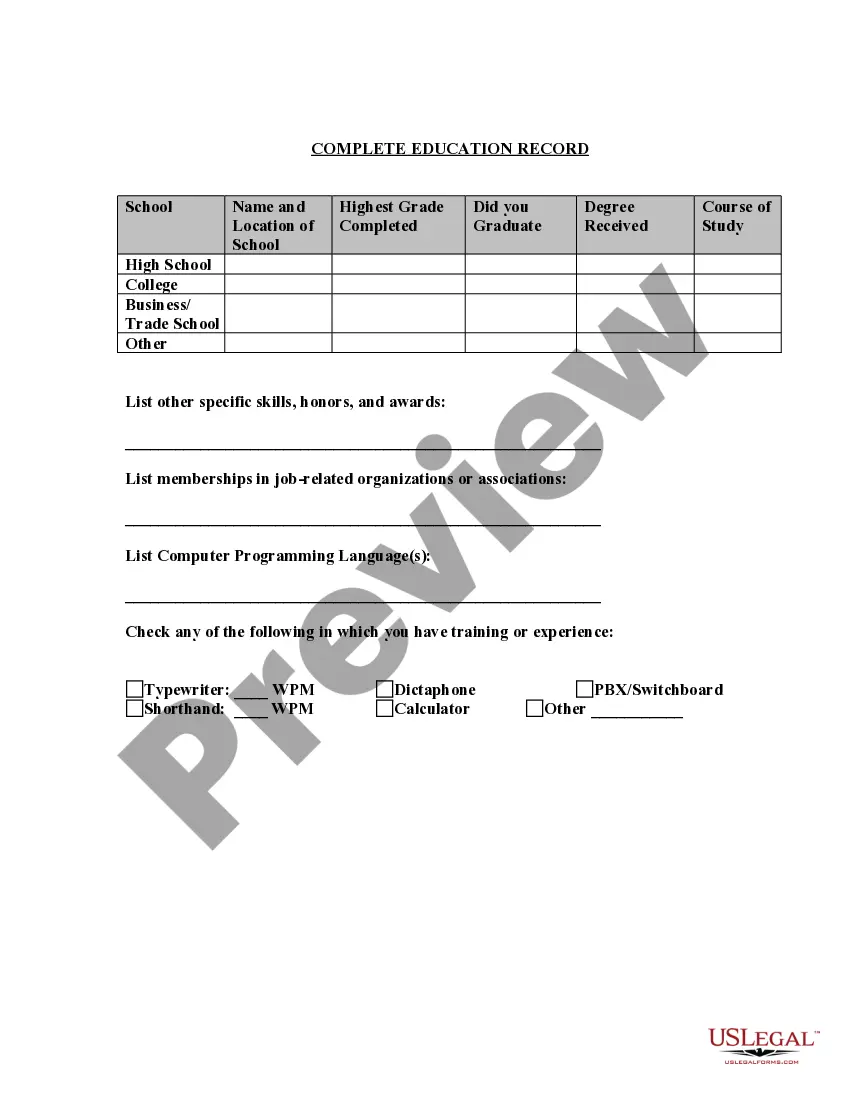
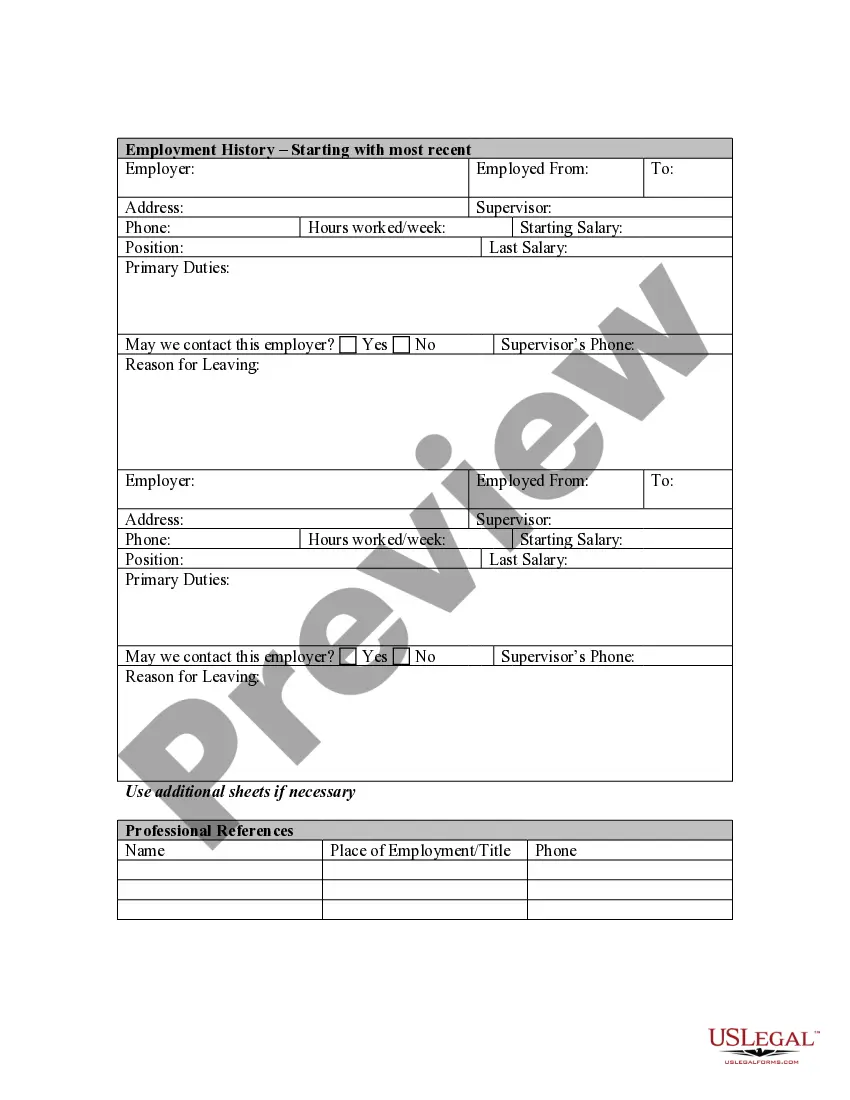
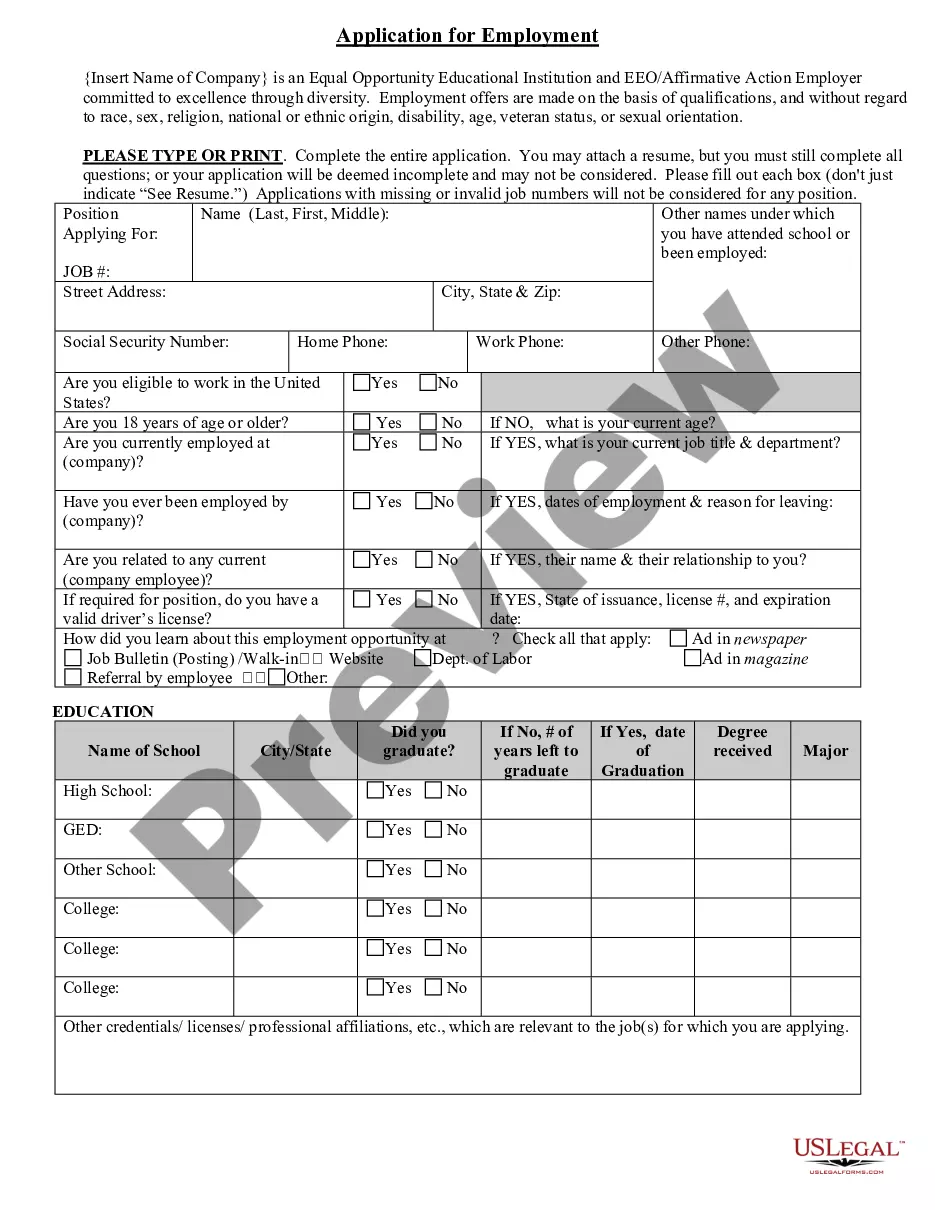
Guam Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
US Legal Forms - among the most important collections of legal forms in the USA - offers a broad selection of legal document templates that you can download or create.
By using the website, you can access thousands of forms for personal and business purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can find the latest versions of forms like the Guam Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position in seconds.
If you hold a monthly subscription, Log In to access the Guam Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position from the US Legal Forms catalog. The Download option will be displayed on every form you view. You have access to all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
Every design you added to your account does not have an expiration date and is your possession forever. Therefore, to download or print another copy, simply navigate to the My documents section and click on the form you need.
