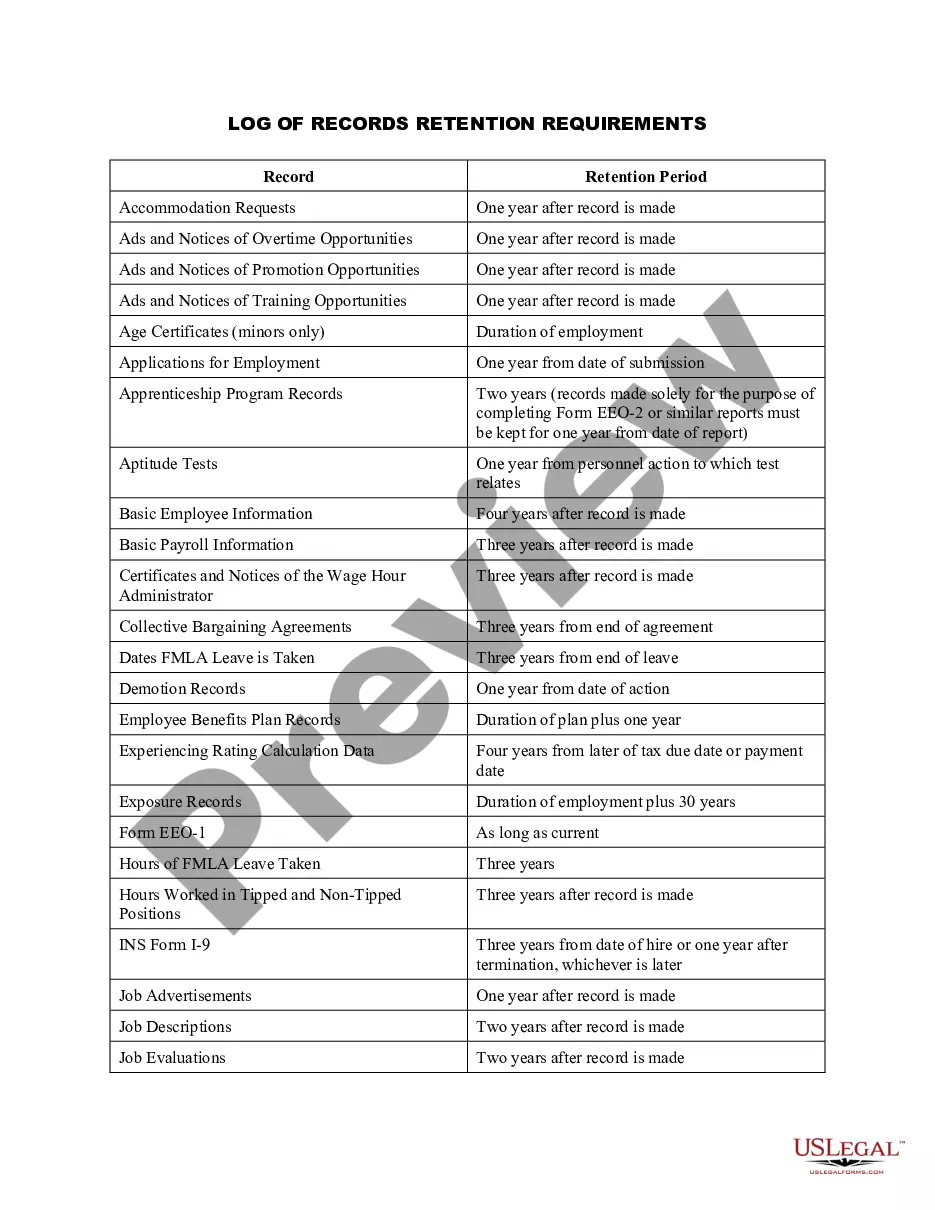
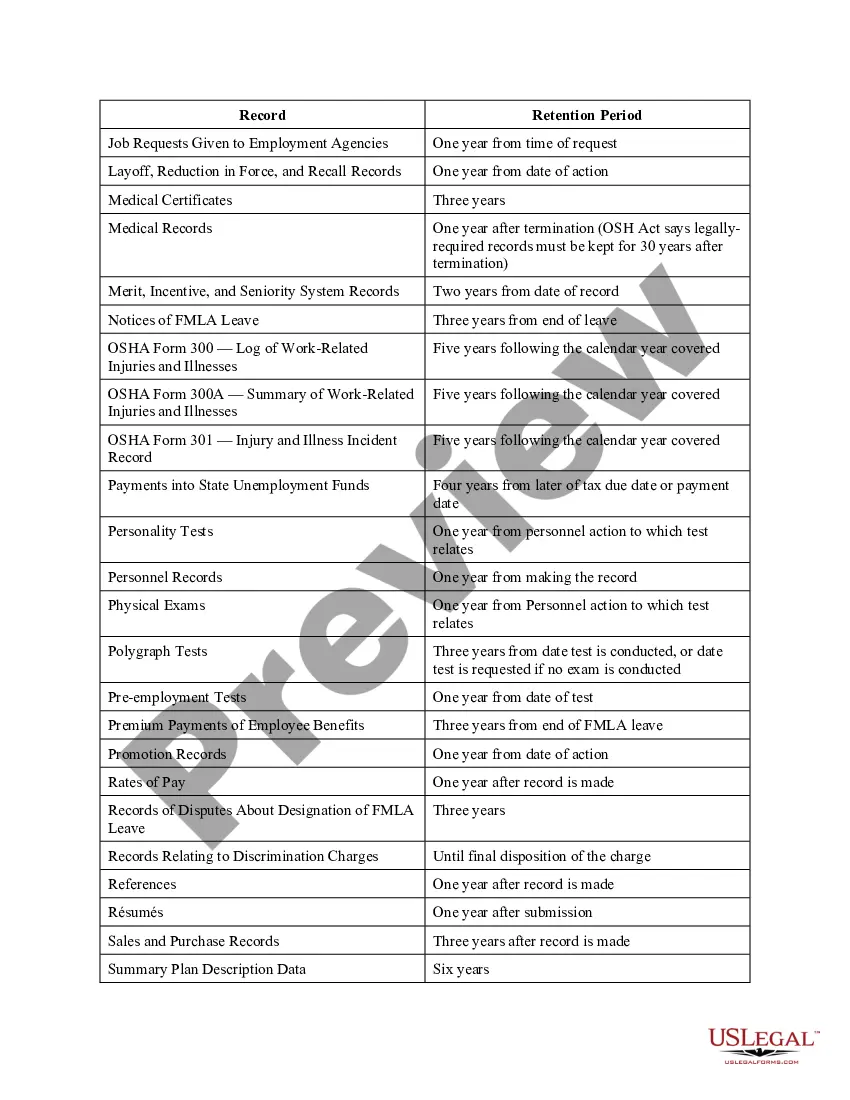
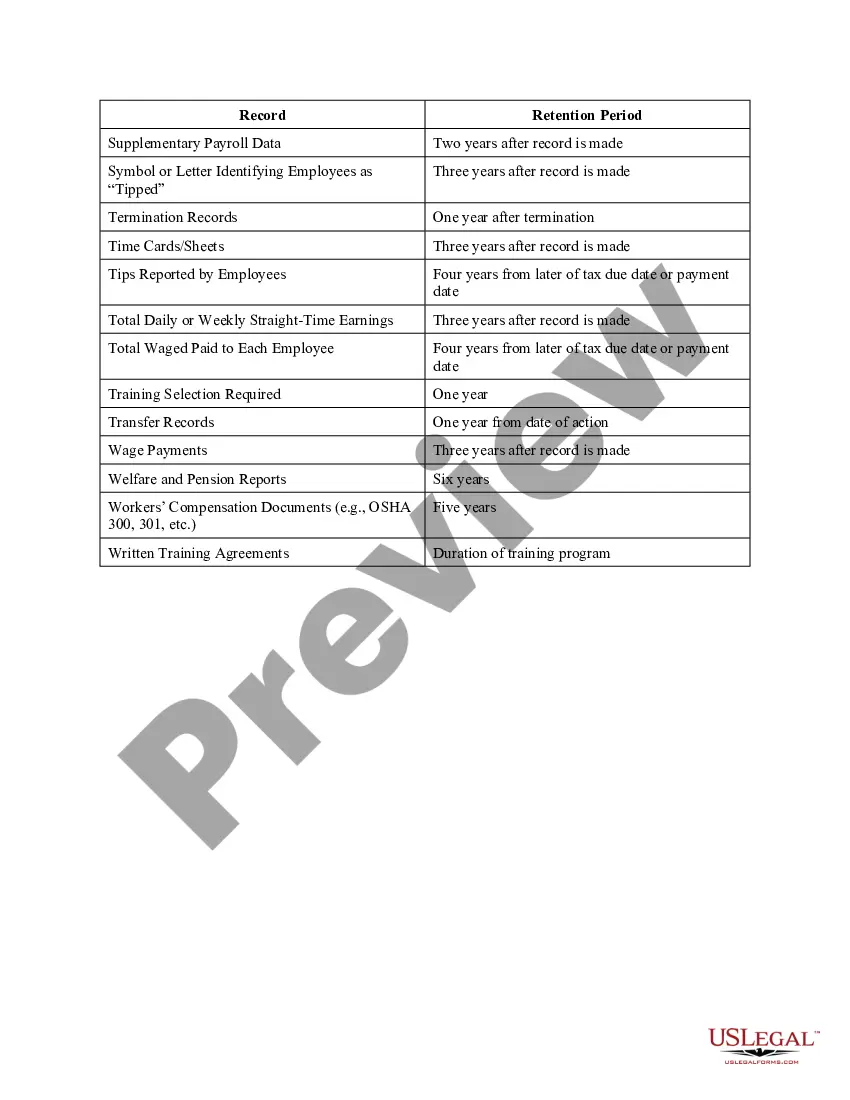
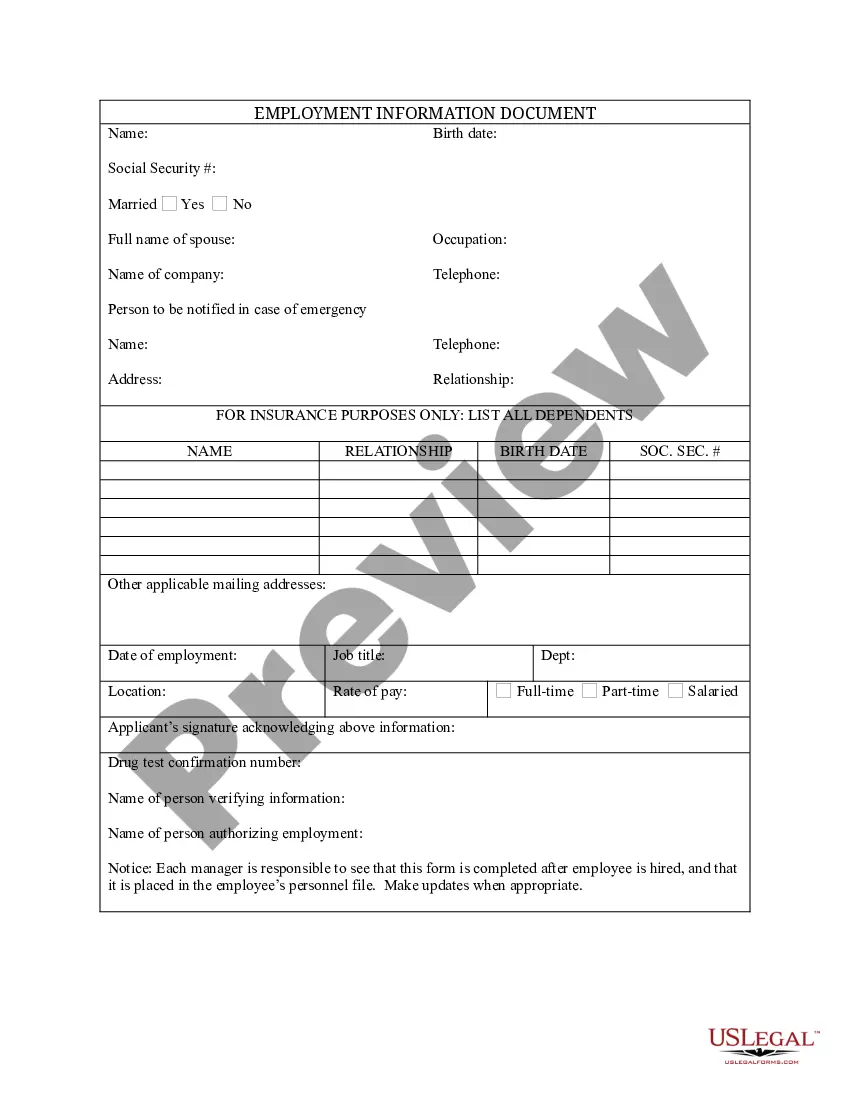
Alaska Log of Records Retention Requirements
Description
How to fill out Log Of Records Retention Requirements?
You might spend hours online attempting to locate the legal document template that complies with the state and federal requirements you desire.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of legal forms that have been assessed by experts.
It is easy to obtain or create the Alaska Log of Records Retention Requirements through the service.
If you want to find a different version of the form, utilize the Search box to locate the template that suits your needs and requirements.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and select the Download button.
- Subsequently, you can fill out, edit, print, or sign the Alaska Log of Records Retention Requirements.
