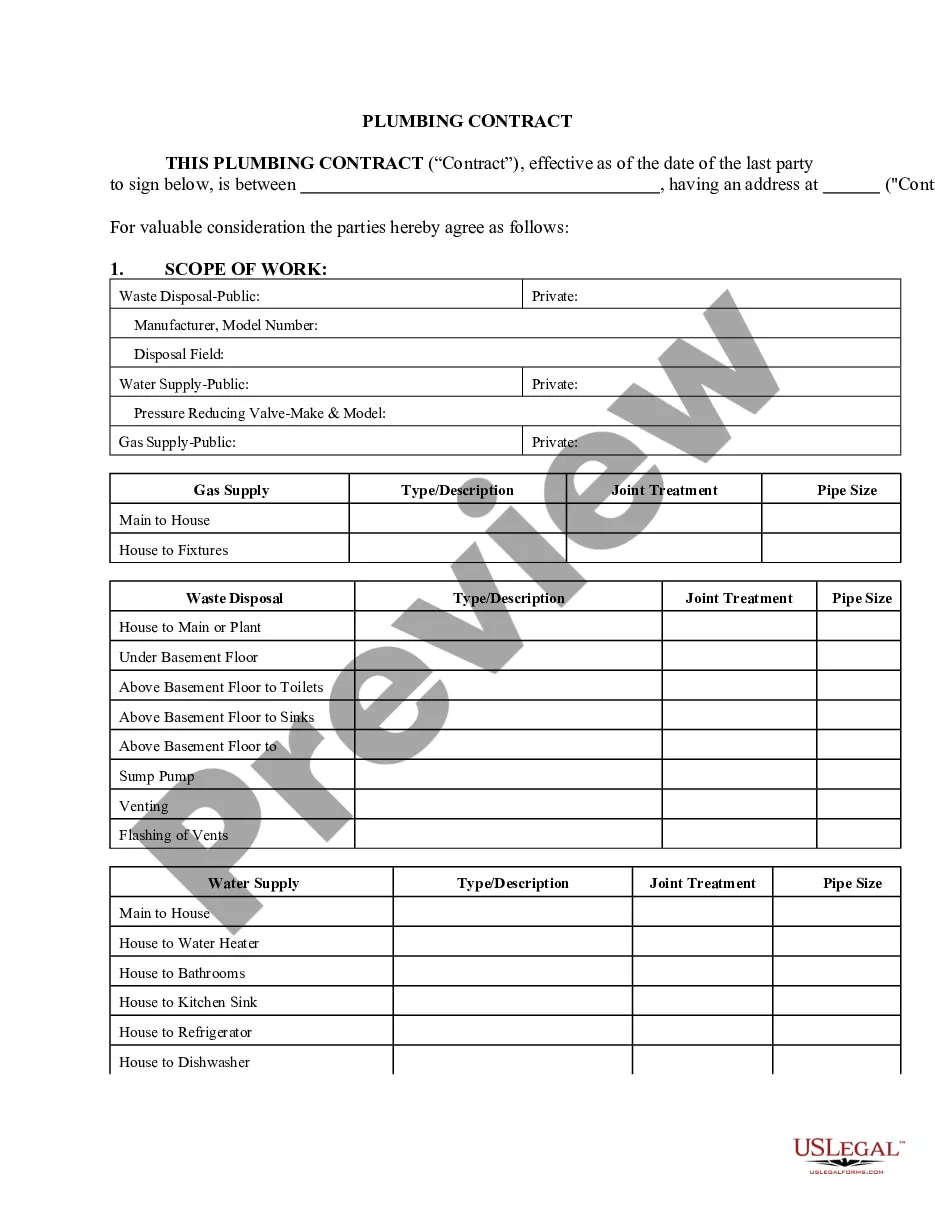
A Protective Covenant For Indemnity In Orange
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In the UK, indemnity covenants are agreements between two parties in which one party, the indemnifier, agrees to compensate the other party, the indemnified party, for any losses or damages that may occur as a result of a specific event or occurrence.
An indemnity clause is a contractual clause providing that one party is responsible for any losses or damages arising from a certain event or set of circumstances. In effect, the indemnity clause shifts the risk of that event occurring from the indemnified party to the indemnifying party.
Although they are generally referred to collectively as restrictive, or restrictive and protective, covenants, there are two types of such covenants: (i) restrictions on the use of the property, and (ii) affirmative obligations imposed on the owner of the properties.
How to Write an Indemnity Agreement Consider the Indemnity Laws in Your Area. Draft the Indemnification Clause. Outline the Indemnification Period and Scope of Coverage. State the Indemnification Exceptions. Specify How the Indemnitee Notifies the Indemnitor About Claims. Write the Settlement and Consent Clause.
Heading to court Or you can go to the Upper Tribunal (Lands Chamber) and ask them to consider modifying or discharging the covenant. The Tribunal will examine whether it is in the public interest, review the covenant's rationale and validity, and assess whether there are grounds to develop or modify the land use.
An indemnity insurance policy covers a legal defect with the property that either can't be resolved or would be very costly and/or time consuming to do so. So, instead of trying to fix the problem, you simply take out the insurance to protect you against an expensive bill in the future.
In its widest sense, "indemnity" means protection against, or compensation for, a loss or liability. Some indemnity claims arise by operation of law.
The Indemnity bond should be signed by two witnesses and two sureties (name, address and signature). 12. Affidavit should be verified in presence of a First Class Magistrate or a Notary Public. In the event of verification in the presence of Notary Public, the Affidavit should contain the notarial stamp.
A typical example is an insurance company wherein the insurer or indemnitor agrees to compensate the insured or indemnitee for any damages or losses he/she may incur during a period of time.
The seller agrees to indemnify and hold harmless the buyer, its affiliates, and their respective officers, directors, employees, agents, successors, and assigns (collectively, the “Indemnified Parties”) from and against any and all losses, damages, liabilities, deficiencies, claims, actions, judgments, settlements, ...