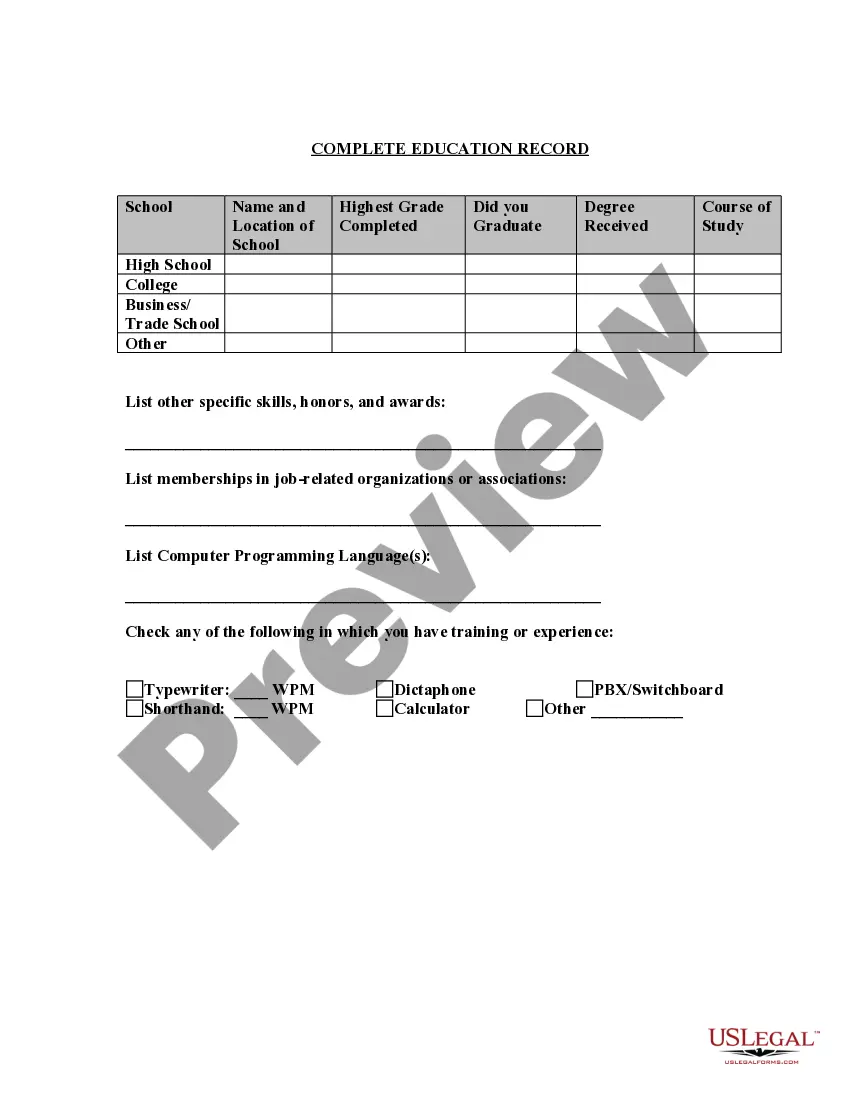
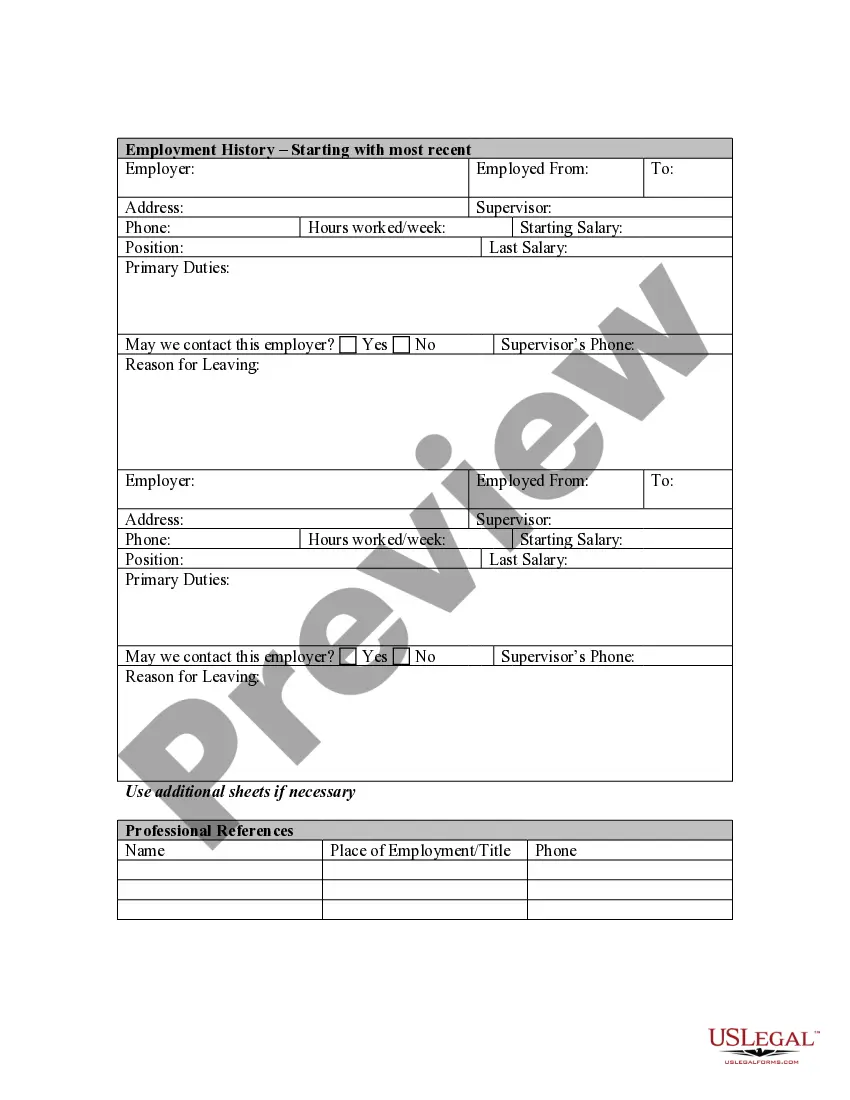
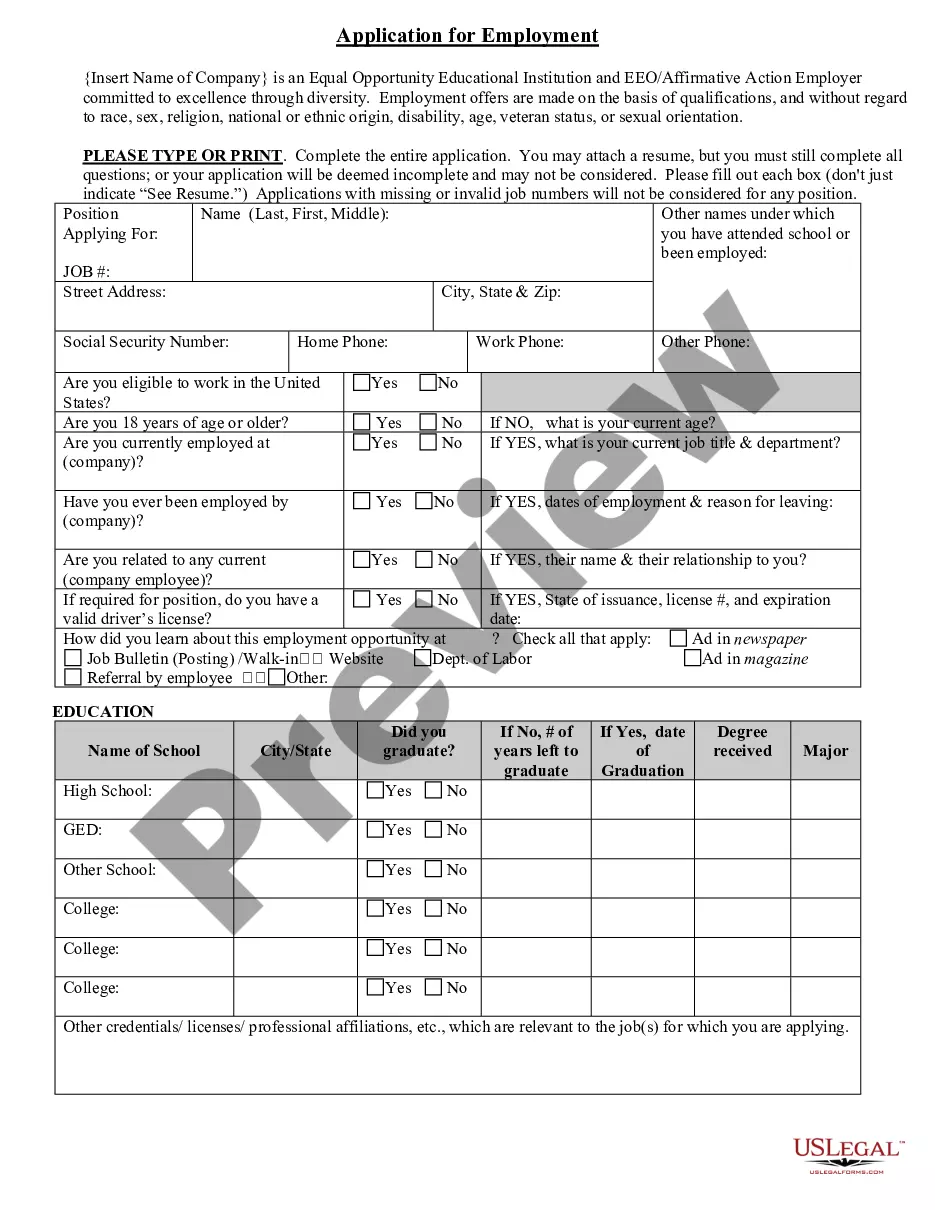
Kansas Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - provides a variety of legal document templates that you can download or print.
By using the website, you can find thousands of forms for business and personal use, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can access the latest forms such as the Kansas Employment Application - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position in just a few moments.
If you have a subscription, Log In and download the Kansas Employment Application - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You can access all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
Proceed with the payment. Use a credit card or PayPal account to finalize the transaction.
Choose the format and download the form to your device. Make modifications. Complete, edit, print, and sign the downloaded Kansas Employment Application - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position. Each template you have added to your account does not have an expiration date and belongs to you indefinitely. So, if you wish to download or print another copy, just go to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Kansas Employment Application - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position with US Legal Forms, one of the most extensive libraries of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/county.
