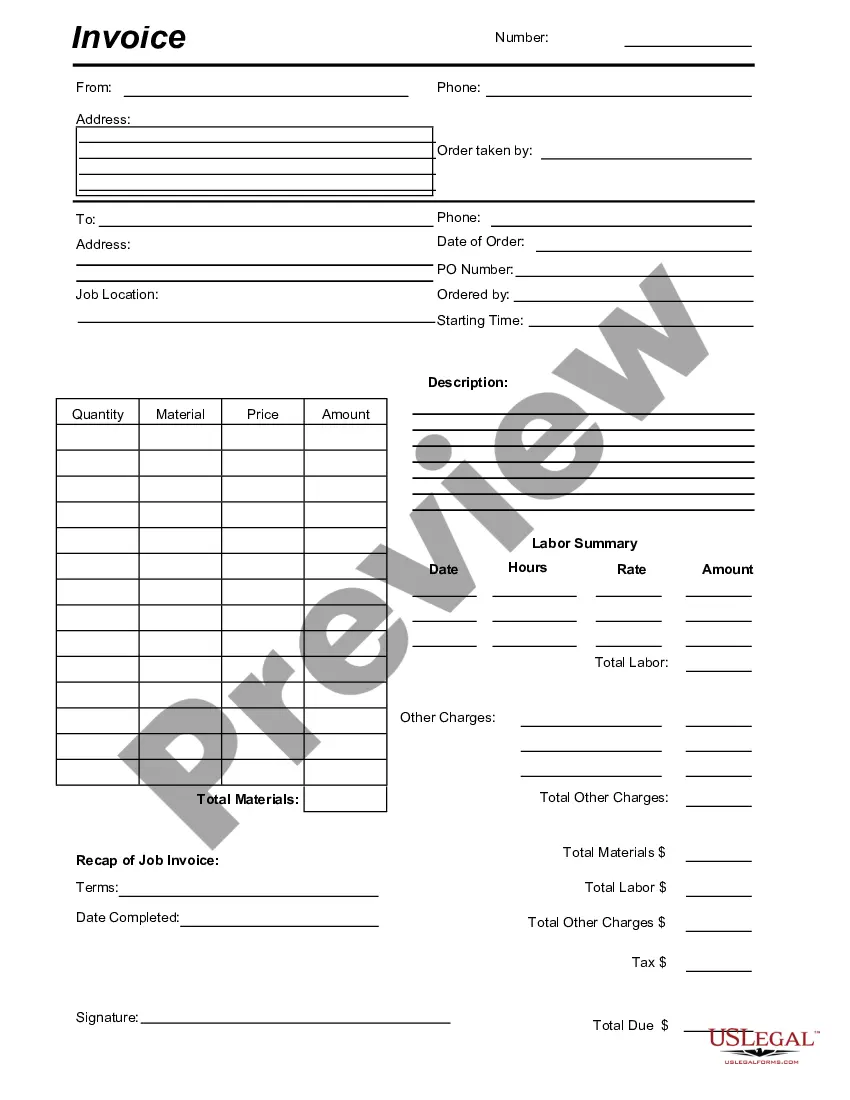
Building Contract For A Home Owner/occupier In California
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
JCT Minor Works contracts are generally used when works are relatively straightforward and low value. These contracts are not as detailed as the JCT Design and Build and Standard Building Contracts and contain more basic provisions, particularly in relation to insurance, variations and claiming extensions of time.
These two are the RIBA DBC and the JCT HO/O. The JCT HO/O, at a third of the length of RIBA DBC, is less detailed, however, the building work would need to be defined clearly in advance, the project would need to be straight forward in nature, with no contractor design, and timing would not be a critical factor.
Legal Requirements: California law prohibits hiring unlicensed contractors for projects exceeding $500 in labor and materials costs. Contractor Licensing: Verify contractor licenses through the Contractors State License Board (CSLB) website before hiring.
Owner-as-Contractor is a type of Owner-Builder where you personally act as your own General Contractor, the permit is taken out in your name and you hire California licensed sub-contractors to perform portions of the construction work.
JCT contracts facilitate the process of constructing buildings. In simple terms, contracts set out the responsibilities of all parties within the construction process and their obligations, so it is clear as to what work needs to be done, who is doing it, when are they doing it by, and for how much.
The RIBA DBC contains dispute avoidance mechanisms, whereas the JCT HO/O doesn't. The JCT commercial building contracts include a collaborative working clause (in the Supplemental Conditions), and prompt notification and negotiation of matters that may give rise to a dispute.
In California, most construction work is required to be performed by a licensed contractor. In certain instances, the owner of the property may secure a permit as an owner-builder, but there are strict limitations on when this may occur.
Generally, NEC contracts are aimed at engineering projects but are easily adapted to building works. JCT contracts are aimed at building works rather than engineering projects but again can be adapted for both.
Lesson Summary. A contract is a legal agreement between two or more parties in which they agree to each other's rights and responsibilities. Offer, acceptance, awareness, consideration, and capacity are the five elements of an enforceable contract.
To be legally enforceable, an agreement must contain all of the following criteria: An offer and acceptance; Certainty of terms; Consideration; An intention to create legal relations; Capacity of the parties; and, Legality of purpose.