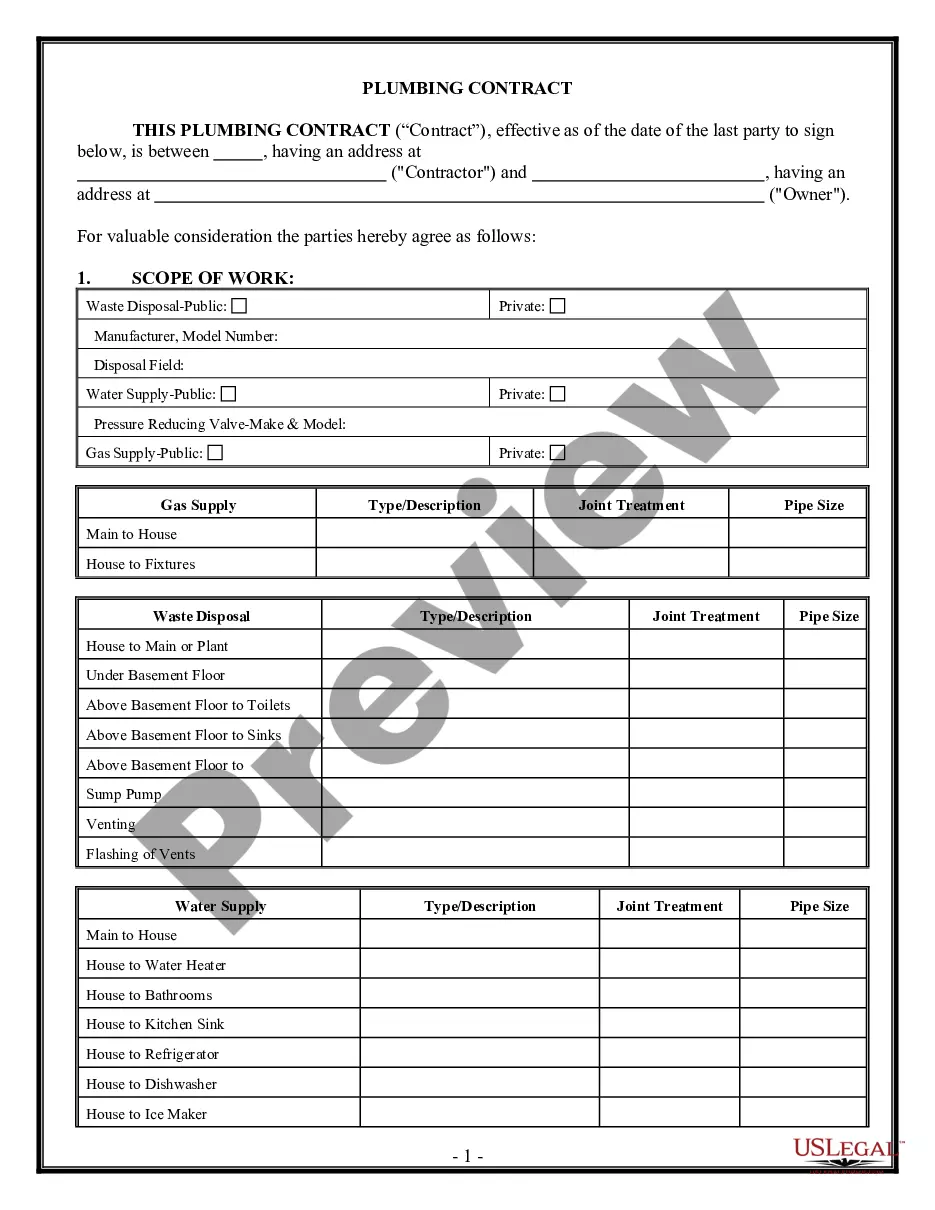
This office lease provision states that the parties desire to allocate certain risks of personal injury, bodily injury or property damage, and risks of loss of real or personal property by reason of fire, explosion or other casualty, and to provide for the responsibility for insuring those risks permitted by law.
Idaho Provision Allocation Risks and Setting Forth Insurance Obligations of Both the Landlord and the Tenant
Description
How to fill out Provision Allocation Risks And Setting Forth Insurance Obligations Of Both The Landlord And The Tenant?
You may commit several hours on-line looking for the authorized record design that meets the state and federal requirements you want. US Legal Forms gives a huge number of authorized forms which can be analyzed by experts. It is possible to download or print the Idaho Provision Allocation Risks and Setting Forth Insurance Obligations of Both the Landlord and the Tenant from our assistance.
If you already possess a US Legal Forms accounts, you are able to log in and click the Obtain option. Next, you are able to comprehensive, revise, print, or indication the Idaho Provision Allocation Risks and Setting Forth Insurance Obligations of Both the Landlord and the Tenant. Each authorized record design you buy is the one you have permanently. To have yet another copy of any acquired type, proceed to the My Forms tab and click the related option.
If you are using the US Legal Forms web site the first time, stick to the straightforward instructions beneath:
- Very first, make certain you have selected the best record design for that state/city of your choosing. Look at the type explanation to ensure you have selected the appropriate type. If readily available, utilize the Review option to look from the record design as well.
- If you would like find yet another version of your type, utilize the Research industry to get the design that fits your needs and requirements.
- After you have located the design you would like, just click Get now to proceed.
- Pick the pricing program you would like, enter your qualifications, and register for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Total the financial transaction. You can use your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal accounts to fund the authorized type.
- Pick the structure of your record and download it for your device.
- Make adjustments for your record if possible. You may comprehensive, revise and indication and print Idaho Provision Allocation Risks and Setting Forth Insurance Obligations of Both the Landlord and the Tenant.
Obtain and print a huge number of record templates while using US Legal Forms site, which provides the largest assortment of authorized forms. Use specialist and state-particular templates to tackle your business or personal requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
A tenant can move rather than pay the increase. Idaho Code Section 55-307. 2. If a lease agreement sets the amount of rent for a given period of time (such as 6 months, 1 year, etc.), a landlord cannot raise the rent during this time.
Unfortunately, the law doesn't give guidelines as to how often the carpet has to be replaced. you can always request it be replaced, however.
Idaho Code 6-320 allows a tenant to go to court to enforce the landlord's duties. Prior to doing so, the tenant must give the landlord 3-days' notice, listing each failure or breach upon which his action will be premised and written demand requiring performance or cure.
However, there are certain rights established by Idaho law that cannot be avoided by the lease. In brief, these rights include the right to privacy, the right of quiet use and enjoyment, the right to safety and health, the right against discrimination, and the right to possession of the premises.
You can deduct money for rent failure and rental property damage. It's not possible to use the security deposit to cover for normal wear and tear.
If a tenant damages the walls through unauthorized painting or fails to restore them to their original state, the landlord may deduct the cost of repairs or repainting from the security deposit.
Ing to Idaho's security deposit law, landlords have 21 days to return tenants' security deposits once they move out. This period may be extended or shortened if both parties reach an agreement. In such cases, the period must not exceed 30 days.
Landlord-tenant relationships are governed by a mixture of property law, contract law, and negligence law. Tom rented an apartment from Margaret on a month-to-month basis, with rent due on the first of the month. This type of tenancy is known as a "tenancy at will."