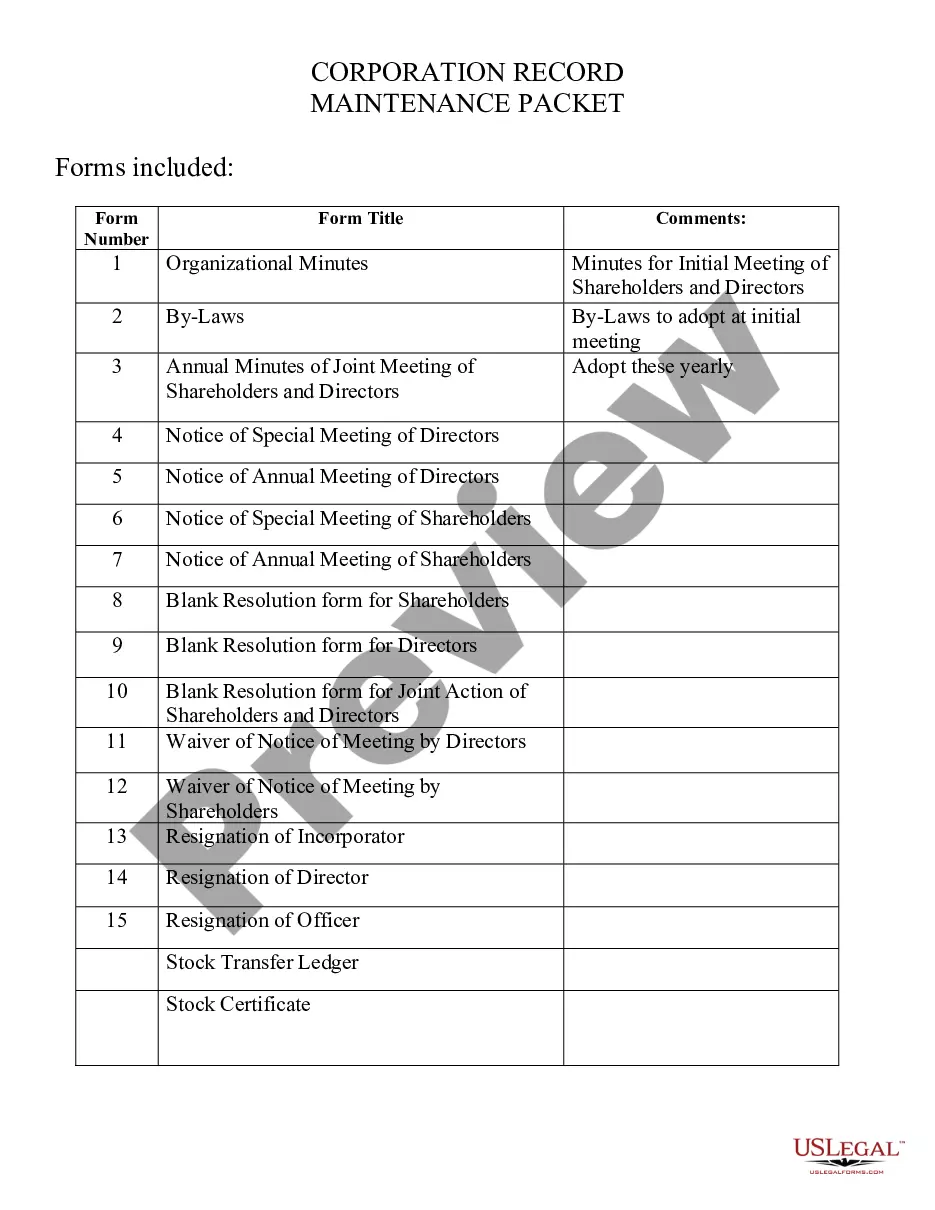
Sample Statement Of Claim For Job Application In Dallas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Small claims basics Generally, you can only sue for up to $12,500 in small claims court (or up to $6,250 if you're a business). You can ask a lawyer for advice before you go to court, but you can't have one with you in court. Starting November 1, 2021, you can sue or be sued for COVID-19 rental debt in small claims.
Don't say you expect to recover any more than £10,000 - if you do, your case won't be treated as a small claim. If you're making a claim for something your landlord hasn't repaired, the maximum amount you can get in a small claims case is £1,000.
Filing Your Case Online Texas's eFileTexas site uses guided interviews to help you create your forms. The website will ask you certain questions and use your answers to build your forms.
Debt Claims The claim can be for no more than $20,000, including attorney fees, if any, but excluding statutory interest and costs. Debt Claims Cases are governed by Justice Court Rules 500 to 507, and Rules 508.1 to 508.3 of the Texas Rules of Civil Procedure.
Small Claims Cases in Texas The limit to the amount that a person can sue for in small claims cases is $20,000.
Please prepare a one-page statement in relation to the advertised role, outlining: how your skills, knowledge and experience will be relevant to this role; why you are interested in the role and what you can offer us; any specific examples or achievements that demonstrate your ability to perform the role.
In other words, you cannot sue the government unless the government allows you to do so. Many states, including Texas, have waived sovereign immunity for some negligence claims. As a result, citizens can sue the state, county, city, and local governments and agencies for injuries.
Under this rule, the government must give people permission to sue them. The State of Texas, however, like many other states, grants citizens the right to sue the State, cities, and/or counties by Statute. The Statute is called the Texas Tort Claims Act.
If you are suing Dallas County or the City of Dallas, the limits are $100,000 per person for injury, $300,000 per accident, and $100,000 for property damage. You also cannot win punitive damages against a state or local government entity.
In Texas, municipalities, or any governmental entity, generally have “sovereign immunity” from law suits. As a result, there are strict guidelines to follow when suing a municipality, i.e. the government. One such guideline is the six month notice requirement under the Texas Tort Claims Act (TTCA).