- Every legal document template you download is yours indefinitely.
- To obtain another copy of a purchased form, go to the My documents section and select the appropriate option.
- If this is your first time using the US Legal Forms website, follow these straightforward steps.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct document template for your chosen state/city.
- Review the form description to confirm you have picked the right one.
Form popularity
FAQ
As a general rule of thumb, tax returns, financial statements and accounting records should be retained for a minimum of six years.
For example, if financial records have a retention period of five years, and the records were created during the 1995-1996 fiscal year (July 1, 1995 - June 30, 1996), the five-year retention period begins on July 1, 1996 and ends five years later on July 1, 2001.
Records retention is a practice by which organizations maintain confidential records for set lengths of time, and then employ a system of actions to either redirect, store or dispose of them.
A data retention period is the amount of time that data must be stored according to internal and external requirements. Time periods vary by organization and industry, but generally range from three to ten years. Once its objective has been fulfilled, the data should be archived, anonymized, or destroyed.
To be on the safe side, McBride says to keep all tax records for at least seven years. Keep forever. Records such as birth and death certificates, marriage licenses, divorce decrees, Social Security cards, and military discharge papers should be kept indefinitely.
Records retention is the process of ensuring that organizations maintain and store their records in a safe and secure manner for the purposes of archival, data retrieval, reporting, record-keeping, and billing. Records retention has two main purposes: legal documentation and disaster recovery.
A records retention schedule is a policy that defines how long data items must be kept and provides disposal guidelines for how data items should be discarded.
Keep records for 3 years from the date you filed your original return or 2 years from the date you paid the tax, whichever is later, if you file a claim for credit or refund after you file your return. Keep records for 7 years if you file a claim for a loss from worthless securities or bad debt deduction.
Retention policies help to manage many risks including lost or stolen information, excessive backlog of paper files, loss of time and space while internally managing records and lack of organization system for records, making them hard to find, just to name a few.
Records retention is a practice by which organizations maintain confidential records for set lengths of time, and then employ a system of actions to either redirect, store or dispose of them.