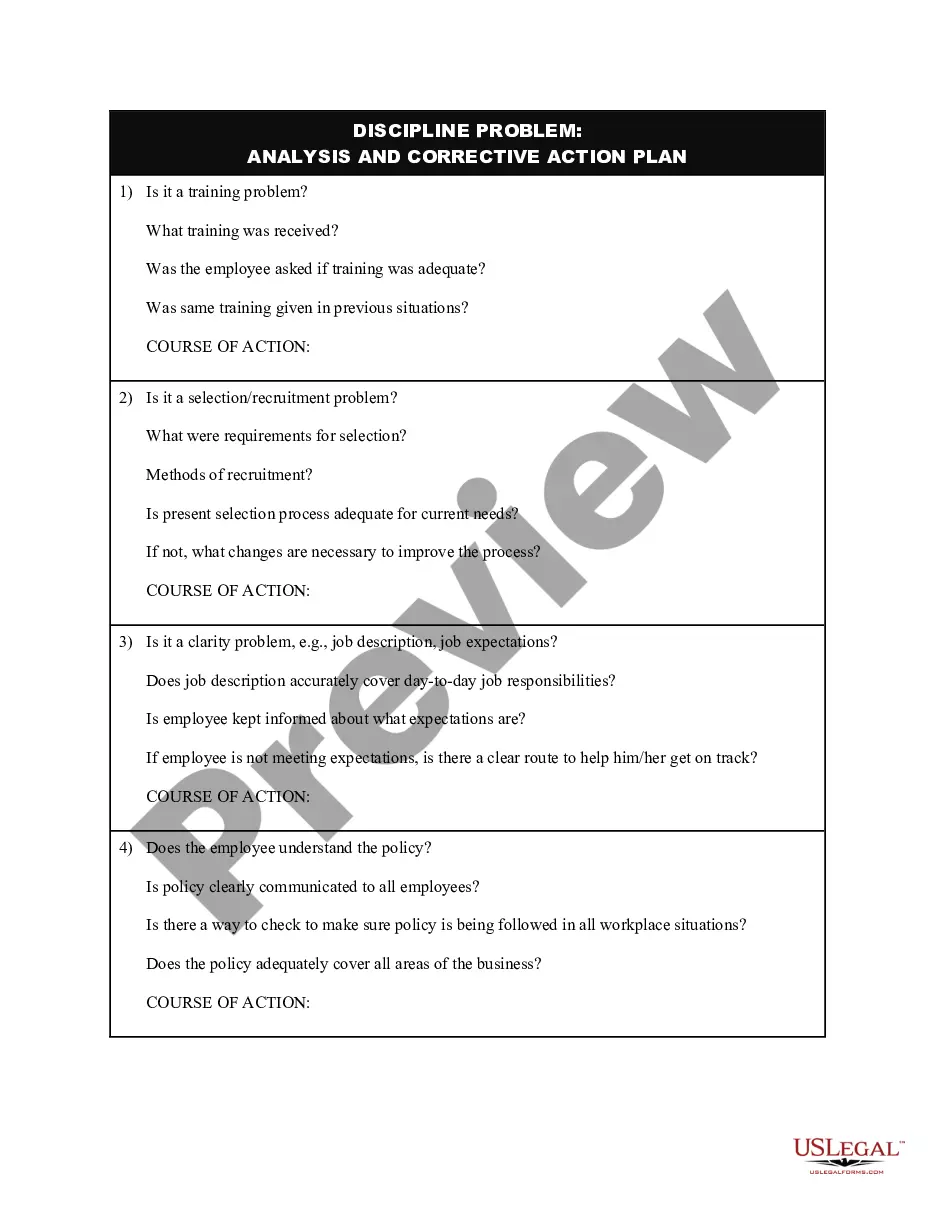
Asking Why? may be a favorite technique of your 3-year-old child in driving you crazy, but it could teach you a valuable Six Sigma quality lesson. The 5 Whys is a technique used in the Analyze phase of the Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology.
It is the responsibility of the entire team to sit and analyze the defects and contribute to the product and process improvement. In this tutorial, you have got a basic understanding of RCA, steps to be followed for doing an efficient RCA and different tools to be used such as Fishbone analysis and 5 Why Technique.
Five whys (or 5 whys) is an iterative interrogative technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem. The primary goal of the technique is to determine the root cause of a defect or problem by repeating the question "Why?". Each answer forms the basis of the next question.
Root Cause Analysis is a useful process for understanding and solving a problem. Figure out what negative events are occurring. Then, look at the complex systems around those problems, and identify key points of failure. Finally, determine solutions to address those key points, or root causes.
In order to go through the RCA process, you must be familiar with the following five steps:Define the problem. Analyze what you see happening, and identify the precise symptoms so that you can form a problem statement.Gather data.Identify causal factors.Determine the root cause(s).Recommend and implement solutions.
A decision is made to form a small team to conduct the root cause analysis. Team members are selected from the business process/area of the organization that experiences the problem. The team might be supplemented by: A line manager with decision authority to implement solutions.
With a corrective action, you fix an existing problem or nonconformance; with preventive action, you take proactive steps to prevent potential problems, often by considering other situations in which a known problem may also occur.
The RCA is a critical step in each of these examples....The following information must be determined and documented:Who discovered the problem?What exactly happened?Where in the process was the problem discovered?When was the problem discovered?How many / How often does it happen?How was the problem detected?
The Root Cause Analysis ProcessThe methodology of Root Cause Analysis.Forming RCA teams Who needs to be involved?Define the event.Find causes.Finding the root cause.Find solutions.Take action.Assess solution effectiveness.More items...?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a problem-solving approach that tries to identify the specific cause(s) of problems, not just addressing symptoms.