Access the Guam Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive collection of legal document templates. Utilize a vast number of professional and state-specific templates that fulfill your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Ensure that you have selected the correct form for your city/county. Click the Review button to examine the form's content. Check the form description to confirm that you have chosen the appropriate form.
- If the form doesn't meet your needs, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking on the Purchase now button. Then, select your preferred pricing plan and provide your details to create an account.
- Process the transaction. Use a credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Choose the format and download the form to your device.
- Make modifications. Fill out, edit, print, and sign the downloaded Guam Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
Form popularity
FAQ
Exempt or Nonexempt.Employees whose jobs are governed by the FLSA are either "exempt" or "nonexempt." Nonexempt employees are entitled to overtime pay. Exempt employees are not.
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).
What Is an Exempt Employee? The term exempt employee refers to a category of employees set out in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Exempt employees do not receive overtime pay, nor do they qualify for minimum wage. When an employee is exempt, it primarily means that they are exempt from receiving overtime pay.
Exempt positions are excluded from minimum wage, overtime regulations, and other rights and protections afforded nonexempt workers. Employers must pay a salary rather than an hourly wage for a position for it to be exempt.
Key Takeaways. An exempt employee is an employee who does not receive overtime pay or qualify for minimum wage. Exempt employees are paid a salary rather than by the hour, and their work is executive or professional in nature.
Tips For Drafting Job Descriptions for Exempt EmployeesAccuracy is King. The job description must be accurate.Accuracy Does Not Mean Exhaustion.Strong Verbs, Clear Impact.Focus on Exempt Functions.Don't Shy Away From Degree Requirements.Assist With Can Diminish a Role.Consider Requiring Acknowledgement.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
Exempt employees refer to workers in the United States who are not entitled to overtime pay. This simply implies that employers of exempt employees are not bound by law to pay them for any extra hours of work. The federal standard for work hours in the United States is 40 hours per workweek.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.