- Click the Review button to evaluate the contents of the form.
- Check the form summary to confirm that you have chosen the right one.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, validate your choice by clicking the Get now button.
- Then, select your preferred payment plan and provide your information to register for the account.
Form popularity
FAQ
Salaried: An individual who receives the same salary from week to week regardless of how many hours he or she works. Exempt employees must be paid on a salary basis, as discussed above. Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary basis for a fixed number of hours or under the fluctuating workweek method.
To pay a non-exempt employee a salary, the employer pays the employee the fixed amount per week and pays overtime at a rate of 1.5x the employee's regular rate. The regular rate in this method is determined by dividing the salary by the number of hours the salary is intended to compensate.
Exempt employees refer to workers in the United States who are not entitled to overtime pay. This simply implies that employers of exempt employees are not bound by law to pay them for any extra hours of work. The federal standard for work hours in the United States is 40 hours per workweek.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
Federal Exemptions from Overtime: To be considered "exempt," these employees must generally satisfy three tests: Salary-level test. Effective January 1, 2020, employers must pay employees a salary of at least $684 per week. The FLSA's minimum salary requirement is set to remain the same in 2022.
Employees who do not meet the requirements to be classified as exempt from the Minimum Wage Act are considered nonexempt. Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis. Employees who do not qualify for an exemption but are paid on a salary basis are considered salaried nonexempt.
On September 24, 2019, the DOL issued a new final rule that raises the minimum salary threshold for exemption from $23,660 per year ($455 per week) to $35,568 per year ($684 per week). No changes to the duties test are made in this ruling. The ruling is effective as of January 1, 2020.
An exempt employee must receive the full salary for any week in which the employee performs any work without regard to the number of days or hours worked. If the employee is ready, willing and able to work, deductions may not be made for time when work is not available (i.e., inclement weather).
Who is eligible for overtime pay? To qualify as an exempt employee one who does not receive overtime pay staff members must meet all the requirements under the duties and salary basis tests.
To qualify for exemption from overtime pay, employees must meet certain tests regarding their job duties and be paid on a salary basis at or above the minimum salary threshold. At K-State, the minimum salary threshold is currently $47,476 per year ($913 per week).