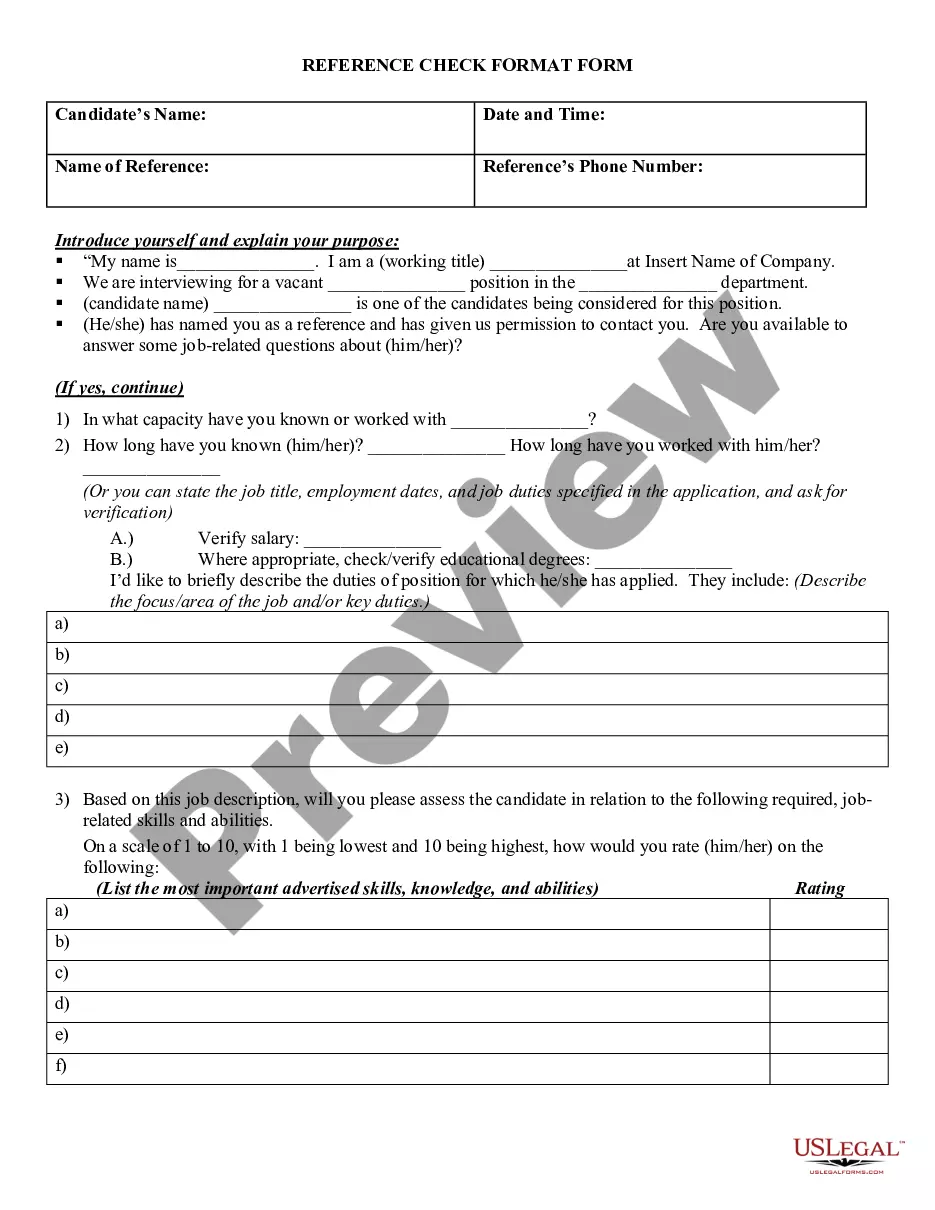
Libel With Intent In Franklin
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Someone can make a libelous statement about a person or business in print or online. Examples of potentially libelous statements include: a social media post spreading a false rumor about a person having a sexually transmitted infection. a Yelp review that falsely claims the reviewer got food poisoning at a restaurant.
For traditional libel under the Revised Penal Code, the penalty is imprisonment ranging from six months and one day to four years and two months, along with a fine.
The GREATER the truth, the greater the libel It is more objectionable to the person concerned if something critical or offensive but nonetheless true is written about them ...
Libel is a method of defamation expressed by print, writing, pictures, signs, effigies, or any communication embodied in physical form that is injurious to a person's reputation; exposes a person to public hatred, contempt or ridicule; or injures a person in their business or profession.
Libel is a written statement which wrongly accuses someone of something, and which is therefore against the law. Compare slander.
Defamatory words — that is, words which defame — are words that can cause real damage. If someone said you were a secret unicorn hunter, that would be a silly, not defamatory, lie. If someone said you were a thief or a traitor, and you weren't, that would be defamatory.
Article 353 of the Code defines libel as a public and malicious imputation of a crime, or of a vice or defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status, or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit, or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or to blacken the memory of the dead.
The most common defenses to defamation are: 1) truth; 2) consent; 3) privilege; and 4) the statute of limitations. Perhaps the most distinct aspect of the defamation cause of action is that falsity is required.
Defamation lawsuits are not easy to win because the plaintiff must both prove the difficult elements of his or her case and avoid the many defenses to defamation. This article discusses some of the standard defenses to defamation, including truth and privilege.
To prove prima facie defamation, a plaintiff must show four things: 1) a false statement purporting to be fact; 2) publication or communication of that statement to a third person; 3) fault amounting to at least negligence ; and 4) damages , or some harm caused to the reputation of the person or entity who is the ...