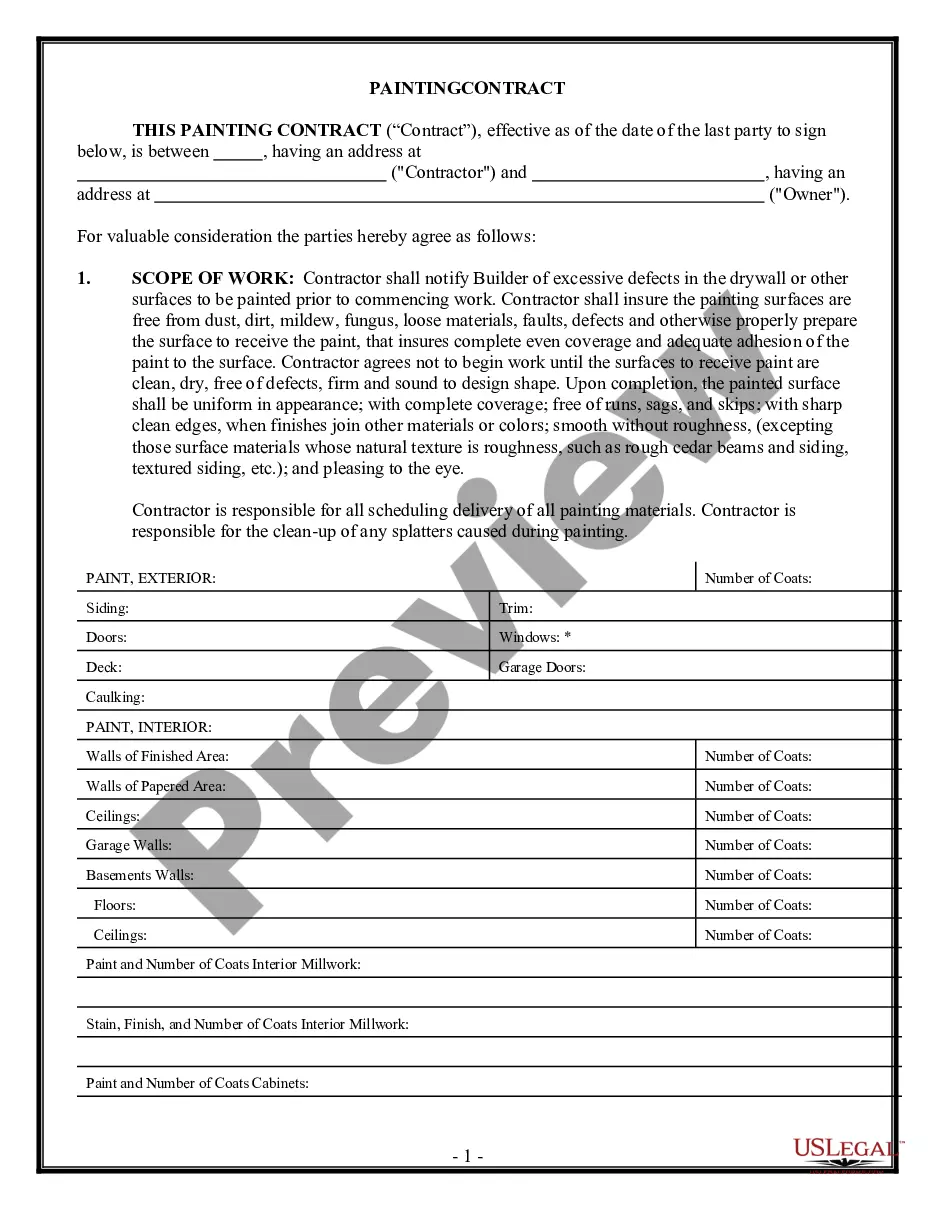
Iowa Jury Instruction - 3.3 Breach of Fiduciary Duty
Description
How to fill out Jury Instruction - 3.3 Breach Of Fiduciary Duty?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest libraries of authorized varieties in the States - provides a wide range of authorized record themes you can download or print. Utilizing the website, you can get 1000s of varieties for company and person purposes, sorted by groups, states, or key phrases.You will discover the latest models of varieties like the Iowa Jury Instruction - 3.3 Breach of Fiduciary Duty within minutes.
If you already have a registration, log in and download Iowa Jury Instruction - 3.3 Breach of Fiduciary Duty in the US Legal Forms collection. The Download button will appear on every single type you perspective. You have access to all earlier delivered electronically varieties in the My Forms tab of your bank account.
If you want to use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are easy directions to help you get began:
- Ensure you have chosen the proper type for your personal city/area. Go through the Preview button to examine the form`s articles. Read the type description to ensure that you have chosen the proper type.
- When the type doesn`t satisfy your demands, make use of the Search field at the top of the display to get the one that does.
- If you are happy with the shape, verify your decision by clicking the Buy now button. Then, choose the costs plan you like and give your accreditations to sign up for the bank account.
- Method the purchase. Make use of your credit card or PayPal bank account to finish the purchase.
- Choose the structure and download the shape on your product.
- Make alterations. Complete, change and print and sign the delivered electronically Iowa Jury Instruction - 3.3 Breach of Fiduciary Duty.
Every web template you included in your money does not have an expiry particular date and is yours eternally. So, if you would like download or print yet another backup, just check out the My Forms section and click on around the type you require.
Obtain access to the Iowa Jury Instruction - 3.3 Breach of Fiduciary Duty with US Legal Forms, probably the most comprehensive collection of authorized record themes. Use 1000s of professional and status-distinct themes that satisfy your company or person needs and demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
The comments section of the Iowa Rules of Professional Conduct state that an attorney's advertisement that the attorney publishes or causes to be published should be relevant, dignified and disseminated in an objective and understandable fashion that would assist a prospective client to make an informed choice about ...
1.2 Scope of Representation and Allocation of Authority Between Client and Lawyer. Subject to paragraphs (c) and (d), a lawyer shall abide by a client's decisions concerning the objectives of representation and, as required by Rule 1.4, shall consult with the client as to the means by which they are to be pursued.
2.24(2)New trial. a. Motion generally. A motion for new trial by the defendant shall be made not later than 45 days after verdict of guilty or special verdict upon which a judgment of conviction may be rendered and not later than 5 days before the date set for pronouncing judgment.
Rule .3 - SOLICITATION OF CLIENTS (a)Solicitation" or "solicit" denotes a communication initiated by or on behalf of a lawyer or law firm that is directed to a specific person the lawyer knows or reasonably should know needs legal services in a particular matter and that offers to provide, or reasonably can be ...
Rule .7 - CONFLICT OF INTEREST: CURRENT CLIENTS (a) Except as provided in paragraph (b), a lawyer shall not represent a client if the representation involves a concurrent conflict of interest.
(b) Except as stated in paragraph (c), a lawyer may withdraw from representing a client if: (1) withdrawal can be accomplished without material adverse effect on the interests of the client; (2) the client persists in a course of action involving the lawyer's services that the lawyer reasonably believes is criminal or ...
Any party resisting the motion shall file and serve a resistance within 15 days, unless otherwise ordered by the presiding officer, from the date a copy of the motion was served.