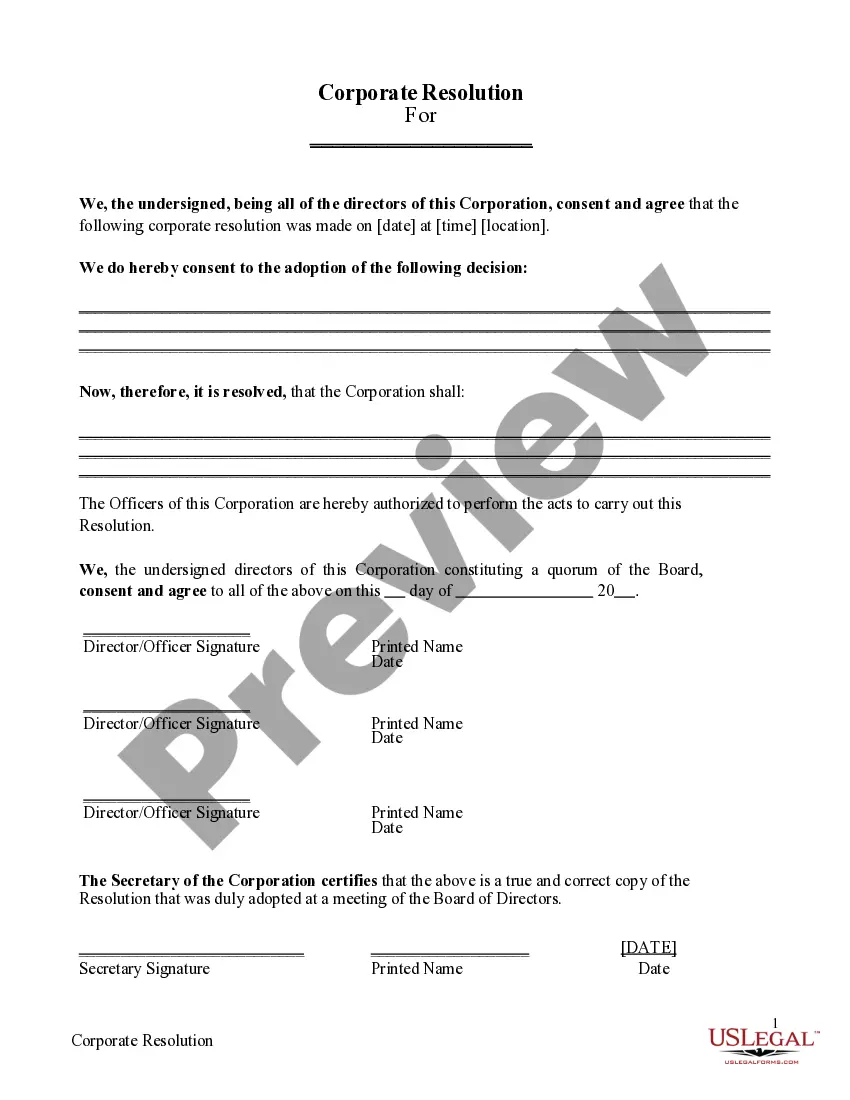
Letter Engagement Statement For Accounting Services In Chicago
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Engagement letters for your accounting or CPA firm is a legal document agreement sent to your clients that describes the overall business relationship with your client, clearly defining: Services included and how they'll play out. Each other's responsibilities. The clearly-defined scope of your work.
Your designated audit firm will prepare the specific terms of engagement using the appropriate AICPA-issued engagement letter template. It should be noted that there are many terms for audit engagements that are deemed required by the AICPA and therefore unable to be negotiated.
The service provider typically prepares the Letter of Engagement, be it a law firm, accounting agency, consultancy, or any professional offering services.
Engagement letters are important because they outline the expectations and responsibilities of both the bookkeeper and the client. They also help protect both parties in case of any disputes or misunderstandings, especially involving the scope of work to be completed.
Who Prepares a Letter of Engagement? An engagement letter is drafted by the company rendering the service, often with the help of a lawyer. It is than presented to the client, and both parties must sign in order for it to be legally binding.
The service provider typically prepares the Letter of Engagement, be it a law firm, accounting agency, consultancy, or any professional offering services.
Who Prepares a Letter of Engagement? An engagement letter is drafted by the company rendering the service, often with the help of a lawyer. It is than presented to the client, and both parties must sign in order for it to be legally binding.
Is an Engagement Letter the Same As a Contract? Engagement letters are less formal and generally shorter than a traditional contract. However, they also share some important traits, such as being legally binding and designed to reduce liability.
Unlike compilation or review engagements, an audit requires examination of source documentation on a sample basis (like invoices, bank statements, and cheques) to confirm the existence, completeness, accuracy, and validity of the financial information.