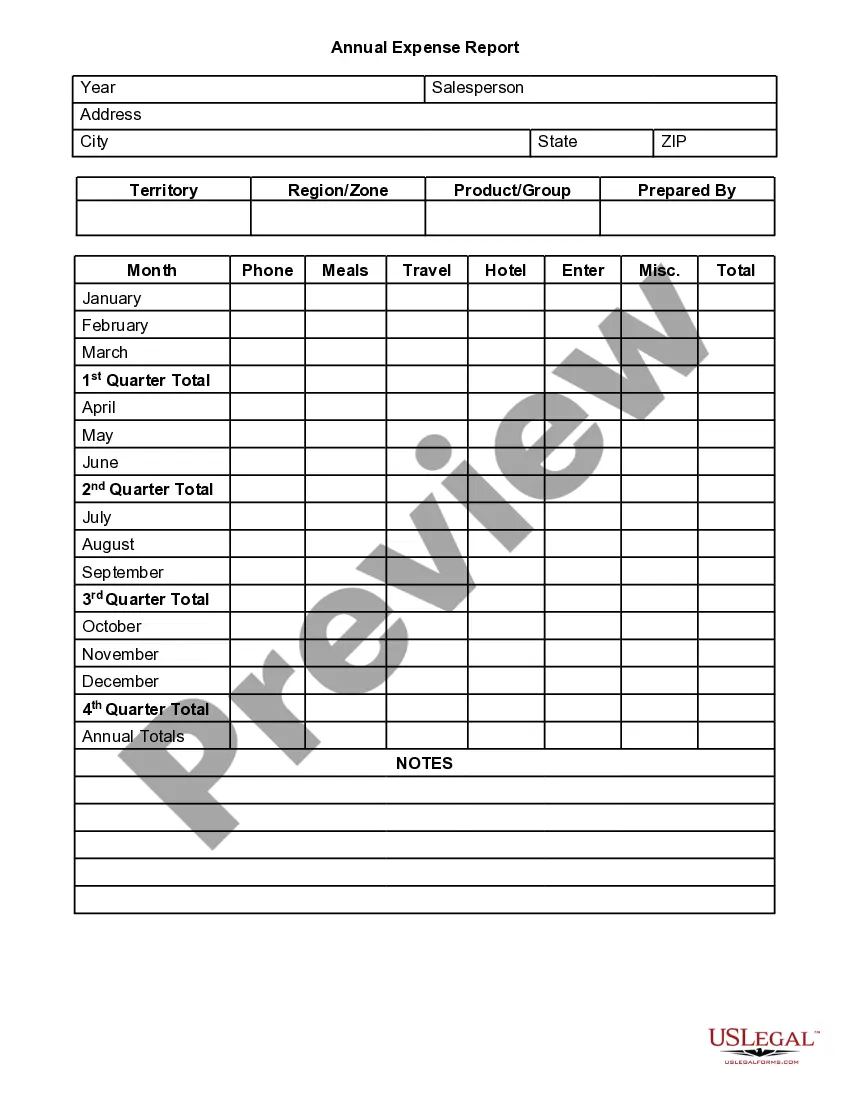
Sample Claim Statement With Defamation In San Bernardino
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The most common defenses to defamation are: 1) truth; 2) consent; 3) privilege; and 4) the statute of limitations. Perhaps the most distinct aspect of the defamation cause of action is that falsity is required.
The burden of proof may require a party to raise a reasonable doubt concerning the existence or nonexistence of a fact or that he establish the existence or nonexistence of a fact by a preponderance of the evidence, by clear and convincing proof, or by proof beyond a reasonable doubt.
In California, a claim for defamation involves a false statement made by one person about another person, which causes harm to a person's property, business, profession or occupation.
In cases involving public figures or matters of public concern, the burden is on you to prove falsity. In cases involving matters of purely private concern, the burden of proving the truth is on the defendant. A defendant does not have to show the literal truth of every word in an alleged defamatory statement.
Truth, or substantial truth, is a complete defense to a claim of defamation.
An effective defamation cease and desist letter will usually begin with a clear and factual introduction of the involved parties. Following this, the letter should present the facts in a chronological order, beginning with the earliest incident and progressing through subsequent events.
California, though, is not one of the U.S. states with criminal defamation laws. While California defamation defendants do not face potential imprisonment, they could be subject to civil lawsuits and hefty damages (including punitive damages), depending on the nature and harm caused by their false statements.
Defamation Per Se Under California Defamation Law In most California slander and libel cases, plaintiffs must prove how the communications under review caused material harm — except in per se lawsuits. A statement is considered defamatory per se if harm to the victim is inherent.
For example, if someone spreads a false rumor about a person's professional conduct that leads to job loss or social stigma, it qualifies as defamation. Another example could be a newspaper publishing false claims about a celebrity's behavior that results in loss of endorsements.
To damage the reputation of a person or group by saying or writing bad things about them that are not true: Mr Turnock claimed the editorial had defamed him.