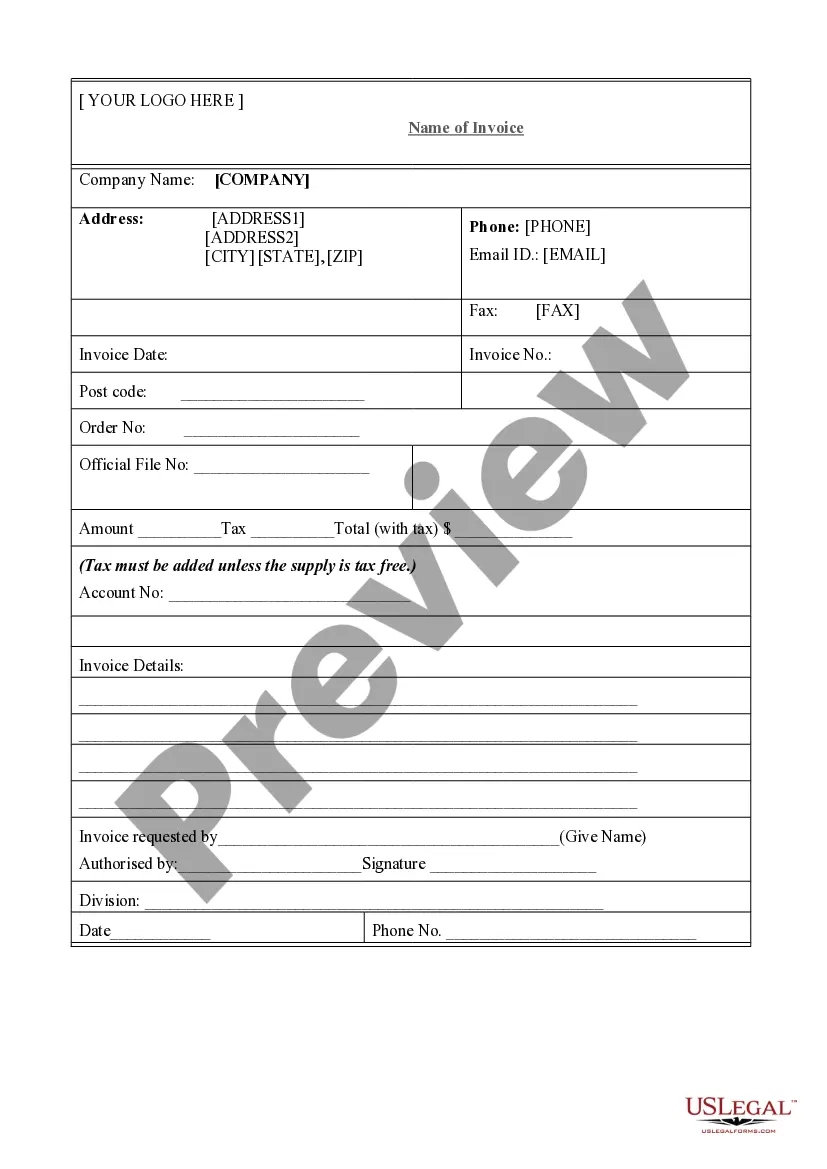
Arbitration In Dispute Resolution In Fulton
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Arbitration is a quasi-judicial proceeding, wherein the parties in dispute appoint an arbitrator by agreement to adjudicate the said dispute and to that extent differs from court proceedings. The power and functions of arbitral tribunal are statutorily regulated.
In arbitration, a neutral third party serves as a judge who is responsible for resolving the dispute. The arbitrator listens as each side argues its case and presents relevant evidence, then renders a binding decision.
Arbitration is a procedure in which a dispute is submitted, by agreement of the parties, to one or more arbitrators who make a binding decision on the dispute. In choosing arbitration, the parties opt for a private dispute resolution procedure instead of going to court.
An arbitration is a hearing where a commissioner gives both parties an opportunity to present their cases regarding the issue in dispute by leading evidence, presenting documents, cross examination of witnesses, and even conducting of inspection of premises, where that is necessary.
In arbitration, a neutral third party serves as a judge who is responsible for resolving the dispute. The arbitrator listens as each side argues its case and presents relevant evidence, then renders a binding decision.
The 'FLAC method' (facts, law, analysis, conclusion) is an analysis tool where a paragraph or more is devoted in turn to the facts specific to the issue, the law specific to the issue, an analysis applying the law to the facts and a conclusion. This helps to avoid errors, omissions and ambiguities.
What is an example of arbitration? If two companies contract to engage in commerce and the contract includes an arbitration agreement, then the two companies are required to use arbitration rather than the court system to settle disputes.
During the arbitration hearing, the parties will present their cases to the arbitrator, who then considers the evidence and arguments. The hearing may be conducted in person, by video conference, or by other means agreed upon by the parties.
In arbitration, a neutral third party serves as a judge who is responsible for resolving the dispute. The arbitrator listens as each side argues its case and presents relevant evidence, then renders a binding decision.