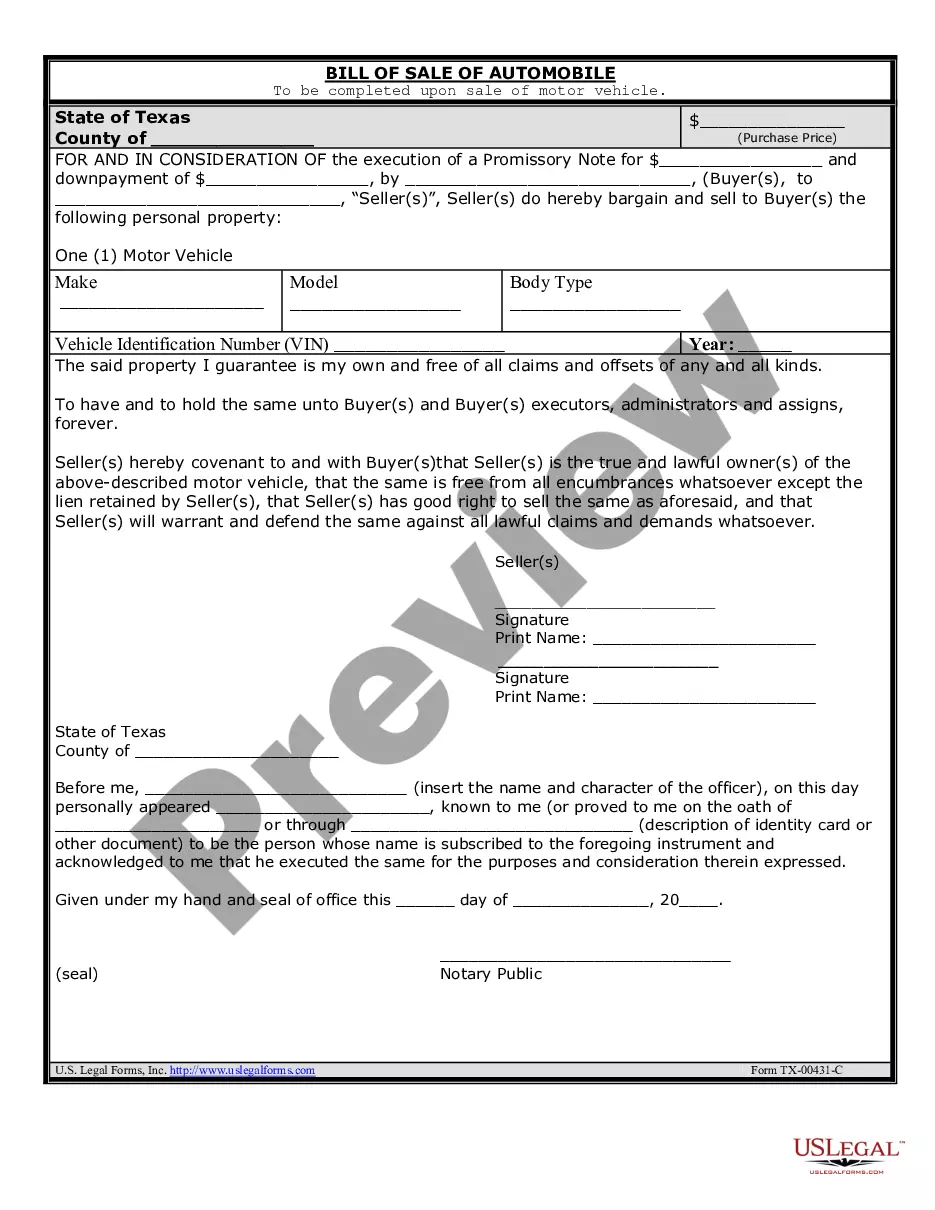
Fake Forged Document In Chicago
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Any person who forges any document or electronic record is guilty of an offence which, unless otherwise stated, is a felony and he is liable, unless owing to the circumstances of the forgery or the nature of the thing forged some other punishment is provided, to imprisonment for three years.
Whoever commits forgery shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to two years, or with fine, or with both.
Forgery can refer to a completely fabricated document or a document that has been altered to show fraudulent information. Forging or counterfeiting a document is a criminal offense, as is knowingly using or possessing a forged or counterfeit document.
Forgery refers to the fraudulent creation or alteration of a document with the intent to deceive others. This could involve signing someone else's name or altering an existing document in a way that misrepresents the truth.
The offense is a wobbler. A conviction on misdemeanor charges will result in up to one year in jail, a maximum fine of $1,000, or both. A conviction on felony charges results in 16 months, two or three years in jail, a maximum fine of $10,000, or both.
Document forgery is the act of creating a document from scratch, imitating a genuine one.
Forgery. n. 1) the crime of creating a false document, altering a document, or writing a false signature for the illegal benefit of the person making the forgery.
What are the three types of forgery? Three common types of forgery are signature forgery, art forgery, and document forgery. Each of these types of forgery involves different methods of creating or altering documents, signifiers, and objects with the intent to deceive.
Forgery, in law, making of a false writing with an intent to defraud. Writing, to be forgery, must either have legal significance or be commonly relied upon in business transactions. It need not be handwriting; the law of forgery covers printing, engraving, and typewriting as well.