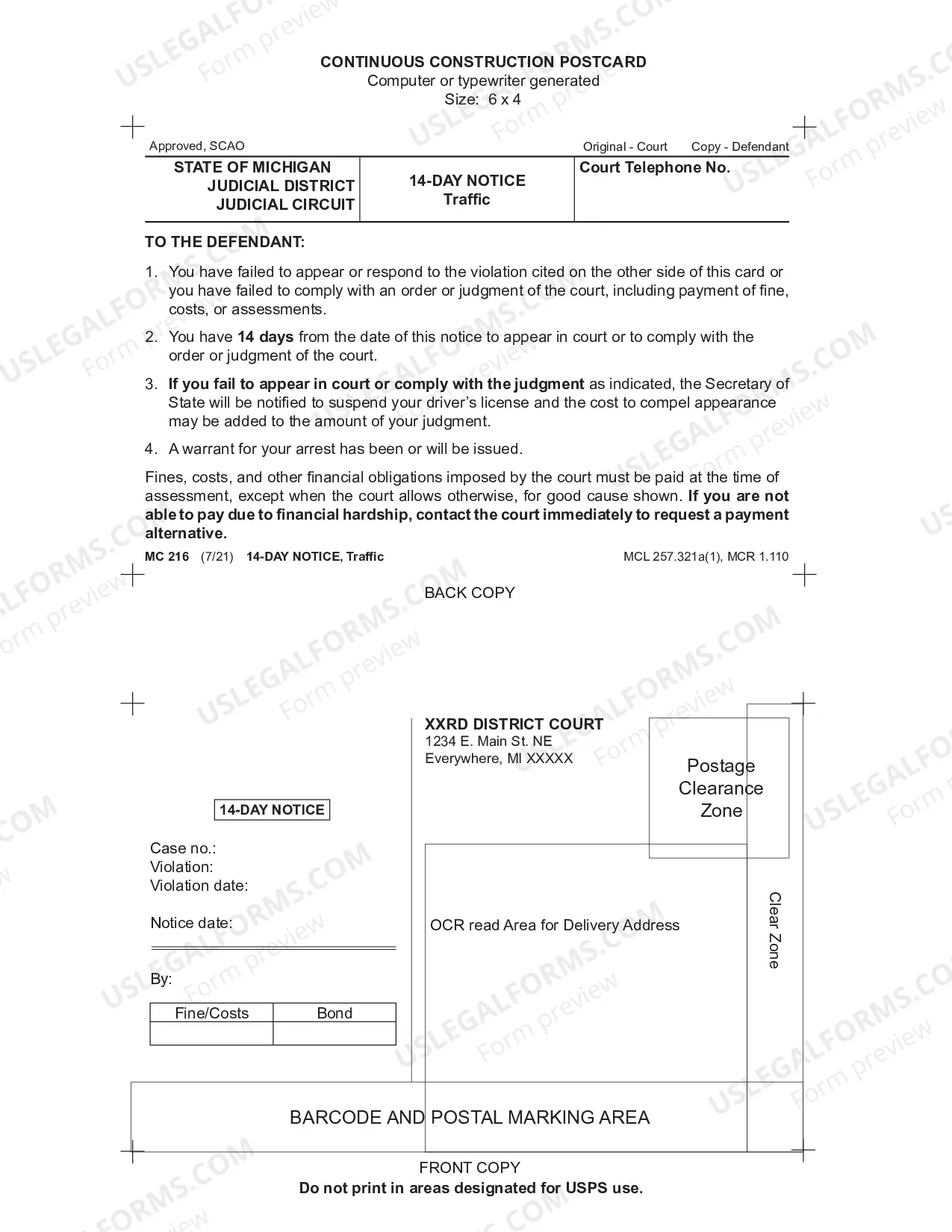
Contingency In Law Meaning In Travis
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Contingent means that an event may or may not occur in the future, depending on the fulfillment of some condition that is uncertain. This term is often used in contracts where the event will not take effect until the specified condition occurs.
Contingency planning ensures that we know what to do when disaster strikes, and have the systems and tools to respond fast. It means anticipating the types of disasters we might face and knowing practically how to manage disasters when they do strike.
Examples of contingency plans in business could include: Strategies to ensure minimal operational disruption during crises, such as unexpected market shifts, regulatory compliance changes, or severe staff shortages.
Contingency planning means preparing an organization to be ready to respond effectively in the event of an emergency. It is an important part of the IFRC's work supporting National Society preparedness.
Contingent adj 1 : likely but not certain to happen compare executory. 2 : intended for use in circumstances not completely foreseen a fund 3 : dependent on or conditioned by something else a claim a legacy on the marriage compare vested.
/kənˈtɪn.dʒənt/ contingent on/upon something. depending on something else in the future in order to happen: Outdoor activities are, as ever, contingent on the weather.
Contingent means that an event may or may not occur in the future, depending on the fulfillment of some condition that is uncertain. This term is often used in contracts where the event will not take effect until the specified condition occurs.
Contingency refers to an event that may or may not occur in the future. In other words, it depends on fulfillment of a condition, which is uncertain or incidental.
Outdoor activities are, as ever, contingent on the weather. Our success is contingent upon your support. The allowances she gave her sons were contingent on their completing certain household chores. The plans are contingent on extra funding being made available.